| Look up amphetamine in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Amphetamine is a stimulant drug.
Contents
Amphetamine may also refer to:
| Look up amphetamine in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Amphetamine is a stimulant drug.
Amphetamine may also refer to:
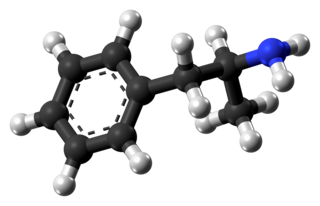
Amphetamine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. Amphetamine was discovered in 1887 and exists as two enantiomers: levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. Amphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical, the racemic free base, which is equal parts of the two enantiomers in their pure amine forms. The term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers, or to either of them alone. Historically, it has been used to treat nasal congestion and depression. Amphetamine is also used as an athletic performance enhancer and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. It is a prescription drug in many countries, and unauthorized possession and distribution of amphetamine are often tightly controlled due to the significant health risks associated with recreational use.

A psychiatric or psychotropic medication is a psychoactive drug taken to exert an effect on the chemical makeup of the brain and nervous system. Thus, these medications are used to treat mental illnesses. These medications are typically made of synthetic chemical compounds and are usually prescribed in psychiatric settings, potentially involuntarily during commitment. Since the mid-20th century, such medications have been leading treatments for a broad range of mental disorders and have decreased the need for long-term hospitalization, therefore, lowering the cost of mental health care. The recidivism or rehospitalization of the mentally ill is at a high rate in many countries and the reasons for the relapses are under research.

Stimulants is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and invigorating, or drugs that have sympathomimetic effects. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines as well as without a prescription as performance-enhancing or recreational drugs. Among narcotics, stimulants produce a noticeable crash or comedown at the end of their effects. The most frequently prescribed stimulants as of 2013 were lisdexamfetamine, methylphenidate (Ritalin), and amphetamine. It was estimated in 2015 that the percentage of the world population that had used cocaine during a year was 0.4%. For the category "amphetamines and prescription stimulants" the value was 0.7%, and for Ecstasy 0.4%.
In chemistry, a racemic mixture, or racemate, is one that has equal amounts of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule. The first known racemic mixture was racemic acid, which Louis Pasteur found to be a mixture of the two enantiomeric isomers of tartaric acid. A sample with only a single enantiomer is an enantiomerically pure or enantiopure compound.

Benzphetamine is a substituted amphetamine used short-term along with a doctor-approved, reduced-calorie diet, exercise, and behavioral program for weight loss. It is prescribed for obesity in individuals who have been unable to lose weight through exercise and dieting alone. It is a prodrug to dextroamphetamine and dextromethamphetamine.

Methcathinone is a monoamine alkaloid and psychoactive stimulant, a substituted cathinone. It is used as a recreational drug due to its potent stimulant and euphoric effects and is considered to be addictive, with both physical and psychological withdrawal occurring if its use is discontinued after prolonged or high-dosage administration. It is usually snorted, but can be smoked, injected, or taken orally.

Dextroamphetamine (D-AMP) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and an amphetamine enantiomer that is prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used as an athletic performance and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. Dextroamphetamine was also used in the past by some countries' military forces to fight fatigue during extended combat operations.
In chemistry, racemization is a conversion, by heat or by chemical reaction, of an optically active compound into a racemic form. Half of the optically active substance becomes its mirror image (enantiomer) referred as racemic mixtures. If the racemization results in a mixture where the D and L enantiomers are present in equal quantities, the resulting sample is described as a racemic mixture or a racemate. Racemization can proceed through a number of different mechanisms, and it has particular significance in pharmacology as different enantiomers may have different pharmaceutical effects.
An anorectic or anorexic is a drug which reduces appetite, resulting in lower food consumption, leading to weight loss. By contrast, an appetite stimulant is referred to as orexigenic.

Adderall and Mydayis are trade names for a combination drug called mixed amphetamine salts containing four salts of amphetamine. The mixture is composed of equal parts racemic amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, which produces a (3:1) ratio between dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine, the two enantiomers of amphetamine. Both enantiomers are stimulants, but differ enough to give Adderall an effects profile distinct from those of racemic amphetamine or dextroamphetamine, which are marketed as Evekeo and Dexedrine/Zenzedi, respectively. Adderall is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used as an athletic performance enhancer, cognitive enhancer, appetite suppressant, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. It is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the phenethylamine class.

Armodafinil is the enantiopure compound of the eugeroic modafinil (Provigil). It consists of only the (R)-(−)-enantiomer of the racemic modafinil. Armodafinil is produced by the pharmaceutical company Cephalon Inc. and was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in June 2007. In 2016, the FDA granted Mylan rights for the first generic version of Cephalon's Nuvigil to be marketed in the U.S.
Dexamyl was a brand name combination drug composed of sodium amobarbital and dextroamphetamine sulfate (Dexedrine) within the same pill. It was widely abused, and is no longer manufactured.

Lisdexamfetamine, sold under the brand name Vyvanse among others, is a stimulant medication that is mainly used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in people over the age of five as well as moderate-to-severe binge eating disorder in adults. Lisdexamfetamine is taken by mouth. Its effects generally begin within 2 hours and last for up to 14 hours. In the United Kingdom, it is usually less preferred than methylphenidate.
Mesocarb is a drug that is currently being developed for Parkinson's disease.

Obetrol was the brand name of a drug combining several amphetamine salts indicated for the treatment of exogenous obesity. It was originally sold by the American company Obetrol Pharmaceuticals. Obetrol was a popular diet pill in America in the 1950s and 1960s.
Dex or DEX may refer to:

Levoamphetamine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant known to increase wakefulness and concentration in association with decreased appetite and fatigue. Pharmaceuticals that contain levoamphetamine are currently indicated and prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), obesity, and narcolepsy in some countries.

Ortetamine (INN), also known as 2-methylamphetamine, is a stimulant drug of the amphetamine class. In animal drug discrimination tests it substituted for dextroamphetamine more closely than either 3- or 4-methylamphetamine, although with only around 1/10 the potency of dextroamphetamine itself.
Substituted amphetamines are a class of compounds based upon the amphetamine structure; it includes all derivative compounds which are formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the amphetamine core structure with substituents. The compounds in this class span a variety of pharmacological subclasses, including stimulants, empathogens, and hallucinogens, among others. Examples of substituted amphetamines are amphetamine (itself), methamphetamine, ephedrine, cathinone, phentermine, mephentermine, bupropion, methoxyphenamine, selegiline, amfepramone, pyrovalerone, MDMA (ecstasy), and DOM (STP).
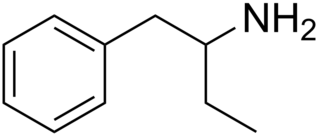
Phenylisobutylamine, also known as α-ethylphenethylamine, Butanphenamine, B or AEPEA, is a stimulant drug of the phenethylamine class. It is a higher homologue of amphetamine, differing from amphetamine's molecular structure only by the substitution of the methyl group at the alpha position of the side chain with an ethyl group. Compared to amphetamine, phenylisobutylamine has strongly reduced dopaminergic effects, and instead acts as a selective norepinephrine releasing agent. The dextroisomer of phenylisobutylamine partially substitutes for dextroamphetamine in rats.