Related Research Articles

Polysaccharides, or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with water (hydrolysis) using amylase enzymes as catalyst, which produces constituent sugars. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Examples include storage polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen and galactogen and structural polysaccharides such as cellulose and chitin.

Cosmetics are composed of mixtures of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources or synthetically created ones. Cosmetics have various purposes, including personal and skin care. They can also be used to conceal blemishes and enhance natural features. Makeup can also add colour to a person's face, enhance a person's features or change the appearance of the face entirely to resemble a different person, creature, or object.
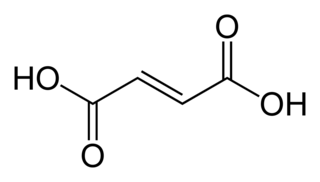
Fumaric acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH=CHCO2H. A white solid, fumaric acid occurs widely in nature. It has a fruit-like taste and has been used as a food additive. Its E number is E297. The salts and esters are known as fumarates. Fumarate can also refer to the C
4H
2O2−
4 ion (in solution). Fumaric acid is the trans isomer of butenedioic acid, while maleic acid is the cis isomer.

Microalgae or microphytes are microscopic algae invisible to the naked eye. They are phytoplankton typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist individually, or in chains or groups. Depending on the species, their sizes can range from a few micrometers (μm) to a few hundred micrometers. Unlike higher plants, microalgae do not have roots, stems, or leaves. They are specially adapted to an environment dominated by viscous forces.

Hyaluronic acid, also called hyaluronan, is an anionic, nonsulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. It is unique among glycosaminoglycans as it is non-sulfated, forms in the plasma membrane instead of the Golgi apparatus, and can be very large: human synovial HA averages about 7 million Da per molecule, or about 20,000 disaccharide monomers, while other sources mention 3–4 million Da.

Alginic acid, also called algin, is a naturally occurring, edible polysaccharide found in brown algae. It is hydrophilic and forms a viscous gum when hydrated. With metals such as sodium and calcium, its salts are known as alginates. Its colour ranges from white to yellowish-brown. It is sold in filamentous, granular, or powdered forms.

A thickening agent or thickener is a substance which can increase the viscosity of a liquid without substantially changing its other properties. Edible thickeners are commonly used to thicken sauces, soups, and puddings without altering their taste; thickeners are also used in paints, inks, explosives, and cosmetics.
Natural skin care uses topical creams and lotions made of ingredients available in nature. Much of the recent literature reviews plant-derived ingredients, which may include herbs, roots, flowers and essential oils, but natural substances in skin care products include animal-derived products such as beeswax, and minerals. These substances may be combined with various carrier agents, preservatives, surfactants, humectants and emulsifiers.

Algaculture is a form of aquaculture involving the farming of species of algae.
Fucoidan is a long chain sulfated polysaccharide found in various species of brown algae. Commercially available fucoidan is commonly extracted from the seaweed species Fucus vesiculosus (wracks), Cladosiphon okamuranus, Laminaria japonica and Undaria pinnatifida (wakame). Variant forms of fucoidan have also been found in animal species, including the sea cucumber.
Restylane is the trade name for a range of injectable fillers with a specific formulation of non-animal sourced hyaluronic acid (HA).
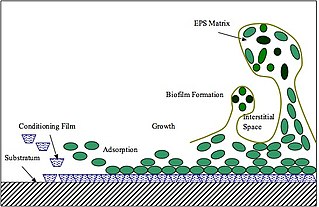
Extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) are natural polymers of high molecular weight secreted by microorganisms into their environment. EPSs establish the functional and structural integrity of biofilms, and are considered the fundamental component that determines the physicochemical properties of a biofilm. EPS in the matrix of biofilms provides compositional support and protection of microbial communities from the harsh environments. Components of EPS can be of different classes of polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins, lipopolysaccharides, and minerals.

Algae fuel, algal biofuel, or algal oil is an alternative to liquid fossil fuels that uses algae as its source of energy-rich oils. Also, algae fuels are an alternative to commonly known biofuel sources, such as corn and sugarcane. When made from seaweed (macroalgae) it can be known as seaweed fuel or seaweed oil.

Hyaluronan synthase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HAS2 gene.
Levan is a naturally occurring fructan present in many plants and microorganisms. This polymer is made up of fructose, a monosaccharide sugar, connected by 2,6 beta glycosidic linkages. Levan can have both branched and linear structures of relatively low molecular weight. Branched levan forms a very small, sphere-like structure with basal chains 9 units long. The 2,1 branching allows methyl ethers to form and create a spherical shape. The ends of levan also tend to contain a glucosyl residue. Branched levan tends to be more stable than linear polysaccharides. However, the amount of branching and length of polymerization tends to vary among different species. The shortest levan is 6-kestose, a chain of two fructose molecules and a terminal glucose molecule.

Streptococcus zooepidemicus is a Lancefield group C streptococcus that was first isolated in 1934 by P. R. Edwards, and named Animal pyogens A. It is a mucosal commensal and opportunistic pathogen that infects several animals and humans, but most commonly isolated from the uterus of mares. It is a subspecies of Streptococcus equi, a contagious upper respiratory tract infection of horses, and shares greater than 98% DNA homology, as well as many of the same virulence factors.

Edible seaweed, or sea vegetables, are seaweeds that can be eaten and used for culinary purposes. They typically contain high amounts of fiber. They may belong to one of several groups of multicellular algae: the red algae, green algae, and brown algae. Seaweeds are also harvested or cultivated for the extraction of polysaccharides such as alginate, agar and carrageenan, gelatinous substances collectively known as hydrocolloids or phycocolloids. Hydrocolloids have attained commercial significance, especially in food production as food additives. The food industry exploits the gelling, water-retention, emulsifying and other physical properties of these hydrocolloids.

Microalgae or microscopic algae grow in either marine or freshwater systems. They are primary producers in the oceans that convert water and carbon dioxide to biomass and oxygen in the presence of sunlight.
Isomaltooligosaccharide (IMO) is a mixture of short-chain carbohydrates which has a digestion-resistant property. IMO is found naturally in some foods, as well as being manufactured commercially. The raw material used for manufacturing IMO is starch, which is enzymatically converted into a mixture of isomaltooligosaccharides.
Injectable filler is a soft tissue filler made of polysaccharides injected into the skin at different depths.