Egyptology is the scientific study of ancient Egypt. The topics studied include ancient Egyptian history, language, literature, religion, architecture and art from the 5th millennium BC until the end of its native religious practices in the 4th century AD.

The National Endowment for Democracy (NED) is a quasi-autonomous non-governmental organization in the United States founded in 1983 with the stated aim of advancing democracy worldwide, by promoting political and economic institutions, such as political groups, business groups, trade unions, and free markets.
The Fulbright Program, including the Fulbright–Hays Program, is one of several United States cultural exchange programs with the goal of improving intercultural relations, cultural diplomacy, and intercultural competence between the people of the United States and other countries through the exchange of persons, knowledge, and skills. Via the program, competitively-selected American citizens including students, scholars, teachers, professionals, scientists, and artists may receive scholarships or grants to study, conduct research, teach, or exercise their talents abroad; and citizens of other countries may qualify to do the same in the United States.

The National Endowment for the Humanities (NEH) is an independent federal agency of the U.S. government, established by the National Foundation on the Arts and the Humanities Act of 1965, dedicated to supporting research, education, preservation, and public programs in the humanities. The NEH is housed in the Constitution Center at 400 7th St SW, Washington, D.C. From 1979 to 2014, NEH was at 1100 Pennsylvania Avenue, N.W., Washington, D.C., in the Nancy Hanks Center at the Old Post Office.

The International Republican Institute (IRI) is an American nonprofit organization founded in 1983 and funded and supported by the United States federal government. Most of its board is drawn from the Republican Party. Its public mission is to advance freedom and democracy worldwide by helping political parties to become more issue-based and responsive, assisting citizens to participate in government planning, and working to increase the role of marginalized groups in the political process, including women and youth. It has been repeatedly accused of foreign interference and has been implicated in the 2004 Haitian coup d'état. It was initially known as the National Republican Institute for International Affairs.

A financial endowment is a legal structure for managing, and in many cases indefinitely perpetuating, a pool of financial, real estate, or other investments for a specific purpose according to the will of its founders and donors. Endowments are often structured so that the inflation-adjusted principal or "corpus" value is kept intact, while a portion of the fund can be spent each year, utilizing a prudent spending policy.

The National Democratic Institute (NDI) is a non-profit American non-governmental organization whose stated mission is to "support and strengthen democratic institutions worldwide through citizen participation, openness and accountability". It is funded primarily by the United States and other Western governments, by major corporations and by nonprofits like the Open Society Foundations.

The Arab Academy for Science, Technology & Maritime Transport (AASTMT) or (AAST) is a regional university operated by the Arab League, which runs programs in marine transportation, business, and engineering. AASTMT started as a notion in the Arab League Transport Committee's meetings on 11 March 1970. The academy's inception was in 1972 in the city of Alexandria, Egypt. Later on, it expanded into Cairo.

David Bourke O'Connor was an Australian-American Egyptologist who primarily worked in the fields of Ancient Egypt and Nubia.

The Asian Cultural Council (ACC) is a non-profit organization dedicated to advancing international cultural exchange between Asia and the U.S. and between the countries of Asia through the arts. Founded by John D. Rockefeller III in 1963, ACC has invested over $100 million in grants to artists and arts professionals representing 16 fields and 26 countries through over 6,000 exchanges. ACC supports $1.4 million in grants annually for individuals and organizations.

The Institute of Museum and Library Services (IMLS) is an independent agency of the United States federal government established in 1996. It is the main source of federal support for libraries and museums within the United States, having the mission to advance, support, and empower America’s museums, libraries, and related organizations through grantmaking, research, and policy development.” In fiscal year 2023, IMLS had a budget of $313.58 million. As of 2023, IMLS currently has 70 full-time employees, many of whom still work remotely. In 2022, the employees voted to unionize, joining hundreds of thousands of federal workers who have joined the American Federation of Government Employees (AFGE) to “build power and have a voice at work.”

Theban Tomb 69 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official named Menna, whose titles included ‘Overseer of Fields of Amun’, and ‘Overseer of Fields of the Lord of the Two Lands’. Traditionally, TT 69 has been dated to the reign of Thutmosis IV. However, recent art historical studies of artistic style suggest the majority of the tomb was decorated during the reign of Amenhotep III.
AED, formerly the Academy for Educational Development, was a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization that focused on education, health and economic development for the "least advantaged in the United States and developing countries throughout the world." AED operated more than 250 programs in the United States and in 150 other countries.
The office of American Schools and Hospitals Abroad (ASHA) is an organizational unit within the Bureau of Democracy, Conflict, and Humanitarian Assistance (DCHA) at the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). ASHA is charged by the President of the United States with administering a worldwide assistance program with the objective of promoting American ideas and values abroad.

Democracy promotion by the United States aims to encourage governmental and non-governmental actors to pursue political reforms that will lead ultimately to democratic governance.
The Walter Chapin Simpson Center for the Humanities, located in Seattle, Washington, is one of the largest and most comprehensive humanities centers in the United States. Housed in the College of Arts and Sciences at the University of Washington (UW), it offers UW scholars a spectrum of local opportunities for intellectual community and grant support that advances crossdisciplinarity, collaboration, and research while networking them nationally and internationally.
The American Center of Research (ACOR) is a private, not-for-profit scholarly and educational organization. Based in Alexandria, Virginia, with a facility in Amman, Jordan, ACOR promotes knowledge of Jordan and the interconnected region, past and present. Prior to 2020, ACOR was known as The American Center of Oriental Research.
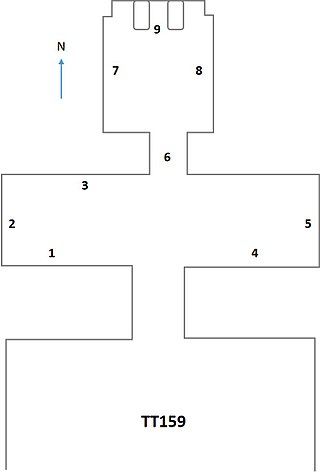
The Theban Tomb TT159 is located in Dra' Abu el-Naga', part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor.
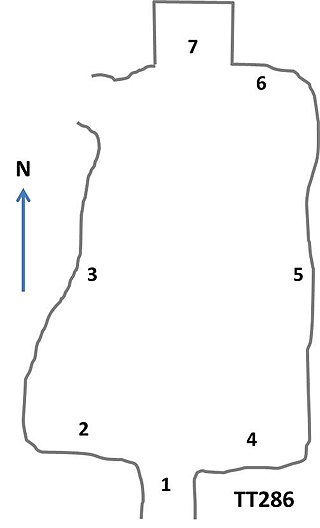
The Theban Tomb TT286 is located in Dra' Abu el-Naga', part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor.
Most cultural policy in the United States is enacted at the local and state level, though federal programs also exist to carry out cultural policy. These promote the culture of the United States, including visual art, performing arts, heritage, language, museums, libraries, and sports.