Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology.
The Monsanto Company was an American agrochemical and agricultural biotechnology corporation founded in 1901 and headquartered in Creve Coeur, Missouri. Monsanto's best-known product is Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbicide, developed in the 1970s. Later, the company became a major producer of genetically engineered crops. In 2018, the company ranked 199th on the Fortune 500 of the largest United States corporations by revenue.

The medical uses of silver include its use in wound dressings, creams, and as an antibiotic coating on medical devices. Wound dressings containing silver sulfadiazine or silver nanomaterials may be used to treat external infections. The limited evidence available shows that silver coatings on endotracheal breathing tubes may reduce the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia. There is tentative evidence that using silver-alloy indwelling catheters for short-term catheterizing will reduce the risk of catheter-acquired urinary tract infections.

A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than sterilization, which is an extreme physical or chemical process that kills all types of life. Disinfectants are generally distinguished from other antimicrobial agents such as antibiotics, which destroy microorganisms within the body, and antiseptics, which destroy microorganisms on living tissue. Disinfectants are also different from biocides—the latter are intended to destroy all forms of life, not just microorganisms. Disinfectants work by destroying the cell wall of microbes or interfering with their metabolism. It is also a form of decontamination, and can be defined as the process whereby physical or chemical methods are used to reduce the amount of pathogenic microorganisms on a surface.
The American Dental Association (ADA) is an American professional association established in 1859 which has more than 161,000 members. Based in the American Dental Association Building in the Near North Side of Chicago, the ADA is the world's largest and oldest national dental association. The organization lobbies on behalf of the American dental profession and provides dental accreditation.

Chlorhexidine is a disinfectant and antiseptic with the molecular formula C22H30Cl2N10, which is used for skin disinfection before surgery and to disinfect surgical instruments. It is also used for cleaning wounds, preventing dental plaque, treating yeast infections of the mouth, and to keep urinary catheters from blocking. It is used as a liquid or a powder. It is commonly used in salt form, either the gluconate or the acetate.

This discussion of the dental amalgam controversy outlines the debate over whether dental amalgam should be used. Supporters claim that it is safe, effective and long-lasting, while critics argue that amalgam is unsafe because it may cause mercury poisoning and other toxicity.

Clear aligners are orthodontic devices that are a transparent, plastic form of dental braces used to adjust teeth.
Ethicon, Inc. is a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson. It was incorporated as a separate company under the Johnson & Johnson umbrella in 1949 to expand and diversify the Johnson & Johnson product line.
The pharmaceutical industry in India was valued at an estimated US$42 billion in 2021 and is estimated to reach $130 billion by 2030. India is the world's largest provider of generic medicines by volume, with a 20% share of total global pharmaceutical exports. It is also the largest vaccine supplier in the world by volume, accounting for more than 60% of all vaccines manufactured in the world. Indian pharmaceutical products are exported to various regulated markets including the US, UK, European Union and Canada.

Genzyme was an American biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts. From its acquisition in 2011 to 2022 Genzyme operated as a fully owned subsidiary of Sanofi. In 2010, Genzyme was the world's third-largest biotechnology company, employing more than 11,000 people around the world. As a subsidiary of Sanofi, Genzyme had a presence in approximately 65 countries, including 17 manufacturing facilities and 9 genetic-testing laboratories. Its products were also sold in 90 countries. In 2007, Genzyme generated $3.8 billion in revenue with more than 25 products on the market. In 2006 and 2007, Genzyme was named one of Fortune magazine’s “100 Best Companies to Work for”. The company donated $83 million worth of products worldwide; in 2006, it made $11 million in cash donations. In 2005, Genzyme was awarded the National Medal of Technology, the highest level of honor awarded by the president of the United States to America's leading innovators. In February 2022, Sanofi's new corporate brand was unveiled and former entity "Sanofi Genzyme" got integrated into Sanofi.
Henry Schein, Inc. is an American distributor of health care products and services with a presence in 33 countries. Ethisphere named Henry Schein as one of the 2024 World's Most Ethical Companies for the 13th consecutive year. For eight consecutive years, the company has received the Equality 100 Award: Leader in LGBTQ+ Workplace Inclusion by the Human Rights Campaign Foundation.

