Distance education, also known as distance learning, is the education of students who may not always be physically present at school, or where the learner and the teacher are separated in both time and distance. Traditionally, this usually involved correspondence courses wherein the student corresponded with the school via mail. Distance education is a technology-mediated modality and has evolved with the evolution of technologies such as video conferencing, TV, and the Internet. Today, it usually involves online education and the learning is usually mediated by some form of technology. A distance learning program can either be completely a remote learning, or a combination of both online learning and traditional offline classroom instruction. Other modalities include distance learning with complementary virtual environment or teaching in virtual environment (e-learning).

The UCL Institute of Education (IOE) is the faculty of education and society of University College London (UCL). It specialises in postgraduate study and research in the field of education and is one of UCL's 11 constituent faculties. Prior to merging with UCL in 2014, it was a constituent college of the University of London. The IOE is ranked first in the world for education in the QS World University Rankings, and has been so every year since 2014.

Birkbeck, University of London, is a research university, in Bloomsbury London, England, and a member institution of the University of London. Established in 1823 as the London Mechanics' Institute by its founder, Sir George Birkbeck, and its supporters, Jeremy Bentham, J. C. Hobhouse and Henry Brougham, Birkbeck is one of the few universities to specialise in evening higher education in the United Kingdom.
Julia Bell MA Dubl (1901) MRCS LRCP (1920) MRCP (1926) FRCP (1938) was one of the pioneers of human genetics. Her early career as a statistical assistant to Karl Pearson (1857–1936) marked the beginning of a lifelong professional association with the Galton Laboratory for National Eugenics at University College London. Bell's work as a human geneticist was based on her statistical investigations into the inheritance of anomalies and diseases of the eye, nervous diseases, muscular dystrophies, and digital anomalies.
Educational technology is the combined use of computer hardware, software, and educational theory and practice to facilitate learning. When referred to with its abbreviation, "EdTech," it often refers to the industry of companies that create educational technology. In EdTech Inc.: Selling, Automating and Globalizing Higher Education in the Digital Age, Tanner Mirrlees and Shahid Alvi (2019) argue "EdTech is no exception to industry ownership and market rules" and "define the EdTech industries as all the privately owned companies currently involved in the financing, production and distribution of commercial hardware, software, cultural goods, services and platforms for the educational market with the goal of turning a profit. Many of these companies are US-based and rapidly expanding into educational markets across North America, and increasingly growing all over the world."
Gilly Salmon has been a digital learning innovator for more than 30 years. She is the founder and C.E.O of Education Alchemists Ltd - a company formed around her life's work including Carpe Diem learning design methodology, pedagogical transformation, online teaching, technology enhanced learning, the 5 stage model and e-tivities.
Networked learning is a process of developing and maintaining connections with people and information, and communicating in such a way so as to support one another's learning. The central term in this definition is connections. It adopts a relational stance in which learning takes place both in relation to others and in relation to learning resources. In design and practice, networked learning is intended to facilitate evolving sets of connections between learners and their interpersonal communities, knowledge contexts, and digital technologies.
Daniel Miller is an anthropologist who is closely associated with studies of human relationships to things, the consequences of consumption and digital anthropology. His theoretical work was first developed in Material Culture and Mass Consumption and is summarised more recently in his book Stuff. This work transcends the usual dualism between subject and object and studies how social relations are created through consumption as an activity.

The term digital native describes a person who has grown up in the information age. The term "digital native" was coined by Marc Prensky, an American writer, speaker and technologist who wrote several articles referencing this subject. This term specifically applied to the generation that grew up in the "digital age," predominantly regarding individuals born after the year 1980, namely Millennials, Generation Z, and Generation Alpha. Individuals from these demographic cohorts can consume digital information quickly and comfortably through electronic devices and platforms such as computers, mobile phones, and social media.

George Siemens is a Canadian expatriate professor of psychology at the University of Texas at Arlington and professor and director of the Centre for Change and Complexity in Learning at the University of South Australia. He is known for his theory of connectivism, which seeks to understand learning in the digital age. He played a role in the early development of massive online open courses (MOOCs).

