The Tujia, with a total population of over 8 million, is the 8th largest ethnic minority in the People's Republic of China. They live in the Wuling Mountains, straddling the common borders of Hunan, Hubei and Guizhou Provinces, and Chongqing Municipality.

Xiangxi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture is an autonomous prefecture of the People's Republic of China. It is located in western Hunan province. It consists of 1 city, Jishou, and 7 counties: Baojing, Fenghuang, Guzhang, Huayuan, Longshan, Luxi, Yongshun. The capital is Jishou. Twenty-five nationalities gather here, of the total 2,480,000 population, 66.6 per cent are ethnic minorities, including 860,000 Tujia and 790,000 Miao.

Xiangyang is a prefecture-level city in northwestern Hubei province, China and the second largest city in Hubei by population. It was known as Xiangfan from 1950 to 2010. The Han River runs through Xiangyang's centre and divides the city north-south. The city itself is an agglomeration of two once separate cities: Fancheng and Xiangcheng. What remains of old Xiangyang is located south of the Han River and contains one of the oldest still-intact city walls in China, while Fancheng is located to the north of the Han River. Both cities served prominent historical roles in both ancient and pre-modern Chinese history. Today, the city has been a target of government and private investment as the country seeks to urbanize and develop the interior provinces. In 2017, population of the prefecture-level city was 5.65 million, in which 3.37 million were urban residents.
Nancheng may refer to the following places in China:

Luotian County is located in the northeast of Hubei province, China and it is under the administration of Huanggang City. The county is on the south side of the Dabie Mountains with the highest peak, Tiantangzhai, situated in the northeastern part of the county. Luotian county covers an area of 2,144 square kilometres (828 sq mi) and had a population of about 600,000 in 2016. The Dabie Mountains attract thousands of tourists from all over the province every year and the most popular tourist sites include Tiantangzhai National Forest Park, Bodaofeng National Forest Park, and Sanlifan Hot Spring.
Liulin primarily refers to Liulin County (柳林县), Shanxi, China.
Hengshan may refer to the following locations in mainland China or Taiwan:

Pingli County is a county the southeast of Shaanxi province, China, bordering Chongqing to the south and Hubei province to the east. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Ankang.
Liuji, derived from the Standard Mandarin pinyin 'Liújí', may refer to:
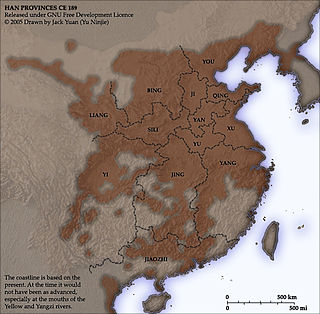
Jingzhou or Jing Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China referenced in Chinese historical texts such as the Tribute of Yu, Erya and Rites of Zhou. It became an administrative division during the reign of Emperor Wu in the Western Han dynasty.
Yandian may refer to the following locations in China:
Guang Prefecture was a prefecture of imperial China centered on modern Huangchuan County, Henan. It was created in the 6th century under the Liang dynasty and existed intermittently until 1913, after the establishment of the Republic.
Guizhou or Gui Prefecture (歸州) was a zhou (prefecture) in imperial China centering on modern Zigui County, Hubei, China. In the Yuan dynasty it was briefly called Guizhou Military Commission (歸州安撫司) and Guizhou Route (歸州路). It existed (intermittently) from 619 until 1912.
Fuzhou or Fu Prefecture (復州) was a zhou (prefecture) in imperial China, centering on modern Xiantao, Hubei, China. It existed (intermittently) from mid-6th century until 1278. Between 1275 and 1278 during the Yuan dynasty it was known as Fuzhou Route (復州路).
Huangzhou or Huang Prefecture was a zhou (prefecture) in imperial China, centering on modern Huangzhou District, Huanggang, Hubei, China. It existed (intermittently) from 585 until 1279.
Xiázhou or Xiá Prefecture was a zhou (prefecture) in imperial China centering on modern Yichang, Hubei, China. It existed (intermittently) from the 6th century to 1376.