Related Research Articles

Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to protect against the risk of a contingent or uncertain loss.
A tax is a mandatory financial charge or levy imposed on a taxpayer by a governmental organization to support government spending and public expenditures collectively or to regulate and reduce negative externalities. Tax compliance refers to policy actions and individual behavior aimed at ensuring that taxpayers are paying the right amount of tax at the right time and securing the correct tax allowances and tax relief. The first known taxation occurred in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC. Taxes consist of direct or indirect taxes and may be paid in money or as labor equivalent.
Cost accounting is defined by the Institute of Management Accountants as "a systematic set of procedures for recording and reporting measurements of the cost of manufacturing goods and performing services in the aggregate and in detail. It includes methods for recognizing, allocating, aggregating and reporting such costs and comparing them with standard costs". Often considered a subset of managerial accounting, its end goal is to advise the management on how to optimize business practices and processes based on cost efficiency and capability. Cost accounting provides the detailed cost information that management needs to control current operations and plan for the future.
Cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something or deliver a service, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it is counted as cost. In this case, money is the input that is gone in order to acquire the thing. This acquisition cost may be the sum of the cost of production as incurred by the original producer, and further costs of transaction as incurred by the acquirer over and above the price paid to the producer. Usually, the price also includes a mark-up for profit over the cost of production.
Cost of goods sold (COGS) is the carrying value of goods sold during a particular period.

A fee is the price one pays as remuneration for rights or services. Fees usually allow for overhead, wages, costs, and markup. Traditionally, professionals in the United Kingdom receive a fee in contradistinction to a payment, salary, or wage, and often use guineas rather than pounds as units of account. Under the feudal system, a Knight's fee was what was given to a knight for his service, usually the usage of land. A contingent fee is an attorney's fee which is reduced or not charged at all if the court case is lost by the attorney.
Total cost of ownership (TCO) is a financial estimate intended to help buyers and owners determine the direct and indirect costs of a product or service. It is a management accounting concept that can be used in full cost accounting or even ecological economics where it includes social costs.
Title insurance is a form of indemnity insurance, predominantly found in the United States and Canada, that insures against financial loss from defects in title to real property and from the invalidity or unenforceability of mortgage loans. Unlike some land registration systems in countries outside the United States, US states' recorders of deeds generally do not guarantee indefeasible title to those recorded titles. Title insurance will defend against a lawsuit attacking the title or reimburse the insured for the actual monetary loss incurred up to the dollar amount of insurance provided by the policy.

In accounting and economics, fixed costs, also known as indirect costs or overhead costs, are business expenses that are not dependent on the level of goods or services produced by the business. They tend to be recurring, such as interest or rents being paid per month. These costs also tend to be capital costs. This is in contrast to variable costs, which are volume-related and unknown at the beginning of the accounting year. Fixed costs have an effect on the nature of certain variable costs.
A flat fee, also referred to as a flat rate or a linear rate refers to a pricing structure that charges a single fixed fee for a service, regardless of usage. Less commonly, the term may refer to a rate that does not vary with usage or time of use.
Indirect costs are costs that are not directly accountable to a cost object. Like direct costs, indirect costs may be either fixed or variable. Indirect costs include administration, personnel and security costs. These are those costs which are not directly related to production. Some indirect costs may be overhead, but other overhead costs can be directly attributed to a project and are direct costs.
In business, an overhead or overhead expense is an ongoing expense of operating a business. Overheads are the expenditure which cannot be conveniently traced to or identified with any particular revenue unit, unlike operating expenses such as raw material and labor. Overheads cannot be immediately associated with the products or services being offered, and so do not directly generate profits. However, they are still vital to business operations as they provide critical support for the business to carry out profit making activities. One example would be the rent for a factory, which allows workers to manufacture products which can then be sold for a profit. Such expenses are incurred for output generally and not for particular work order; e.g., wages paid to watch and ward staff, heating and lighting expenses of factory, etc. Overheads are an important cost element, alongside direct materials and direct labor.
Job costing is accounting which tracks the costs and revenues by "job" and enables standardized reporting of profitability by job. For an accounting system to support job costing, it must allow job numbers to be assigned to individual items of expenses and revenues. A job can be defined to be a specific project done for one customer, or a single unit of product manufactured, or a batch of units of the same type that are produced together.
Factory overhead, also called manufacturing overhead, manufacturing overhead costs, work overhead, or factory burden in American English, is the total cost involved in operating all production facilities of a manufacturing business that cannot be traced directly to a product. It generally applies to indirect labor and indirect cost. Overhead also includes all costs involved in manufacturing with the exception of the cost of raw materials. Examples include supplies, indirect materials such as lubricants, indirect manufacturing labor such as plant maintenance and cleaning labor, plant rent, plant insurance, property taxes on the plant, plant depreciation, and the compensation of plant managers.
In the United States, health insurance helps pay for medical expenses through privately purchased insurance, social insurance, or a social welfare program funded by the government. Synonyms for this usage include "health coverage", "health care coverage", and "health benefits". In a more technical sense, the term "health insurance" is used to describe any form of insurance providing protection against the costs of medical services. This usage includes both private insurance programs and social insurance programs such as Medicare, which pools resources and spreads the financial risk associated with major medical expenses across the entire population to protect everyone, as well as social welfare programs like Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program, which both provide assistance to people who cannot afford health coverage.
Soft Cost is a construction industry term but more specifically a contractor accounting term for an expense item that is not considered direct construction cost. Soft costs include architectural, engineering, financing, and legal fees, and other pre- and post-construction expenses. The term has been replaced in most contractor accrual accounting with the term General & Administrative abbreviated G&A.
Taxes in Germany are levied at various government levels: the federal government, the 16 states (Länder), and numerous municipalities (Städte/Gemeinden). The structured tax system has evolved significantly, since the reunification of Germany in 1990 and the integration within the European Union, which has influenced tax policies. Today, income tax and Value-Added Tax (VAT) are the primary sources of tax revenue. These taxes reflect Germany's commitment to a balanced approach between direct and indirect taxation, essential for funding extensive social welfare programs and public infrastructure. The modern German tax system accentuate on fairness and efficiency, adapting to global economic trends and domestic fiscal needs.
The following is a glossary of terms relating to construction cost estimating.

Jerome Lee Nicholson was an American accountant, industrial consultant, author and educator at the New York University and Columbia University, known as pioneer in cost accounting. He is considered in the United States to be the "father of cost accounting."
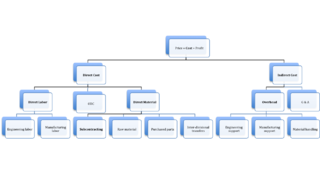
In business economics cost breakdown analysis is a method of cost analysis, which itemizes the cost of a certain product or service into its various components, the so-called cost drivers. The cost breakdown analysis is a popular cost reduction strategy and a viable opportunity for businesses.