Related Research Articles
In morphology and syntax, a clitic is a morpheme that has syntactic characteristics of a word, but depends phonologically on another word or phrase. In this sense, it is syntactically independent but phonologically dependent—always attached to a host. A clitic is pronounced like an affix, but plays a syntactic role at the phrase level. In other words, clitics have the form of affixes, but the distribution of function words. For example, the contracted forms of the auxiliary verbs in I'm and we've are clitics.
Hurrian is an extinct Hurro-Urartian language spoken by the Hurrians (Khurrites), a people who entered northern Mesopotamia around 2300 BC and had mostly vanished by 1000 BC. Hurrian was the language of the Mitanni kingdom in northern Mesopotamia and was likely spoken at least initially in Hurrian settlements in modern-day Syria. It is generally believed that the speakers of this language originally came from the Armenian Highlands and spread over southeast Anatolia and northern Mesopotamia at the beginning of the 2nd millennium BC.

Spanish is a grammatically inflected language, which means that many words are modified ("marked") in small ways, usually at the end, according to their changing functions. Verbs are marked for tense, aspect, mood, person, and number. Nouns follow a two-gender system and are marked for number. Personal pronouns are inflected for person, number, gender, and a very reduced case system; the Spanish pronominal system represents a simplification of the ancestral Latin system.
Mbula is an Austronesian language spoken by around 2,500 people on Umboi Island and Sakar Island in the Morobe Province of Papua New Guinea. Its basic word order is subject–verb–object; it has a nominative–accusative case-marking strategy.

Tzeltal or Tseltal is a Mayan language spoken in the Mexican state of Chiapas, mostly in the municipalities of Ocosingo, Altamirano, Huixtán, Tenejapa, Yajalón, Chanal, Sitalá, Amatenango del Valle, Socoltenango, Las Rosas, Chilón, San Juan Cancuc, San Cristóbal de las Casas and Oxchuc. Tzeltal is one of many Mayan languages spoken near this eastern region of Chiapas, including Tzotzil, Chʼol, and Tojolabʼal, among others. There is also a small Tzeltal diaspora in other parts of Mexico and the United States, primarily as a result of unfavorable economic conditions in Chiapas.
Tamambo, or Malo, is an Oceanic language spoken by 4,000 people on Malo and nearby islands in Vanuatu.
Pohnpeian is a Micronesian language spoken as the indigenous language of the island of Pohnpei in the Caroline Islands. Pohnpeian has approximately 30,000 (estimated) native speakers living in Pohnpei and its outlying atolls and islands with another 10,000-15,000 (estimated) living off island in parts of the US mainland, Hawaii and Guam. It is the second-most widely spoken native language of the Federated States of Micronesia.
The grammar of Macedonian is, in many respects, similar to that of some other Balkan languages, especially Bulgarian. Macedonian exhibits a number of grammatical features that distinguish it from most other Slavic languages, such as the elimination of case declension, the development of a suffixed definite article, the lack of an infinitival verb, and the constructions with ima/nema formed with the auxiliary "to have", among others.
Araki is a nearly extinct language spoken in the small island of Araki, south of Espiritu Santo Island in Vanuatu. Araki is gradually being replaced by Tangoa, a language from a neighbouring island.
Ughele is an Oceanic language spoken by about 1200 people on Rendova Island, located in the Western Province of the Solomon Islands.
The Wuvulu-Aua language is spoken on Wuvulu and Aua Islands by speakers scattered around the Manus Province of Papua New Guinea. Although the Wuvulu-Aua language has a similar grammatical structure, word order, and tense to other Oceanic languages, it has an unusually complex morphology.
Bororo (Borôro), also known as Boe, is the sole surviving language of a small family believed to be part of the Macro-Gê languages. It is spoken by the Bororo, hunters and gatherers in the central Mato Grosso region of Brazil.
Somali is an agglutinative language, using many affixes and particles to determine and alter the meaning of words. As in other related Afroasiatic languages, Somali nouns are inflected for gender, number and case, while verbs are inflected for persons, number, tenses, and moods.
Paamese, or Paama, is the language of the island of Paama in Northern Vanuatu. There is no indigenous term for the language; however linguists have adopted the term Paamese to refer to it. Both a grammar and a dictionary of Paamese have been produced by Terry Crowley.
Maia is a Papuan language spoken in the Madang Province of Papua New Guinea, and is a member of the Trans-New Guinea language family. It has a language endangerment status of 6a, which means that it is a vigorous and sustainable language spoken by all generations. According to a 2000 census, there are approximately 4,500 living speakers of the language, who are split between twenty-two villages in the Almani district of the Bogia sub-district.
Mavea is an Oceanic language spoken on Mavea Island in Vanuatu, off the eastern coast of Espiritu Santo. It belongs to the North–Central Vanuatu linkage of Southern Oceanic. The total population of the island is approximately 172, with only 34 fluent speakers of the Mavea language reported in 2008.
Mizo grammar is the grammar of the Mizo language, a Tibeto-Burman language spoken by about a million people in Mizoram, Manipur, Tripura, Burma and Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh. It is a highly inflected language, with fairly complex noun phrase structure and word modifications. Nouns and pronouns are declined, and phrasal nouns also undergo an analogous declension.
Vamale (Pamale) is a Kanak language of northern New Caledonia. The Hmwaeke dialect, spoken in Tiéta, is fusing with Haveke and nearly extinct. Vamale is nowadays spoken in Tiendanite, We Hava, Téganpaïk and Tiouandé. It was spoken in the Pamale valley and its tributaries Vawe and Usa until the colonial of war of 1917, when its speakers were displaced.
Wamesa is an Austronesian language of Indonesian New Guinea, spoken across the neck of the Doberai Peninsula or Bird's Head. There are currently 5,000–8,000 speakers. While it was historically used as a lingua franca, it is currently considered to under-documented, endangered language. This means that fewer and fewer children have an active command of Wamesa. Instead, Papuan Malay has become increasingly dominant in the area.
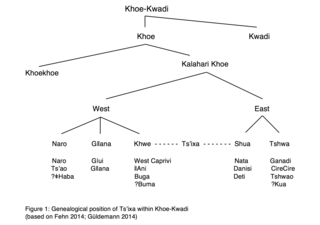
Tsʼixa is a critically endangered African language that belongs to the Kalahari Khoe branch of the Khoe-Kwadi language family. The Tsʼixa speech community consists of approximately 200 speakers who live in Botswana on the eastern edge of the Okavango Delta, in the small village of Mababe. They are a foraging society that consists of the ethnically diverse groups commonly subsumed under the names "San", "Bushmen" or "Basarwa". The most common term of self-reference within the community is Xuukhoe or 'people left behind', a rather broad ethnonym roughly equaling San, which is also used by Khwe-speakers in Botswana. Although the affiliation of Tsʼixa within the Khalari Khoe branch, as well as the genetic classification of the Khoisan languages in general, is still unclear, the Khoisan language scholar Tom Güldemann posits in a 2014 article the following genealogical relationships within Khoe-Kwadi, and argues for the status of Tsʼixa as a language in its own right. The language tree to the right presents a possible classification of Tsʼixa within Khoe-Kwadi:
References
- ↑ "Anaphoric Clitic". SIL Glossary of Linguistic Terms. 2015-12-03. Retrieved 2018-04-20.