Related Research Articles

Ambulatory care or outpatient care is medical care provided on an outpatient basis, including diagnosis, observation, consultation, treatment, intervention, and rehabilitation services. This care can include advanced medical technology and procedures even when provided outside of hospitals.

Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, is the application of healthcare measures to prevent diseases. Disease and disability are affected by environmental factors, genetic predisposition, disease agents, and lifestyle choices, and are dynamic processes that begin before individuals realize they are affected. Disease prevention relies on anticipatory actions that can be categorized as primal, primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention.
Behavioral medicine is concerned with the integration of knowledge in the biological, behavioral, psychological, and social sciences relevant to health and illness. These sciences include epidemiology, anthropology, sociology, psychology, physiology, pharmacology, nutrition, neuroanatomy, endocrinology, and immunology. The term is often used interchangeably, but incorrectly, with health psychology. The practice of behavioral medicine encompasses health psychology, but also includes applied psychophysiological therapies such as biofeedback, hypnosis, and bio-behavioral therapy of physical disorders, aspects of occupational therapy, rehabilitation medicine, and physiatry, as well as preventive medicine. In contrast, health psychology represents a stronger emphasis specifically on psychology's role in both behavioral medicine and behavioral health.
In the healthcare industry, pay for performance (P4P), also known as "value-based purchasing", is a payment model that offers financial incentives to physicians, hospitals, medical groups, and other healthcare providers for meeting certain performance measures. Clinical outcomes, such as longer survival, are difficult to measure, so pay for performance systems usually evaluate process quality and efficiency, such as measuring blood pressure, lowering blood pressure, or counseling patients to stop smoking. This model also penalizes health care providers for poor outcomes, medical errors, or increased costs. Integrated delivery systems where insurers and providers share in the cost are intended to help align incentives for value-based care.
A chronic condition is a health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term chronic is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three months. Common chronic diseases include diabetes, functional gastrointestinal disorder, eczema, arthritis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, autoimmune diseases, genetic disorders and some viral diseases such as hepatitis C and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. An illness which is lifelong because it ends in death is a terminal illness. It is possible and not unexpected for an illness to change in definition from terminal to chronic. Diabetes and HIV for example were once terminal yet are now considered chronic due to the availability of insulin for diabetics and daily drug treatment for individuals with HIV which allow these individuals to live while managing symptoms.

Self-care has been defined as the process of establishing behaviors to ensure holistic well-being of oneself, to promote health, and actively manage illness when it occurs. Individuals engage in some form of self-care daily with food choices, exercise, sleep, and hygiene. Self-care is not only a solo activity, as the community—a group that supports the person performing self-care—overall plays a role in access to, implementation of, and success of self-care activities.

The Massachusetts Department of Public Health is a governmental agency of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts with various responsibilities related to public health within that state. It is headquartered in Boston and headed by Commissioner Monica Bharel.

