Related Research Articles
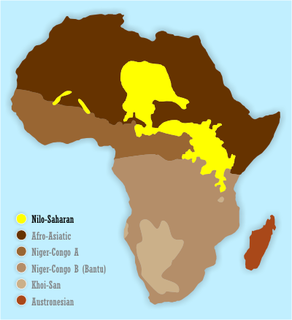
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50–60 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. The languages extend through 17 nations in the northern half of Africa: from Algeria to Benin in the west; from Libya to the Democratic Republic of the Congo in the centre; and from Egypt to Tanzania in the east.

Colin Macmillan Turnbull was a British-American anthropologist who came to public attention with the popular books The Forest People and The Mountain People, and one of the first anthropologists to work in the field of ethnomusicology.

Meroë is an ancient city on the east bank of the Nile about 6 km north-east of the Kabushiya station near Shendi, Sudan, approximately 200 km north-east of Khartoum. Near the site are a group of villages called Bagrawiyah. This city was the capital of the Kingdom of Kush for several centuries. The Kushitic Kingdom of Meroë gave its name to the Island of Meroë, which was the modern region of Butana, a region bounded by the Nile, the Atbarah and the Blue Nile.

Pygmy music refers to the sub-Saharan African music traditions of the Central African foragers, predominantly in the Congo, the Central African Republic and Cameroon.
In music, hocket is the rhythmic linear technique using the alternation of notes, pitches, or chords. In medieval practice of hocket, a single melody is shared between two voices such that alternately one voice sounds while the other rests.

The Anthology of American Folk Music is a six-album compilation released in 1952 by Folkways Records, comprising eighty-four American folk, blues and country music recordings that were originally issued from 1927 to 1932.

The Aka or Bayaka are a nomadic Mbenga pygmy people. They live in southwestern Central African Republic and in northern Republic of the Congo. An ecologically diverse people, they occupy 11 different ecological zones of the Western Congo Basin. They are related to the Baka people of Cameroon, Gabon, northern Congo, and southwestern Central African Republic.

Benishangul-Gumuz, also known as Benshangul/Gumuz, is one of the nine ethnic divisions (kililoch) of Ethiopia. It was previously known as Region 6. The region's capital is Assosa. Following the adoption of the 1995 constitution, the Region was created from the westernmost portion of the Gojjam province, and the northwestern portion of the Welega Province. The name of the region comes from two local ethnic groups – Berta and Gumuz.

The Merowe Dam, also known as Merowe High Dam, Merowe Multi-Purpose Hydro Project or Hamdab Dam, is a large dam near Merowe Town in northern Sudan, about 350 kilometres (220 mi) north of the capital Khartoum. Its dimensions make it the largest contemporary hydropower project in Africa. It is situated on the river Nile, close to and inundating the 4th Cataract where the river divides into multiple smaller branches with large islands in between. Merowe is a city about 40 kilometres (25 mi) downstream from the construction site at Hamdab. The main purpose for building the dam was the generation of electricity.
Unesco Collection: A Musical Anthology of the Orient is a series of recordings of traditional music that was made for the International Music Council by the International Institute for Comparative Music Studies and Documentation (Berlin/Venice) and released on the Musicaphon label by Bärenreiter (Kassel/Basel/London). The series was directed by Alain Daniélou.
Hamza El Din was a Nubian Egyptian/Sudanese composer, oud player, tar player, and vocalist.

Pandit Laxmi Ganesh Tewari is a Hindustani vocalist from India. He is an exponent of the Gwalior gharana (tradition) of vocal music. After studying with Dr. Lalmani Misra at Banaras Hindu University in Varanasi, he pursued education and teaching opportunities in America. At Sonoma State University since 1974, his career has combined performance, scholarship and teaching.
Cynthia Tse Kimberlin is an American ethnomusicologist. She is the Executive Director and Publisher of the Music Research Institute and MRI Press, based in Point Richmond, California. Her primary area of expertise is the music of Africa, in particular Ethiopia and Eritrea.
Jean-Pierre Hallet was a Belgian ethnologist, naturalist, and humanitarian known best for his extensive work with the Efé (Bambuti) pygmies of the Ituri Rainforest. He wrote the 1964 autobiographical book, Congo Kitabu, the 1973 ethnologic book Pygmy Kitabu, and the 1968 book Animal Kitabu, which details his extraordinary collection of animals in the Congo and in Kenya. He initiated the Pygmy Fund for the benefit of the Efé.

