The American Treaty Shore is an identification of the historical coastal area where American vessels had the right to fish, and to process fish on unsettled coves and bays, on the shore of the Colony of Newfoundland. This entailed the entire Labrador coast, as well and the Newfoundland coast from Quirpon Island southward to Cape Ray, and from that cape eastward to the Ramea Islands.
These rights were stipulated in the Anglo-American Convention of 1818.

The Gulf of St. Lawrence fringes the shores of the provinces of Quebec, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Newfoundland and Labrador, in Canada, plus the islands Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, possessions of France, in North America.

Fogo Island is the largest of the offshore islands of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The Town of Fogo Island encompasses Fogo, Joe Batt's Arm-Barr'd Islands-Shoal Bay, Seldom-Little Seldom and Tilting, with the unincorporated areas of Fogo Island. It lies off the northeast coast of Newfoundland, northwest of Musgrave Harbour across Hamilton Sound, just east of the Change Islands. The island is about 25 km (16 mi) long and 14 km (8.7 mi) wide. The total area is 237.71 km2 (91.78 sq mi).

An outport is the term given for a small coastal community in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. Originally, the term was used for coastal communities on the island of Newfoundland, but the term has now been adopted for those on the mainland area of Labrador as well.
Bonavista Bay (BB) is a large bay located on the northeast coast of the island of Newfoundland in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador in Canada. It opens directly onto the Atlantic Ocean.

Cape Ray is a headland located at the southwestern extremity of the island of Newfoundland in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Cape St. John is a headland located on the north coast of Newfoundland in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador.

Conche is a community on the Northern Peninsula of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. Its population in 2021 was 149.

Atlantic Canadian English is a class of Canadian English dialects spoken in Atlantic Canada that is notably distinct from Standard Canadian English. It is composed of Maritime English and Newfoundland English. It was mostly influenced by British and Irish English, Irish and Scottish Gaelic, and some Acadian French. Atlantic Canada is the easternmost region of Canada, comprising four provinces located on the Atlantic coast: Newfoundland and Labrador, plus the three Maritime provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island. Regions such as Miramichi and Cape Breton have a wide variety of phrases and words not spoken outside of their respective regions.
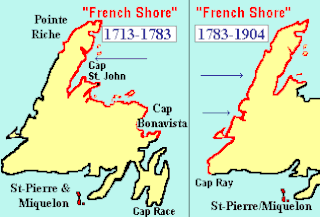
The French Shore, also called The Treaty Shore, resulted from the 1713 ratifications of the Treaty of Utrecht. The provisions of the treaty allowed the French to fish in season along the north coast of Newfoundland between Cape Bonavista and Point Riche. This area had been frequented by fishermen from Brittany since the early 16th century, which they called "le petit nord".

The Cape Shore is a region on the southwestern portion of the Avalon Peninsula on the island of Newfoundland, Canada.

The headland of Cape St. Francis is the outer extremity marking the boundary of Conception Bay on the Avalon Peninsula of the island of Newfoundland in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. The International Maritime Organization also designates Cape St. Francis as the southern extremity of the Labrador Sea.
The Headland of Point Riche is located near the community of Port au Choix on the Great Northern Peninsula of the island of Newfoundland in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador.

The headland of Cape St. Mary's is located at the southern tip of the south-western arm of the Avalon Peninsula of the island of Newfoundland in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Osmond is an unincorporated place in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The settlement was a stop on the Newfoundland Railway.

A headland, also known as a head, is a coastal landform, a point of land usually high and often with a sheer drop, that extends into a body of water. It is a type of promontory. A headland of considerable size often is called a cape. Headlands are characterised by high, breaking waves, rocky shores, intense erosion, and steep sea cliff.

Cod fisheries are fisheries for cod. Cod is the common name for fish of the genus Gadus, belonging to the family Gadidae, and this article is confined to three species that belong to this genus: the Atlantic cod, the Pacific cod and the Greenland cod. Although there is a fourth species of the cod genus Gadus, Alaska pollock, it is commonly not called cod and therefore currently not covered here.

Franco-Newfoundlanders, also known as Franco-Terreneuvians in English or Franco-Terreneuviens in French, are francophone and/or French Canadian residents of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. The name Franco-Terreneuvian derives from Terre-Neuve, the French name of Newfoundland.

Newfoundland is a large island within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is situated off the eastern coast of the North American mainland and the geographical region of Labrador.
Lodge Bay is a local service district and designated place in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is on the southeast coast of Labrador. Encompassing a population of less than one hundred residents, the community has uniquely evolved from both early European colonization of Labrador, and the inimitable patterns of land and resource use by the migratory Inuit population. The name Lodge Bay originated from the title Ranger Lodge, which was the name given to the area by trader and explorer, Captain George Cartwright in the late 18th century. "Ranger" was the name of the wooden-mercantile ship Cartwright used to trade, map and explore the Labrador coast, while "Lodge" was the name given to English hunting camps in Great Britain at that time.

Terre-Neuve ("Newfoundland") was a colony in New France that existed from 1655 to 1713, and which consisted of the southern portion of Newfoundland island. The most, and sometimes only, populated region was Placentia, called "Plaisance" in French. Because of Placentia's geographic position, its main economic activity was fishing, and the settlement could serve as a pit stop for ships traveling to and from France and other New France colonies like Canada or Acadia. Terre-Neuve ceased to exist in 1713, when France evacuated its settlers and transplanted them to Cape Breton. But, France regained the Saint Pierre and Miquelon islands of this colony in 1763, and still has possession over them today.