Clinical pharmacy is the branch of pharmacy in which clinical pharmacists provide direct patient care that optimizes the use of medication and promotes health, wellness, and disease prevention. Clinical pharmacists care for patients in all health care settings but the clinical pharmacy movement initially began inside hospitals and clinics. Clinical pharmacists often work in collaboration with physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and other healthcare professionals. Clinical pharmacists can enter into a formal collaborative practice agreement with another healthcare provider, generally one or more physicians, that allows pharmacists to prescribe medications and order laboratory tests.
Pharmacy residency is education a pharmacist can pursue beyond the degree required for licensing as a pharmacist. A pharmacy residency program allows for the implementation of skill set and knowledge acquired in pharmacy school through interaction with the public either in a hospital setting or community practice. The program is done over a span of about 2yrs after graduation from pharmacy school and licensure as a pharmacist. Pharmacy residency helps improve the resume of a pharmacist so as to increase chances of obtaining employment outside community practice. A 2022 review suggested that there is sufficient evidence that residency develops key competencies for junior pharmacists.
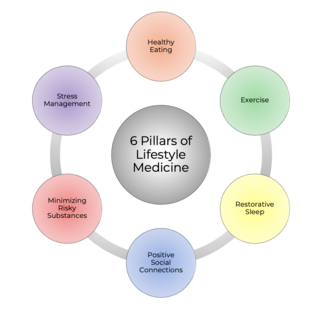
Lifestyle medicine (LM) is a branch of medicine focused on preventive healthcare and self-care dealing with prevention, research, education, and treatment of disorders caused by lifestyle factors and preventable causes of death such as nutrition, physical inactivity, chronic stress, and self-destructive behaviors including the consumption of tobacco products and drug or alcohol abuse. The goal of LM is to improve individuals' health and wellbeing by applying the 6 pillars of lifestyle medicine (nutrition, regular physical activity, restorative sleep, stress management, avoidance of risky substances, and positive social connection) to prevent chronic conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity. By focusing on these 6 areas to improve health, LM can prevent 80% of chronic illnesses and non-communicable diseases (NCD).
Disease or patient registries are collections of secondary data related to patients with a specific diagnosis, condition, or procedure, and they play an important role in post marketing surveillance of pharmaceuticals. Registries are different from indexes in that they contain more extensive data.
The Care Continuum Alliance is an industry trade group of corporations and individuals that "promotes the role of population health improvement in raising the quality of care, improving health outcomes and reducing preventable health care costs for individuals with chronic conditions and those at risk for developing chronic conditions". It supports "care continuum services" such as "health and wellness promotion, disease management, and care coordination" by means of "advocacy, research, and the promotion of best practices in care management".
Health coaching is the use of evidence-based skillful conversation, clinical interventions and strategies to actively and safely engage client/patients in health behavior change. Health coaches are certified or credentialed to safely guide clients and patients who may have chronic conditions or those at moderate to high risk for chronic conditions.
Medication therapy management, generally called medicine use review in the United Kingdom, is a service provided typically by pharmacists, medical affairs, and RWE scientists that aims to improve outcomes by helping people to better understand their health conditions and the medications used to manage them. This includes providing education on the disease state and medications used to treat the disease state, ensuring that medicines are taken correctly, reducing waste due to unused medicines, looking for any side effects, and providing education on how to manage any side effects. The process that can be broken down into five steps: medication therapy review, personal medication record, medication-related action plan, intervention and or referral, and documentation and follow-up.

The Yukon-Kuskokwim Health Corporation (YKHC) administers a health care delivery system for over 50 rural communities in the Yukon–Kuskokwim Delta in southwest Alaska. The YKHC is accredited by the Joint Commission.
Chronic disease in Northern Ontario is a population health problem. The population in Northern Ontario experiences worse outcomes on a number of important health indicators, including higher rates of chronic disease compared to the population in the rest of Ontario.
A collaborative practice agreement (CPA) is a legal document in the United States that establishes a legal relationship between clinical pharmacists and collaborating physicians that allows for pharmacists to participate in collaborative drug therapy management (CDTM).
Comprehensive medication management (CMM) is the process of delivering clinical services aimed at ensuring a patient's medications (including prescribed, over-the-counter, vitamins, supplements and alternative) are individually assessed to determine that they have an appropriate reason for use, are efficacious for treating their respective medical condition or helping meet defined patient or clinical goals, are safe considering comorbidities and other medications being taken, and are able to be taken by the patient as intended without difficulty.
The taxonomy of the burden of treatment is a visualization created for health care professionals to better comprehend the obstacles that interfere with a patient's health care plan. It was created as a result of a worldwide, qualitative-based study that asked adults with chronic conditions to list the personal, environmental, and financial barriers that burden a patient. The purpose of this visualization is to help health care providers develop personalized management strategies that the patient can follow through a narrative paradigm. The goal is to target interventions, achieve an interpersonal doctor-patient relationship, and improve health outcomes.
References
- 1 2 Lenz, Thomas L (March–April 2010). "The ambulatist: a health care professional specializing in lifestyle medicine for chronic disease coordination". American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. 4 (2): 134–137. doi:10.1177/1559827609355909.
- ↑ "Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Archived from the original on 27 February 2011. Retrieved 2011-03-03.
- ↑ Lenz, Thomas L; et al. (2010). "A Lifestyle Medicine Clinic in a Community Pharmacy Setting" (PDF). Innovations in Pharmacy. 1 (1): 1–12. doi: 10.24926/iip.v1i1.186 . Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-20. Retrieved 2011-03-13.
- 1 2 Lenz, Thomas (December 9, 2010). "System and Methods for Sourcing and Managing Healthcare Related Resources". WIPO Patent Application. Retrieved 16 March 2011.