Folk Songs of the Hills is Merle Travis's classic collection of traditional songs from his native Muhlenberg County, Kentucky, including original compositions evoking working life on the railroads and in the coal mines. Each song, accompanied by Travis on his own acoustic guitar, is introduced by a short narrative. Because of these characteristics, the album can be considered an early example of the concept album in popular music, along with Woody Guthrie's Dust Bowl Ballads and Frank Sinatra's In the Wee Small Hours. First issued as a 78 rpm box set album in 1947, this collection has remained in print in LP and CD reissues up to the present, with additional tracks from the same period added in later editions.

Fat Mattress is the debut self-titled studio album by English folk rock band Fat Mattress, released on 15 August 1969.
Musical Sources is a series of recordings of traditional music that was made for the International Music Council by the International Institute for Comparative Music Studies and Documentation (Berlin/Venice) and released on the Philips label. Most of these recordings were later reissued on the Auvidis label. The series was directed by Alain Daniélou. It was part of the larger UNESCO Collection series.
Musical Atlas is a series of recordings of traditional music that was made for the International Music Council by the International Institute for Comparative Music Studies and Documentation (Berlin/Venice) and released on the EMI/Odeon label. The series was directed by Alain Daniélou. It was part of the larger UNESCO Collection series. Most of the recordings were later re-issued on the Naive/Auvidis label.
Kay Kaufman Shelemay is G. Gordon Watts Professor of Music and Professor of African and African American Studies at Harvard University. She won a Guggenheim Fellowship in 2007.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 p. 36, The UNESCO Courier, June 1973
- ↑ Taking the World for a Spin in Europe: An Insider's Look at the World Music Recording Business, René van Peer, Ethnomusicology43, #2 (Spring-Summer 1999), pp. 374-384, JSTOR 852750.
- 1 2 Review of "An Anthology of African Music. Nigeria III: Igbo Music" by David Ames and Cynthia Tse Kimberlin, review by Darius L. Thieme, Ethnomusicology36, #1 (Winter 1992), pp. 137-140, JSTOR 852093.
- ↑ Anthology of World Music: Africa - The Dan, overview, Allmusic. Accessed on line November 24, 2010.
- ↑ Anthology of World Music: Rwanda, overview, Allmusic. Accessed on line November 24, 2010.
- ↑ Anthology of World Music: Africa - The Ba-Benzele Pygmies, overview, Allmusic. Accessed on line November 24, 2010.
- ↑ See Worldcat record Africa, the Ba-Benzélé Pygmies. Anthology of world music. Cambridge, Mass: Rounder Records, 1998. Sound recording, OCLC 39370610, and Worldcat record Arom, Simha, and Geneviève Taurelle. Music of the Ba-Benzélé Pygmies. Unesco collection. Kassel: Bärenreiter-Musicaphon, 1965. Sound recording, OCLC 25082397.
- ↑ Worldcat record Gottlieb, Robert. Sudan: Music of the Blue Nile Province : the Gumuz Tribe = Soudan : Musique De La Province Du Nil Bleu : Tribu Des Gumuz. Unesco collection. France: Auvidis, 1996. Sound recording, OCLC 421844755, and Worldcat record Sudan: Music of the Blue Nile Province : the Gumuz Tribe = Soudan : Musique De La Province Du Nil Bleu : Tribu Des Gumuz. Unesco collection. Gentilly [France: Auvidis/Unesco, 1996. Sound recording, OCLC 36569272.
- ↑ Worldcat record Gottlieb, Robert. Sudan: Music of the Blue Nile Province : the Ingessana and Berta Tribes = Soudan : Musique De La Province Du Nil Bleu : Tribus Des Ingessana Et Des Berta. Unesco collection. France: Auvidis, 1996. Sound recording, OCLC 421844776 and Worldcat record Sudan: Music of the Blue Nile Province : the Ingessana and Berta Tribes = Soudan : Musique De La Province Du Nil Bleu : Tribus Des Ingessana Et Des Berta. Unesco collection. Gentilly [France: Auvidis/Unesco, 1996. Sound recording, OCLC 36569586.
- ↑ Selected Publications, music-research-inst.org.