Open education is an educational movement founded on openness, with connections to other educational movements such as critical pedagogy, and with an educational stance which favours widening participation and inclusiveness in society. Open education broadens access to the learning and training traditionally offered through formal education systems and is typically offered through online and distance education. The qualifier "open" refers to the elimination of barriers that can preclude both opportunities and recognition for participation in institution-based learning. One aspect of openness or "opening up" education is the development and adoption of open educational resources in support of open educational practices.
London Knowledge Lab was a research centre in Bloomsbury, London. It was founded in 2004 as a collaboration between the Institute of Education and Birkbeck, University of London. It was an interdisciplinary research centre, bringing together over 50 researchers from both social sciences and computer science backgrounds. The Institute of Education and Birkbeck announced the end of their collaboration in February 2016. Both institutions are continuing the work in their own separate Knowledge Lab research centres.
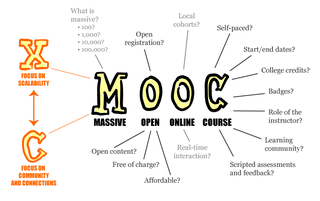
A massive open online course or an open online course is an online course aimed at unlimited participation and open access via the Web. In addition to traditional course materials, such as filmed lectures, readings, and problem sets, many MOOCs provide interactive courses with user forums or social media discussions to support community interactions among students, professors, and teaching assistants (TAs), as well as immediate feedback to quick quizzes and assignments. MOOCs are a widely researched development in distance education, first introduced in 2008, that emerged as a popular mode of learning in 2012, a year called the "Year of the MOOC".
FutureLearn is a British digital education platform founded in December 2012. The company was acquired by Global University Systems in December 2022 and previously jointly owned by The Open University and SEEK Ltd. It is a massive open online course (MOOC), microcredential and degree learning platform.
A Small Private Online Course (SPOC) refers to a version of a MOOC used locally with on-campus students. University of California Berkeley Professor Armando Fox coined the word in 2013 to refer to a localized instance of a MOOC course that was in use in a business-to-business context. In this regard SPOCs are focused on certain groups of students, which are qualified to take the course and ready to interact with others throughout the learning process. Even though most institutions do not yet award formal recognition of SPOCs, Robert Lue, who runs HarvardX, the university’s digital arm, says that it is becoming more likely that prestigious universities begin to create SPOCs for course-credits.

Andrew Burn is an English professor and media theorist. He is best known for his work in the fields of media arts education, multimodality and play, and for the development of the theory of the Kineikonic Mode. He is Emeritus professor of Media at the UCL Institute of Education.

Online learning involves courses offered by primary institutions that are 100% virtual. Online learning, or virtual classes offered over the internet, is contrasted with traditional courses taken in a brick-and-mortar school building. It is a development in distance education that expanded in the 1990s with the spread of the commercial Internet and the World Wide Web. The learner experience is typically asynchronous but may also incorporate synchronous elements. The vast majority of institutions utilize a learning management system for the administration of online courses. As theories of distance education evolve, digital technologies to support learning and pedagogy continue to transform as well.
Daniel Zingaro is an associate professor at the University of Toronto Mississauga. His main areas of research are in evaluating Computer science education and online learning. He has co-authored over 80 articles in peer-reviewed journals and conferences; and also authored a textbook, "Invariants: a Generative Approach to Programming.
Allison Druin is an American computer scientist who studies human–computer interaction, and digital libraries, particularly focusing on children's use of educational technology. She is a professor emerita at the University of Maryland, College Park and Associate Provost for Research and Strategic Partnerships at the Pratt Institute.
Marina Umaschi Bers is the Augustus Long Professor of Education at Boston College. Bers holds a secondary appointment in Boston College's Department of Computer Science. Bers directs the interdisciplinary DevTech Research Group, which she started in 2001 at Tufts University. Her research involves the design and study of innovative learning technologies to promote children's positive development. She is known for her work in the field of early childhood computer science with projects of national and international visibility. Bers is the co-creator of the free ScratchJr programming language, used by 35 million children, and the creator of the KIBO robotic kit, which has no screens or keyboards.








