Related Research Articles

Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a sovereign state in Oceania that occupies the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The western half of New Guinea forms the Indonesian provinces of Papua and West Papua. It is the world's third largest island country with 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).

The prime minister of Papua New Guinea is Papua New Guinea's head of government, consequent on being the leader of the party or coalition with majority support in the National Parliament. The Prime Minister serves as the head of his party the coalition government and the chairman of the National Executive Council. The PM's Office Was Preceded by the Chief Ministry.

The Papuan languages are the non-Austronesian and non-Australian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea, and neighbouring islands, by around 4 million people. It is a strictly geographical grouping, and does not imply a genetic relationship. The concept of Papuan peoples as distinct from Austronesian-speaking Melanesians was first suggested and named by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1892.

The Territory of Papua comprised the southeastern quarter of the island of New Guinea from 1883 to 1975. In 1883, the Government of Queensland annexed this territory for the British Empire. The United Kingdom Government refused to ratify the annexation but in 1884 a Protectorate was proclaimed over the territory, then called "British New Guinea". There is a certain ambiguity about the exact date on which the entire territory was annexed by the British. The Papua Act 1905 recites that this happened "on or about" 4 September 1888. On 18 March 1902, the Territory was placed under the authority of the Commonwealth of Australia. Resolutions of acceptance were passed by the Commonwealth Parliament, who accepted the territory under the name of Papua.

The Papua New Guinea national football team is the national team of Papua New Guinea and is controlled by the Papua New Guinea Football Association. Its nickname is the Kapuls, which is Tok Pisin for Cuscus.

The kina is the currency of Papua New Guinea. It is divided into 100 toea. The kina was introduced on 19 May 1975, and circulated along with the Australian dollar until 31 December 1975. The next day, the dollar ceased to be legal tender.

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, is the Indonesian part of the island of New Guinea. Since the island is alternatively named as Papua, the region is also called West Papua. Lying to the west of the independent state of Papua New Guinea, it is the only Indonesian territory to be situated in Oceania. Considered to be a part of the Australian continent, the territory is mostly in the Southern Hemisphere and also includes nearby islands, including the Schouten and Raja Ampat archipelagoes. The region is predominantly covered with ancient rainforest where numerous traditional tribes live, such as the Dani of the Baliem Valley, although a large proportion of the population live in or near coastal areas, with the largest city being Jayapura.

The National Parliament of Papua New Guinea is the unicameral national legislature in Papua New Guinea. It was created in 1964 as the House of Assembly of Papua and New Guinea but gained its current name after the nation was granted independence in 1975.

The culture of Papua New Guinea is many-sided and complex. It is estimated that more than 7000 different cultural groups exist in Papua New Guinea, and most groups have their own language. Because of this diversity, in which they take pride, many different styles of cultural expression have emerged; each group has created its own expressive forms in art, dance, weaponry, costumes, singing, music, architecture and much more. To unify the nation, the language Tok Pisin, once called Neo-Melanesian has evolved as the lingua franca — the medium through which diverse language groups are able to communicate with one another in Parliament, in the news media, and elsewhere. People typically live in villages or dispersed hamlets which rely on the subsistence farming of yams and taro. The principal livestock in traditional Papua New Guinea is the oceanic pig.

The Papua New Guinea national cricket team, nicknamed the Barramundis, is the team that represents the country of Papua New Guinea in international cricket. The team is organised by Cricket PNG, which has been an Associate Member of the International Cricket Council (ICC) since 1973. Papua New Guinea previously had One-Day International (ODI) status, which it gained by finishing fourth in 2014 World Cup Qualifier. Papua New Guinea lost both their ODI and T20I status in March 2018 after losing a playoff match against Nepal during the 2018 Cricket World Cup Qualifier, a result that earned ODI and T20I status for their opponents. On 26 April 2019, at the final World Cricket League 2 fixture; PNG defeated Oman to finish at the fourth position and reclaim their ODI status.

The Territory of New Guinea was an Australian administered territory on the island of New Guinea from 1920 until 1975. In 1949, the Territory and the Territory of Papua were established in an administrative union by the name of the Territory of Papua and New Guinea. That administrative union was renamed as Papua New Guinea in 1971. Notwithstanding that it was part of an administrative union, the Territory of New Guinea at all times retained a distinct legal status and identity until the advent of the Independent State of Papua New Guinea.
The Papua New Guinea national rugby union team, nicknamed the Pukpuks,, played its first international in 1966, defeating Vanuatu 47-3. Papua New Guinea have not so far qualified for a Rugby World Cup. They participated in the Oceania World Cup qualifying tournaments for the 2007, 2011 and 2015 World Cups, but did not qualify.
Chief Horst Ulrich Beier, commonly known as Ulli Beier, was a German editor, writer and scholar who had a pioneering role in developing literature, drama and poetry in Nigeria, as well as literature, drama and poetry in Papua New Guinea. His second wife, Georgina Beier, born in London, had a similarly instrumental role in stimulating the visual arts during their residencies in both Nigeria and Papua New Guinea.

This page is a list of local-level governments (LLGs) of Papua New Guinea. There are 326 LLGs comprising 6,112 wards as of 2018.

Yule Island is a small island in Central Province, Papua New Guinea. It is located 160 km NW from Port Moresby, on the south coast of Papua New Guinea.
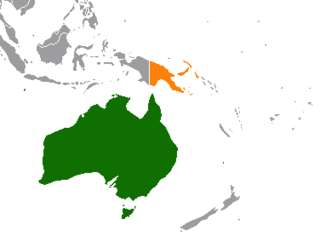
Australia–Papua New Guinea relations are the foreign relations between Australia and Papua New Guinea. Papua New Guinea is Australia's closest neighbour and a former dependent territory of Australia. Both nations share the same continent. Papua New Guinea has developed much closer relations with Australia than with Indonesia, the only country with which it shares a land border. The two countries are Commonwealth realms, and Papua New Guinea benefits from economic development aid from Australia.
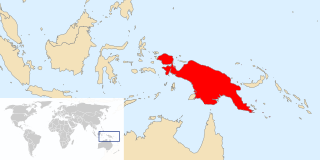
New Guinea is a large island separated by the shallow Torres Strait from the rest of the Australian continent. It is the world's second-largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi), and the largest island wholly or partly within the Southern Hemisphere and Oceania.

The Papua New Guinea national rugby sevens team competes in the Oceania Sevens, where they finished third in 2009, and fourth in 2010, 2015 and 2016.
Papua New Guinean literature is diverse. The emergence of written literature is comparatively recent in Papua New Guinea. It was given its first major stimulus with the setting up of creative writing courses by Ulli Beier at the University of Papua New Guinea. Beier also founded a Papua Pocket Poets series, as well as the literary magazine Kovave, the first of its kind in the country. Some of Papua New Guinea's first noted writers, including John Kasaipwalova, Kumalau Tawali, Apisai Enos and Kama Kerpi, were first published in Kovave.
The Papua New Guinea Rugby Football Union, or Rugby PNG is the governing body for rugby union in Papua New Guinea. It was established in 1962 and was affiliated to the International Rugby Board in 1993.
References
- ↑ Nationalism and Papua New Guinea Writing
- ↑ "API Review of Books". Archived from the original on 2007-10-17. Retrieved 2007-12-13.