
A cleft lip contains an opening in the upper lip that may extend into the nose. The opening may be on one side, both sides, or in the middle. A cleft palate occurs when the palate contains an opening into the nose. The term orofacial cleft refers to either condition or to both occurring together. These disorders can result in feeding problems, speech problems, hearing problems, and frequent ear infections. Less than half the time the condition is associated with other disorders.

Airway management includes a set of maneuvers and medical procedures performed to prevent and relieve airway obstruction. This ensures an open pathway for gas exchange between a patient's lungs and the atmosphere. This is accomplished by either clearing a previously obstructed airway; or by preventing airway obstruction in cases such as anaphylaxis, the obtunded patient, or medical sedation. Airway obstruction can be caused by the tongue, foreign objects, the tissues of the airway itself, and bodily fluids such as blood and gastric contents (aspiration).
Oral and maxillofacial surgery is a surgical specialty focusing on reconstructive surgery of the face, facial trauma surgery, the oral cavity, head and neck, mouth, and jaws, as well as facial cosmetic surgery/facial plastic surgery including cleft lip and cleft palate surgery.
Nasal congestion is the partial or complete blockage of nasal passages, leading to impaired nasal breathing, usually due to membranes lining the nose becoming swollen from inflammation of blood vessels.

Orthognathic surgery, also known as corrective jaw surgery or simply, jaw surgery, is surgery designed to correct conditions of the jaw and lower face related to structure, growth, airway issues including sleep apnea, TMJ disorders, malocclusion problems primarily arising from skeletal disharmonies, and other orthodontic dental bite problems that cannot be treated easily with braces, as well as the broad range of facial imbalances, disharmonies, asymmetries, and malproportions where correction may be considered to improve facial aesthetics and self-esteem.

Ludwig's angina is a type of severe cellulitis involving the floor of the mouth and is often caused by bacterial sources. Early in the infection, the floor of the mouth raises due to swelling, leading to difficulty swallowing saliva. As a result, patients may present with drooling and difficulty speaking. As the condition worsens, the airway may be compromised and hardening of the spaces on both sides of the tongue may develop. Overall, this condition has a rapid onset over a few hours.

Hemifacial microsomia (HFM) is a congenital disorder that affects the development of the lower half of the face, most commonly the ears, the mouth and the mandible. It usually occurs on one side of the face, but both sides are sometimes affected. If severe, it may result in difficulties in breathing due to obstruction of the trachea—sometimes even requiring a tracheotomy. With an incidence in the range of 1:3500 to 1:4500, it is the second most common birth defect of the face, after cleft lip and cleft palate. HFM shares many similarities with Treacher Collins syndrome.
Craniofacial surgery is a surgical subspecialty that deals with congenital and acquired deformities of the head, skull, face, neck, jaws and associated structures. Although craniofacial treatment often involves manipulation of bone, craniofacial surgery is not tissue-specific; craniofacial surgeons deal with bone, skin, nerve, muscle, teeth, and other related anatomy.

Distraction osteogenesis (DO), also called callus distraction, callotasis and osteodistraction, is a process used in orthopedic surgery, podiatric surgery, and oral and maxillofacial surgery to repair skeletal deformities and in reconstructive surgery. The procedure involves cutting and slowly separating bone, allowing the bone healing process to fill in the gap.

Pierre Robin sequence is a congenital defect observed in humans which is characterized by facial abnormalities. The three main features are micrognathia, which causes glossoptosis, which in turn causes breathing problems due to obstruction of the upper airway. A wide, U-shaped cleft palate is commonly also present. PRS is not merely a syndrome, but rather it is a sequence—a series of specific developmental malformations which can be attributed to a single cause.
Pierre Robin was a French stomatologist from Paris. He was professor at the French School of Stomatology, and from 1914, he was editor-in-chief of the Revue de Stomatologie.

Facial trauma, also called maxillofacial trauma, is any physical trauma to the face. Facial trauma can involve soft tissue injuries such as burns, lacerations and bruises, or fractures of the facial bones such as nasal fractures and fractures of the jaw, as well as trauma such as eye injuries. Symptoms are specific to the type of injury; for example, fractures may involve pain, swelling, loss of function, or changes in the shape of facial structures.

Mandibular fracture, also known as fracture of the jaw, is a break through the mandibular bone. In about 60% of cases the break occurs in two places. It may result in a decreased ability to fully open the mouth. Often the teeth will not feel properly aligned or there may be bleeding of the gums. Mandibular fractures occur most commonly among males in their 30s.
A jaw abnormality is a disorder in the formation, shape and/or size of the jaw. In general abnormalities arise within the jaw when there is a disturbance or fault in the fusion of the mandibular processes. The mandible in particular has the most differential typical growth anomalies than any other bone in the human skeleton. This is due to variants in the complex symmetrical growth pattern which formulates the mandible.
Sleep surgery is a surgery performed to treat sleep disordered breathing. Sleep disordered breathing is a spectrum of disorders that includes snoring, upper airway resistance syndrome, and obstructive sleep apnea. These surgeries are performed by surgeons trained in otolaryngology, oral maxillofacial surgery, and craniofacial surgery.
Long face syndrome, also referred to as skeletal open bite, is a relatively common condition characterised by excessive vertical facial development. Its causes may be either genetic or environmental. Long face syndrome is "a common dentofacial abnormality." Its diagnosis, symptomology and treatments are complex and controversial. Indeed, even its existence as a "syndrome" is disputed.
Condylar hypoplasia is known as underdevelopment of the mandibular condyle. Congenitally (primary) caused condylar hypoplasia leads to underdeveloped condyle at birth. Hypoplasia of mandible can be diagnosed during birth, in comparison to the hyperplasia which is only diagnosed later in growth of an individual.
Derek Steinbacher is an American cosmetic plastic, rhinoplasty, and maxillofacial surgeon who is Professor of Plastic Surgery at Yale New Haven Health in Connecticut. He is also the chief of the Dental Department and Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at Yale New Haven Health. He is known for his clinical work, research and incorporation of 3D analysis and printing into jaw surgery, craniofacial surgery and rhinoplasty.
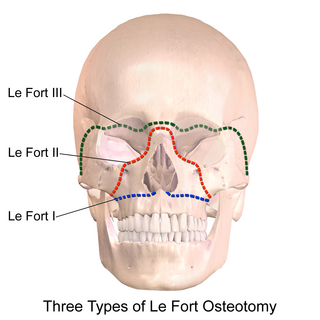
A Le Fort osteotomy is the name for three types of osteotomies of the jaw and face. They are based on the analogous bone fractures described by the French surgeon and physician René Le Fort.

Mandibular setback surgery is a surgical procedure performed along the occlusal plane to prevent bite opening on the anterior or posterior teeth and retract the lower jaw for both functional and aesthetic effects in patients with mandibular prognathism. It is an orthodontic surgery that is a form of reconstructive plastic surgery. There are three main types of procedures for mandibular setback surgery: Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy (BSSO), Intraoral Vertical Ramus Osteotomy (IVRO) and Extraoral Ramus Osteotomy (EVRO), depending on the magnitude of mandibular setback for each patient. Postoperative care aims to minimise postoperative complications, complications includes bite changes, relapse and nerve injury.









