
General surgery is a surgical specialty that focuses on alimentary canal and abdominal contents including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, appendix and bile ducts, and often the thyroid gland. General surgeons also deal with diseases involving the skin, breast, soft tissue, trauma, peripheral artery disease and hernias and perform endoscopic as such as gastroscopy, colonoscopy and laparoscopic procedures.

Urology, also known as genitourinary surgery, is the branch of medicine that focuses on surgical and medical diseases of the urinary system and the reproductive organs. Organs under the domain of urology include the kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, and the male reproductive organs.
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin. It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical doctor who manages diseases related to skin, hair, nails, and some cosmetic problems.

A podiatrist is a medical professional devoted to the treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle, and related structures of the leg. The term originated in North America but has now become the accepted term in the English-speaking world for all practitioners of podiatric medicine. The word chiropodist was previously used in the United States, but it is now regarded as antiquated.

Podiatry, or podiatric medicine and surgery, is a branch of medicine devoted to the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle and lower limb. The healthcare professional is known as a podiatrist. The US podiatric medical school curriculum includes lower extremity anatomy, general human anatomy, physiology, general medicine, physical assessment, biochemistry, neurobiology, pathophysiology, genetics and embryology, microbiology, histology, pharmacology, women's health, physical rehabilitation, sports medicine, research, ethics and jurisprudence, biomechanics, general principles of orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery, and foot and ankle surgery.
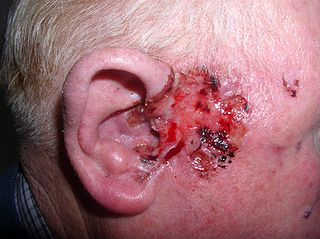
Basal-cell carcinoma (BCC), also known as basal-cell cancer, basalioma or rodent ulcer, is the most common type of skin cancer. It often appears as a painless raised area of skin, which may be shiny with small blood vessels running over it. It may also present as a raised area with ulceration. Basal-cell cancer grows slowly and can damage the tissue around it, but it is unlikely to spread to distant areas or result in death.
Surgical oncology is the branch of surgery applied to oncology; it focuses on the surgical management of tumors, especially cancerous tumors.

The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) is a non-profit professional organization of dermatologists in the United States and Canada, based in Rosemont, Illinois, near Chicago. It was founded in 1938 and has more than 20,500 members. The Academy grants fellowships and associate memberships, as well as fellowships for nonresidents of the United States or Canada. Since 1979, the AAD also publishes a monthly medical journal, the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.

Lentigo maligna is where melanocyte cells have become malignant and grow continuously along the stratum basale of the skin, but have not invaded below the epidermis. Lentigo maligna is not the same as lentigo maligna melanoma, as detailed below. It typically progresses very slowly and can remain in a non-invasive form for years.

Mohs surgery, developed in 1938 by a general surgeon, Frederic E. Mohs, is microscopically controlled surgery used to treat both common and rare types of skin cancer. During the surgery, after each removal of tissue and while the patient waits, the tissue is examined for cancer cells. That examination dictates the decision for additional tissue removal. Mohs surgery is the gold standard method for obtaining complete margin control during removal of a skin cancer using frozen section histology. CCPDMA or Mohs surgery allows for the removal of a skin cancer with very narrow surgical margin and a high cure rate.

Frederic Edward Mohs was an American physician and general surgeon who developed the Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) technique in 1938 to remove skin cancer lesions while still a medical student at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. The Mohs procedure is considered the best method for treating certain types of skin cancer, because it has very high cure rates for even high-risk lesions, combined with maximal preservation of healthy tissues.

Skin biopsy is a biopsy technique in which a skin lesion is removed to be sent to a pathologist to render a microscopic diagnosis. It is usually done under local anesthetic in a physician's office, and results are often available in 4 to 10 days. It is commonly performed by dermatologists. Skin biopsies are also done by family physicians, internists, surgeons, and other specialties. However, performed incorrectly, and without appropriate clinical information, a pathologist's interpretation of a skin biopsy can be severely limited, and therefore doctors and patients may forgo traditional biopsy techniques and instead choose Mohs surgery.
Ronald P. Rapini born 1954 in Akron, Ohio, is an American dermatologist and dermatopathologist. He is the Chernosky Distinguished Professor and Chair of the Department of Dermatology at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston and MD Anderson Cancer Center.
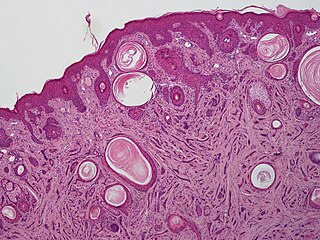
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC) is a rare sweat gland cancer, which often appears as a yellow spot or bump in the skin. It usually occurs in the neck or head, although cases have been documented in other areas of the body. Most diagnosis occur past the age of 50. Although considered an invasive cancer, metastasis rarely occurs. If the tumor spreads, it can grow and invade fat, muscles, and other types of tissue. Main treatments are wide local excision or Mohs micrographic surgery, which ensures that most, if not all, cancer cells are removed surgically.
The American Osteopathic Board of Dermatology (AOBD) is an organization that provides board certification to qualified Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) who specialize in the medical and surgical treatment of disorders of the skin (dermatologists). The board is one of 18 medical specialty certifying boards of the American Osteopathic Association Bureau of Osteopathic Specialists approved by the American Osteopathic Association (AOA).

Lucius Duncan Bulkley was an American dermatologist and alternative cancer treatment advocate.
June K. Robinson is an American dermatologist, academic and researcher. She is a Research Professor of Dermatology at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine.

Perry Robins is Professor Emeritus of Dermatology at New York University, dermatologist, physician, Mohs surgeon, and author. Robins founded the Skin Cancer Foundation, the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology, Journal of Dermatologic Surgery & Oncology, International Society for Dermatologic Surgery, and trained in and taught the Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) technique.
Günter Burg is a German dermatologist. Born in Mayen, Germany, he holds German and Swiss citizenship. He has been married to Dr. Doris Burg-Nicklas, a neurologist, since 1968. They have two sons: Andreas and Thomas.
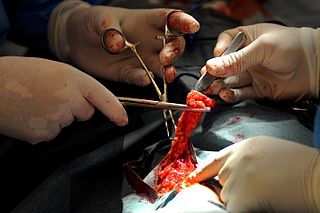
Dermatologic surgical procedures are treatments aimed at managing a wide range of medically necessary and cosmetic conditions, with a long history dating back to ancient times.











