Related Research Articles
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgical field.

The McGill University Health Centre is one of two major healthcare networks in the city of Montreal, Quebec. It is affiliated with McGill University and is one of the largest medical institutions in Canada. It is the largest hospital system in Canada by bed capacity. The majority of its funding comes from Quebec taxpayers through the Ministry of Health and Social Services. The centre provides inpatient and ambulatory care.

Placenta praevia is when the placenta attaches inside the uterus but in an abnormal position near or over the cervical opening. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding in the second half of pregnancy. The bleeding is bright red and tends not to be associated with pain. Complications may include placenta accreta, dangerously low blood pressure, or bleeding after delivery. Complications for the baby may include fetal growth restriction.

Umbilical cord prolapse is when the umbilical cord comes out of the uterus with or before the presenting part of the baby. The concern with cord prolapse is that pressure on the cord from the baby will compromise blood flow to the baby. It usually occurs during labor but can occur anytime after the rupture of membranes.
Tocolytics are medications used to suppress premature labor. Preterm birth accounts for 70% of neonatal deaths. Therefore, tocolytic therapy is provided when delivery would result in premature birth, postponing delivery long enough for the administration of glucocorticoids, which accelerate fetal lung maturity but may require one to two days to take effect.
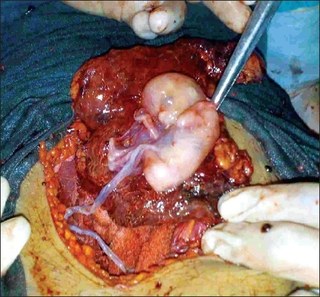
An abdominal pregnancy is a rare type of ectopic pregnancy where the embryo or fetus is growing and developing outside the womb in the abdomen, but not in the Fallopian tube, ovary or broad ligament.

John Clarence Webster was a Canadian-born physician pioneering in Obstetrics and gynaecology who in retirement had a second career as an historian, specializing in the history of his native New Brunswick.

The Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences is one of the constituent faculties of McGill University. It was established in 1829 after the Montreal Medical Institution was incorporated into McGill College as the college's first faculty; it was the first medical faculty to be established in Canada. The Faculty awarded McGill's first degree, and Canada's first medical degree to William Leslie Logie in 1833.

The Centre hospitalier universitaire Sainte-Justine is the largest mother and child centre in Canada and one of the four most important pediatric centres in North America. It is affiliated with the Université de Montréal, located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada.

Montreal Children's Hospital is a children's hospital in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Founded in 1904, it is affiliated with the McGill University Health Centre (MUHC) and McGill University, Faculty of Medicine.
Rima Rozen is a Canadian geneticist who is a professor at McGill University. Her current research focuses on genetic and nutritional deficiencies in folate metabolism and their impact on complex traits.
Arthur Thomas Porter IV was a Canadian physician and hospital administrator.
The Canadian Perinatal Network (CPN) is made up of Canadian researchers who collaborate on research issues relating to perinatal care. The network commenced in September 2005, and includes members from 25 tertiary perinatal units. CPN will enable health care professionals, researchers, and administrators to participate actively in clinical, epidemiologic, health services, health policy, and informatics research aimed at improving the effectiveness and efficiency of perinatal care.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to obstetrics:
Alka Kriplani is an Indian gynecologist, medical writer and academic, known for her contributions to the fields of Reproductive Endocrinology and Gynaecological Endoscopy. She is a professor and the Head of the Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi. A recipient of the Dr. B. C. Roy Award in 2007, she was honoured by the Government of India in 2015 with Padma Shri, the fourth highest Indian civilian award.
Vera Hingorani was an Indian gynaecologist, obstetrician, and medical writer who was a professor and head of the department of gynaecology and obstetrics at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences.
Jennifer R. Niebyl (1942) is a Canadian obstetrics and gynecology researcher and professor. She has made significant contributions to the understanding of drugs in pregnancy and lactation.
Salome Maswime is a South African clinician and global health expert. She is an Obstetrician and Gynaecologist and the Head of Global Surgery at the University of Cape Town. She advocates for women's health rights, equity in surgical and maternal care, and providing adequate health services to remote and underserved populations. She advises and consults for many institutions, including the World Health Organization. In 2017, she was honored with the Trailblazer and Young Achiever Award.
Hans H. Zingg is a Professor Emeritus in the Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics and Wyeth-Ayerst Chair in Women’s Health at McGill University in Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
Graeme Neil Smith is a Canadian obstetrician. He is Head of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology in the Faculty of Health Sciences at Queen's University and clinician-scientist at Kingston General Hospital Research Institute.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Alice Benjamin – Ordre national du Québec". Ordre-national.gouv.qc.ca. Retrieved 31 July 2017.
- ↑ "Alice Benjamin".
- ↑ "Doctors sue MUHC over delivery quotas". Cbc.ca. Retrieved 31 July 2017.
- ↑ "MUHC being sued by obstetricians and gynecologists for quotas limiting deliveries". Globalnews.ca. Retrieved 31 July 2017.
- ↑ "Alice Benjamin, MD FRCS(C) FACS , - Obstetrics and Gynecology - McGill University". Mcgill.ca. Retrieved 31 July 2017.
- ↑ "Obstetrics-gynecology pioneer Dr. Alice Benjamin honoured for life's work". montrealgazette.
- ↑ "Mother's Day Launch for new fund honouring extraordinary obstetrician Dr. Alice Benjamin". The Suburban Newspaper.
- ↑ "CityNews Montreal". CityNews Montreal.
- ↑ "Governor General Announces 114 New Appointments to the Order of Canada". Rideau Hall Press Office. November 27, 2020.