
Chios is the fifth largest Greek island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea, and the tenth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. The island is separated from Turkey by the Chios Strait. Chios is notable for its exports of mastic gum and its nickname is "the Mastic Island". Tourist attractions include its medieval villages and the 11th-century monastery of Nea Moni, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Volissos is the largest village in the northwest part of Chios, Aegean Islands, Greece. The village is situated 40 km away from the main town of Chios.

Mastika or mastiha is a liqueur seasoned with mastic, a resin with a slightly pine or cedar-like flavor gathered from the mastic tree, a small evergreen tree native to the Mediterranean region. In Greece, mastiha or mastichato is a sweet liqueur produced with the mastika resin from the Greek island of Chios, which is distilled after hardening to crystals. Sugar is typically added. It is a sweet liqueur that is typically consumed at the end of a meal. It has a distinctive flavor, reminiscent of pine and herbs. It is claimed to have medicinal properties and to aid digestion.

Chios is the main town and a former municipality on the island of Chios, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it is part of the municipality Chios, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 22.823 km2. It is located on the eastern coast of the island facing the Turkish coastal town of Çeşme. The town has a population of 27,015 (2021) and is the administrative capital and main port of both the island and of the regional unit of Chios. Chios town is one of eight municipal units on the island.
Westfield is an unincorporated community in Harris County, Texas, United States, located along Interstate 45 and the Union Pacific Railroad nineteen miles (30 km) north of Downtown Houston.
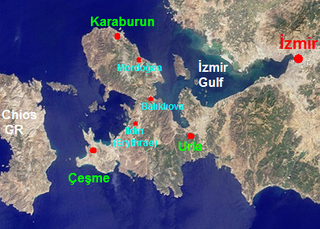
Karaburun Peninsula is a peninsula in the extreme western end of Turkey, a component of the larger Urla-Karaburun-Çeşme Peninsula. The peninsula carries the same name as the town and ilçe, Karaburun, located at a pivotal point in its extremity. It is located west of the city of İzmir, comprised wholly within İzmir Province and is surrounded by the Aegean Sea.
Kato Arodes is a village in the North West of Cyprus close to the Akamas peninsula. It is about 23 km from the town of Paphos.
The Diocese of Chios is a Latin Church diocese of the Catholic Church located on the island of Chios in the ecclesiastical province of Naxos, Andros, Tinos and Mykonos in Greece.

The Chios Byzantine Museum is a museum in Chios, Greece, housed in an Ottoman-era mosque that was known as the Mecidiye Mosque.
The Archaeological Museum of Chios is a museum located on Michalon Street in Chios town, Chios, Greece. Designed by the Greek architects Souzána Antonakáki and Dimitris Antonakakis & Eleni Gousi-Desylla in 1965, it has been widely regarded as a significant building in the architectural history of modern Greece. Constructed in 1966-1971, it covers a total area of 2500 square metres. 1200 square metres of floor space is occupied by the exhibitions.
The Chios Strait, or the Chios Channel as referred to by some sources, is a relatively narrow strait in the eastern Aegean Sea that separates the Greek island of Chios from the Anatolian mainland and from the Aegean Region of Turkey.
Leucae or Leuce was a small town of ancient Ionia, in the neighbourhood of Phocaea. Leucae was situated, according to Pliny in promontorio quod insula fuit, or, "on an island promontory." From Scylax we learn that it was a place with harbours. According to Diodorus, the Persian admiral Tachos founded this town on an eminence on the sea coast, in 352 BCE; but shortly after, when Tachos had died, the Clazomenians and Cymaeans quarrelled about its possession, and the former succeeded by a stratagem in making themselves masters of it. At a later time Leucae became remarkable for the battle fought in its neighbourhood between the consul Publius Licinius Crassus Dives Mucianus and Aristonicus in 131 BCE. Some have supposed this place to be identical with the Leuconium mentioned by Thucydides; but this is impossible, as this latter place must be looked for in Chios. The site of the ancient Leucae is at Üçtepeler, Izmir Province, Turkey, some distance from the coast. Coins were minted at Leucae in the 3rd century BCE.
Rushtown is an unincorporated community in Scioto County, in the U.S. state of Ohio.

Mesta is a Greek traditional village on the island of Chios. It belongs to the Mastic Villages, a group of villages in South Chios where the main activity is the manufacture of mastic. The mastic villages have been added to the representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity of UNESCO. Mesta is characterised by particular architecture since it is a village-castle with perfectly preserved medieval architecture. Mesta is located 35 km south west of Chios (town), 4 km away from the coast. It is built at a height of 120m and it belongs to Chios municipality and Mastichochoria municipal unit. It is also a community that comprises the village Limenas where the port of south west Chios is located.

Pyrgi is a village on the Greek island of Chios, known as the "painted village" on account of the decoration of the houses. This mostly consists of black and white decorative motifs in different shapes. Pyrgi is one of the biggest villages in Chios, located in the south part of the island, 25 km south of the island's capital. It is the traditional seat of the Mastic Villages, a group of villages where the residents engage with mastic agriculture. These villages have been added in representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity of UNESCO. The population of Pyrgi is 1,063 inhabitants according to the 2021 census.
Pteleum or Pteleon was a fortress town in the territory of Erythrae, in Ionia. Pliny the Elder mentions Pteleon, Helos, and Dorium as near Erythrae, but those places are confused by Pliny with the Triphylian towns in Homer's Catalogue of Ships in the Iliad.
Sidussa was a small town of Ionia, belonging to the territory of Erythrae, noted by Thucydides as a strong place, like Pteleum. Pliny the Elder describes it as an island off the coast of Erythrae. It is probable that the place also bore the name of Sidus (Σιδοῦς), as Stephanus of Byzantium mentions a town of this name in the territory of Erythrae.
Polichne, or Polichna (Πολίχνα), was a town of ancient Ionia, near Clazomenae. After the losses of the Athenians in Sicily, Clazomenae revolted with Chios and Erythrae against their Athenian overlords. The Clazomenii at the same time began to fortify Polichne on the main as a place of refuge, if it should be necessary. The Athenians took Polichne, and removed the people back to Clazomenae, except those who had been most active in the revolt; and they went off to a place called Daphnus.

The Battle of Chios took place from 24 November 1912 to 3 January 1913 during the First Balkan War. It resulted in the capture of the eastern Aegean island of Chios by the Kingdom of Greece, ending almost 350 years of rule by the Ottoman Empire.

Emporio is a prehistoric settlement in the southeastern part of the island of Chios in the Mastichochoria municipality of Greece. Pyrgi is the largest village nearby. It was inhabited since the early Neolithic times, around 6000 BC. The fertile valley with drinking water, a natural harbor nearby and the associated access to the sea were favorable conditions for settlement.















