Italian East Africa was an Italian colony in the Horn of Africa. It was formed in 1936 after the Second Italo-Ethiopian War through the merger of Italian Somaliland, Italian Eritrea, and the newly occupied Ethiopian Empire.

The Second Italo-Ethiopian War, also referred to as the Second Italo-Abyssinian War, was a war of aggression waged by Italy against Ethiopia, which lasted from October 1935 to February 1937. In Ethiopia it is often referred to simply as the Italian Invasion, and in Italy as the Ethiopian War. It is seen as an example of the expansionist policy that characterized the Axis powers and the ineffectiveness of the League of Nations before the outbreak of the Second World War.

Gondar, also spelled Gonder, is a city and woreda in Ethiopia. Located in the North Gondar Zone of the Amhara Region, Gondar is north of Lake Tana on the Lesser Angereb River and southwest of the Simien Mountains. As of 2021, Gondar has an estimated population of 443,156.
The Italian order of battle for the Second Italo-Ethiopian War on 8 October 1935. The Ethiopian order of battle is listed separately.

Guglielmo Ciro Nasi was an Italian general who fought in Italian East Africa during World War II.

Luigi Frusci was an Italian military officer in the Italian Royal Army during the Italian conquest of Ethiopia and World War II. He was the last Italian Governor of Eritrea and Amhara.

The Battle of Gondar or Capture of Gondar was the last stand of the Italian forces in Italian East Africa during the Second World War. The battle took place in November 1941, during the East African Campaign. Gondar was the main town of Amhara in the mountains north of Lake Tana in Ethiopia, at an elevation of 7,000 ft (2,100 m) and had an Italian garrison of 40,000 men, commanded by Generale Guglielmo Nasi.

The Battle of Shire was fought on the northern front of what was known as the Second Italo-Abyssinian War. This battle consisted of attacks and counterattacks by Italian forces under Marshal of Italy Pietro Badoglio and Ethiopian forces under Ras Imru Haile Selassie. This battle was primarily fought in the Shire area of Ethiopia.
De Bono's invasion of Ethiopia took place during the opening stages of the Second Italo-Ethiopian War. Italian General Emilio De Bono invaded northern Ethiopia from staging areas in the Italian colony of Eritrea on what was known as the "northern front".
Football is the most popular sport in Ethiopia. Although not one of the leading footballing nations in Africa, Ethiopia has produced some outstanding teams at both club and international level as well as some talented individual players.

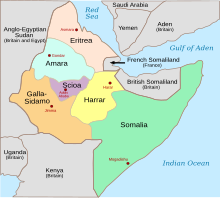
Harar Governorate was one of the six governorates of Italian East Africa. It was formed in 1936 from parts of the conquered Ethiopian Empire following the Second Italo-Ethiopian War.

Galla-Sidamo Governorate was one of the six governorates of Italian East Africa. It was formed in 1936 from parts of the conquered Ethiopian Empire following the Second Italo-Ethiopian War with the capital was Jimma. In November 1938 some territory of Galla-Sidamo in the Scioa region was given to the neighboring Addis Abeba Governorate, enlarging it to the Scioa Governorate.

Ethiopia–Italy relations are the current and historical relations between Ethiopia and Italy.

Italians of Ethiopia are Ethiopian-born citizens who are fully or partially of Italian descent, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Ethiopia starting in the 19th century during the Italian diaspora, or Italian-born people in Ethiopia.

Italian Ethiopia, also known as the Italian Empire of Ethiopia, was the territory of the Ethiopian Empire, which Italy occupied for approximately five years. Italian Ethiopia was not an administrative entity, but the formal name of the former territory of the Ethiopian Empire, which now constituted the Governorates of Amhara, Harar, Galla-Sidamo, and Scioa after the establishment of Italian East Africa.

The Scioa Governorate, also known as the Shewa Governorate, was one of the six governorates of Italian East Africa. It was formed in 1936 from parts of the conquered Ethiopian Empire following the Second Italo-Ethiopian War with its administrative capital being Addis Abeba.
Giuseppe Daodice was an Italian general. He was the 6th Italian governor of Addis Ababa and 3rd Italian governor of Scioa (1940–1941). He was a knight of the Order of Saints Maurice and Lazarus.

The Arbegnoch were Ethiopian anti-fascist World War II resistance fighters in Italian East Africa from 1936 until 1941 who fought against Fascist Italy's occupation of the Ethiopian Empire.
Beginning with the Kingdom of Aksum, Ethiopia's territory evolved significantly through conquest of the lands surrounding it. Strong Aksumite trading partnerships with other world powers gave prominence to its territorial expansion. In 330, Aksum besieged the Nubian city of Meroë, marking the beginning of its great expansion. It finally declined after the rise of Islamic dominion in South Arabia, and it ultimately collapsed in the 10th century.