
Bread is a staple food prepared from a dough of flour and water, usually by baking. Throughout recorded history and around the world, it has been an important part of many cultures' diets. It is one of the oldest human-made foods, having been of significance since the dawn of agriculture, and plays an essential role in both religious rituals and secular culture.

Flour is a powder made by grinding raw grains, roots, beans, nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, is the main ingredient of bread, which is a staple food for many cultures. Corn flour has been important in Mesoamerican cuisine since ancient times and remains a staple in the Americas. Rye flour is a constituent of bread in both Central Europe and Northern Europe.

Sourdough or sourdough bread is a bread made by allowing the dough to ferment using naturally occurring lactobacillaceae and yeast before baking. The fermentation process produces lactic acid, which gives the bread a sour taste and improves its keeping-qualities.

Baking powder is a dry chemical leavening agent, a mixture of a carbonate or bicarbonate and a weak acid. The base and acid are prevented from reacting prematurely by the inclusion of a buffer such as cornstarch. Baking powder is used to increase the volume and lighten the texture of baked goods. It works by releasing carbon dioxide gas into a batter or dough through an acid–base reaction, causing bubbles in the wet mixture to expand and thus leavening the mixture.

A baker is a tradesperson who bakes and sometimes sells breads and other products made of flour by using an oven or other concentrated heat source. The place where a baker works is called a bakery.

Soda bread is a variety of quick bread made in many cuisines in which sodium bicarbonate is used as a leavening agent instead of yeast. The basic ingredients of soda bread are flour, baking soda, salt, and buttermilk. The buttermilk contains lactic acid, which reacts with the baking soda to form bubbles of carbon dioxide. Other ingredients can be added, such as butter, egg, raisins, or nuts. Quick breads can be prepared quickly and reliably, without requiring the time and labor needed for kneaded yeast breads.

Crispbread is a flat and dry type of bread, containing mostly rye flour. Crispbreads are lightweight and keep fresh for a very long time due to their lack of water. Crispbread is a staple food and was for a long time considered a poor man's diet.

Hovis Ltd is a British company that produces flour, yeast and bread. Founded in Stoke-on-Trent, it began mass-production in Macclesfield in 1886.

Associated British Foods plc (ABF) is a British multinational food processing and retailing company headquartered in London, England.
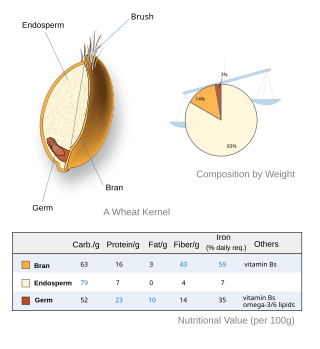
A whole grain is a grain of any cereal and pseudocereal that contains the endosperm, germ, and bran, in contrast to refined grains, which retain only the endosperm.

RHM plc, formerly Rank Hovis McDougall, was a United Kingdom food business. The company owned numerous brands, particularly for flour, where its core business started, and for consumer food products. It was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index but was acquired by Premier Foods in March 2007; many of its brands continue to be produced.

Tip Top Bakeries is an Australian manufacturer of bread products owned by George Weston Foods, a subsidiary of multinational food giant Associated British Foods.

Vienna bread is a type of bread that is produced from a process developed in Vienna, Austria, in the 19th century. The Vienna process used high milling of Hungarian grain, and cereal press-yeast for leavening.

Thomas Richard Allinson was an English physician, dietetic reformer, businessman, journalist and vegetarianism activist. He was a proponent of wholemeal bread consumption. His name is still used today for a bread popular in Europe, Allinson bread.

A dough conditioner, flour treatment agent, improving agent or bread improver is any ingredient or chemical added to bread dough to strengthen its texture or otherwise improve it in some way. Dough conditioners may include enzymes, yeast nutrients, mineral salts, oxidants and reductants, bleaching agents and emulsifiers. They are food additives combined with flour to improve baking functionality. Flour treatment agents are used to increase the speed of dough rising and to improve the strength and workability of the dough.
The 1951 Pont-Saint-Esprit mass poisoning, known in French as Le Pain Maudit, took place on 15 August 1951, in the small town of Pont-Saint-Esprit in Southern France. More than 250 people were involved, including 50 people interned in asylums, and there were seven deaths. A foodborne illness was suspected; among these it was originally believed to be a case of "cursed bread".
The history of California bread as a prominent factor in the field of bread baking dates from the days of the California Gold Rush around 1849, encompassing the development of sourdough bread in San Francisco. It includes the rise of artisan bakeries in the 1980s, which strongly influenced what has been called the "Bread Revolution".
Bread is a staple food throughout Europe. Throughout the 20th century, there was a huge increase in global production, mainly due to a rise in available, developed land throughout Europe, North America and Africa.

A baking mix is a mixed formulation of ingredients used for the cooking of baked goods. Baking mixes may be commercially manufactured or homemade. Baking mixes that cater to particular dietary needs, such as vegan, gluten-free, or kosher baking mixes, can be bought in many places.
Premier FMCG (Pty) Ltd, commonly referred to as Premier, is a South African food manufacturer. The company is headquartered in Waterfall City, Midrand, just north of Johannesburg.