Nobel Biocare is a Swiss company originally founded in Sweden for manufacturing dental implants. It is now headquartered in Kloten, Switzerland near the Zürich Airport. Nobel Biocare in its current form was founded in 2002. It originates from a partnership formed in 1978 between Swedish medical researcher Professor Per-Ingvar Brånemark and Bofors, a Swedish company, to industrialize Brånemark's discovery of osseointegration. Beside dental implants, it also presently develops and commercializes CAD/CAM-based prosthetics equipments to scan teeth and to fabricate individualized dental prosthesis using digital technologies in place of silicone molding.

Lysol is a brand of American cleaning and disinfecting products distributed by Reckitt, which markets the similar Dettol or Sagrotan in other markets. The line includes liquid solutions for hard and soft surfaces, air treatment, and hand washing. The active ingredient in many Lysol products is benzalkonium chloride, but the active ingredient in the Lysol "Power and Free" line is hydrogen peroxide. Lysol has been used since its invention in the late 19th century as a household and industrial cleaning agent, and previously as a medical disinfectant.
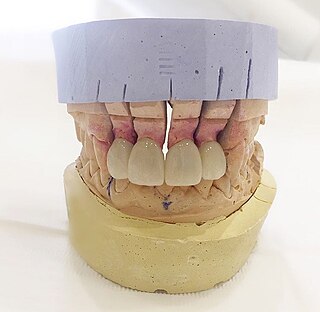
Dental laboratories manufacture or customize a variety of products to assist in the provision of oral health care by a licensed dentist. These products include crowns, bridges, dentures and other dental products. Dental lab technicians follow a prescription from a licensed dentist when manufacturing these items, which include prosthetic devices and therapeutic devices. The FDA regulates these products as medical devices and they are therefore subject to FDA's good manufacturing practice ("GMP") and quality system ("QS") requirements. In most cases, however, they are exempt from manufacturer registration requirements. Some of the most common restorations manufactured include crowns, bridges, dentures, and dental implants. Dental implants is one of the most advanced dental technologies in the field of dentistry.
The University of Puerto Rico School of Dental Medicine is the dental school of the University of Puerto Rico. It is located on the University of Puerto Rico, Medical Sciences Campus in San Juan, Puerto Rico. It is the only dental school in Puerto Rico. It is accredited by the American Dental Association.

United Therapeutics Corporation is an American publicly traded biotechnology company and public benefit corporation listed on the NASDAQ under the symbol UTHR. It develops novel, life-extending technologies for patients in the areas of lung disease and organ manufacturing. United Therapeutics is co-headquartered in Silver Spring, Maryland and Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, with additional facilities in Magog and Bromont, Quebec; Melbourne and Jacksonville, Florida; Blacksburg, Virginia; and Manchester, New Hampshire.
Spotlight Innovation Inc. [STATUS CLOSED] was an American pharmaceutical holding company. The company maintained two subsidiaries: Caretta Therapeutics, Inc. and Celtic Biotech Iowa, Inc. Spotlight Innovation Inc. is based in Urbandale, Iowa and was publicly traded on the OTCQB marketplace under the stock ticker symbol, STLT.
Creolin is a generic name for disinfectants whose composition varies according to origin. It is extracted from the dry distillation of wood. The residue remaining in the autoclave vessel is a dark, syrupy mass called creosote, which is composed mainly of phenolic acid and cresylic acid. The original composition of creolin is a creosote tar oil, caustic soda, soaps, and very little water. It is of low technology and a very powerful disinfectant.

Align Technology, Inc. is an American manufacturer of 3D digital scanners and Invisalign clear aligners used in orthodontics. It was founded in 1997 and is headquartered in Tempe, Arizona. The company manufactures the aligners in Juarez, Mexico, and its scanners in Israel and China. The company is best known for its Invisalign system, which is a clear aligner treatment used to straighten teeth.












