
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is 8,900 km (5,530 mi) long and 200 to 700 km wide and has an average height of about 4,000 m (13,123 ft). The Andes extend from South to North through seven South American countries: Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela.

Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. Peru is a megadiverse country with habitats ranging from the arid plains of the Pacific coastal region in the west to the peaks of the Andes mountains extending from the north to the southeast of the country to the tropical Amazon basin rainforest in the east with the Amazon River. Peru has a population of over 32 million, and its capital and largest city is Lima. At 1,285,216 km2, Peru is the 19th largest country in the world, and the third largest in South America.

The Andean flamingo is a species of flamingo native to the Andes mountains of South America. Until 2014, it was classified in genus Phoenicopterus. It is closely related to James's flamingo, and the two make up the genus Phoenicoparrus. The Chilean flamingo, Andean flamingo, and James' flamingo are all sympatric, and all live in colonies.

Andean music is a group of styles of music from the Andes region in South America.

The Andean condor is a South American New World vulture and is the only member of the genus Vultur. It is found in the Andes mountains and adjacent Pacific coasts of western South America. With a maximum wingspan of 3.3 m and weight of 15 kg (33 lb), the Andean condor is one of the largest flying birds in the world, and is generally considered to be the largest bird of prey in the world.

The Andean Community is a free trade area with the objective of creating a customs union comprising the South American countries of Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. The trade bloc was called the Andean Pact until 1996 and came into existence when the Cartagena Agreement was signed in 1969. Its headquarters are in Lima, Peru.
The Peru–Chile Trench, also known as the Atacama Trench, is an oceanic trench in the eastern Pacific Ocean, about 160 kilometres (99 mi) off the coast of Peru and Chile. It reaches a maximum depth of 8,065 m (26,460 ft) below sea level in Richards Deep and is approximately 5,900 km (3,666 mi) long; its mean width is 64 km (40 mi) and it covers an expanse of some 590,000 km2 (230,000 sq mi).

Edward Allan Wagner Tizón is a Peruvian diplomat who most recently served as the Minister of Foreign Affairs from February 2021 to July 2021. He previously served twice in the position from 2002 to 2003 and from 1985 to 1988. In addition, he served as Minister of Defense from 2006 to 2007.

The Andean Parliament is the governing and deliberative body of the Andean Community, conformed by representatives of its four member states Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador and Peru, and one associate member, Chile. It is composed of 25 parliamentarians, five representing each state.

The G-3 was a free trade agreement between Colombia, Mexico, and Venezuela that came into effect on January 1, 1995, which created an extended market of 149 million consumers with a combined GDP of US$486.5 billion. The agreement states a ten percent tariff reduction over ten years for the trade of goods and services among its members. The agreement is a third generation one, not limited to liberalizing trade, but includes issues such as investment, services, government purchases, regulations to fight unfair competition, and intellectual property rights.
The United States–Peru Trade Promotion Agreement is a bilateral free trade agreement, whose objectives are eliminating obstacles to trade, consolidating access to goods and services and fostering private investment in and between the United States and Peru. Besides commercial issues, it incorporates economic, institutional, intellectual property, labor and environmental policies, among others. The agreement was signed on April 12, 2006; ratified by the Peruvian Congress on June 28, 2006; by the U.S. House of Representatives on November 2, 2007, and by the U.S. Senate on December 4, 2007. The Agreement was implemented on February 1, 2009.
Tecnocumbia is a style of Cumbia where there is a fusion between electronic sounds generated by electronic musical instruments through electronic drums, the electric guitar, synthesisers, and samplers. "Tecnocumbia" was a word developed in Mexico to describe this type of music. However, the style of music was developed throughout South America with different names given to it before the name "Tecnocumbia" was adopted as the single denomination for the music.
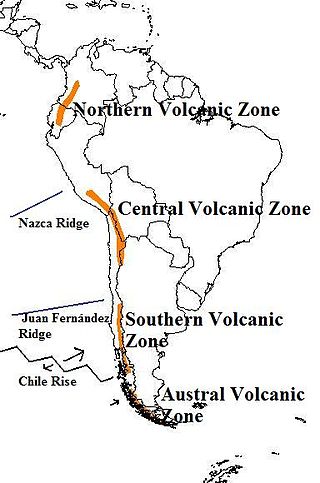
The Andean Volcanic Belt is a major volcanic belt along the Andean cordillera in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. It is formed as a result of subduction of the Nazca Plate and Antarctic Plate underneath the South American Plate. The belt is subdivided into four main volcanic zones which are separated by volcanic gaps. The volcanoes of the belt are diverse in terms of activity style, products, and morphology. While some differences can be explained by which volcanic zone a volcano belongs to, there are significant differences within volcanic zones and even between neighboring volcanoes. Despite being a type location for calc-alkalic and subduction volcanism, the Andean Volcanic Belt has a broad range of volcano-tectonic settings, as it has rift systems and extensional zones, transpressional faults, subduction of mid-ocean ridges and seamount chains as well as a large range of crustal thicknesses and magma ascent paths and different amounts of crustal assimilations.

CAF - Development Bank of Latin America and the Caribbean, formerly the Andean Development Corporation, is a development bank whose mission is to promote sustainable development and regional integration in Latin America and the Caribbean, through the financing of projects of the public and private sectors, the provision of technical cooperation and other specialized services.

Metallurgy in pre-Columbian America is the extraction, purification and alloying of metals and metal crafting by Indigenous peoples of the Americas prior to European contact in the late 15th century. Indigenous Americans had been using native metals from ancient times, with recent finds of gold artifacts in the Andean region dated to 2155–1936 BC, and North American copper finds being dated to approximately 5000 BC. The metal would have been found in nature without the need for smelting, and shaped into the desired form using hot and cold hammering without chemical alteration or alloying. To date "no one has found evidence that points to the use of melting, smelting and casting in prehistoric eastern North America."

The Andean civilizations were South American complex societies of many indigenous people. They stretched down the spine of the Andes for 4,000 km (2,500 mi) from southern Colombia, to Ecuador and Peru, including the deserts of coastal Peru, to north Chile and northwest Argentina. Archaeologists believe that Andean civilizations first developed on the narrow coastal plain of the Pacific Ocean. The Caral or Norte Chico civilization of coastal Peru is the oldest known civilization in the Americas, dating back to 3500 BCE. Andean civilization is one of the six "pristine" civilizations of the world, created independently and without influence by other civilizations.

The Andean orogeny is an ongoing process of orogeny that began in the Early Jurassic and is responsible for the rise of the Andes mountains. The orogeny is driven by a reactivation of a long-lived subduction system along the western margin of South America. On a continental scale the Cretaceous and Oligocene were periods of re-arrangements in the orogeny. The details of the orogeny vary depending on the segment and the geological period considered.

Andean Spanish is a dialect of Spanish spoken in the central Andes, from southern Colombia, with influence as far south as northern Chile and Northwestern Argentina, passing through Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia. While similar to other Spanish dialects, Andean Spanish shows influence from Quechua, Aymara, and other indigenous languages, due to prolonged and intense language contact. This influence is especially strong in rural areas.

The history of human habitation in the Andean region of South America stretches from circa 15,000 BCE to the present day. Stretching for 7,000 km (4,300 mi) long, the region encompasses mountainous, tropical and desert environments. This colonisation and habitation of the region has been affected by its unique geography and climate, leading to the development of unique cultural and socn.

The Andean preceramic refers to the early period of human occupation in the Andean area of South America that preceded the introduction of ceramics. This period is also called pre-ceramic or aceramic.
















