
Lake Van, the largest lake in the Eastern Anatolia Region, Turkey, and the Armenian Highlands, lies in the far east of Turkey in the provinces of Van and Bitlis. It is a saline soda lake, receiving water from many small streams that descend from the surrounding mountains. It is one of the world's few endorheic lakes of greater size than 3,000 square kilometres (1,200 sq mi) and has 38% of the country's surface water. A volcanic eruption blocked its original outlet in prehistoric times. It is situated at 1,640 m (5,380 ft). Despite the high altitude and winter highs below 0 °C (32 °F), high salinity mainly prevents it from freezing at such times. Specifically, the shallow northern section can freeze, but rarely.

Van is a mostly Kurdish-populated city in eastern Turkey's Van Province, located on the eastern shore of Lake Van. The city has a long history as a major urban area. It has been a large city since the first millennium BC, initially as Tushpa, the capital of the kingdom of Urartu from the 9th century BC to the 6th century BC, and later as the center of the Armenian kingdom of Vaspurakan.

The history of Armenia covers the topics related to the history of the Republic of Armenia, as well as the Armenian people, the Armenian language, and the regions historically and geographically considered Armenian.

Hayk, also known as Hayk Nahapet, is the legendary patriarch and founder of the Armenian nation. His story is told in the History of Armenia attributed to the Armenian historian Moses of Chorene.

The Qara Qoyunlu or Kara Koyunlu, also known as the Black Sheep Turkomans, were a Muslim Turkoman monarchy that ruled over the territory comprising present-day Azerbaijan, Georgia, Armenia, northwestern Iran, eastern Turkey, and northeastern Iraq from about 1374 to 1468.

The Kingdom of Armenia, also the Kingdom of Greater Armenia, or simply Greater Armenia, sometimes referred to as the Armenian Empire, was a monarchy in the Ancient Near East which existed from 321 BC to 428 AD. Its history is divided into successive reigns by three royal dynasties: Orontid, Artaxiad and Arsacid (52–428).
The Artsruni were an ancient noble (princely) family of Armenia.

The Armenian Highlands is the most central and the highest of the three plateaus that together form the northern sector of Western Asia. Clockwise starting from the west, the Armenian Highlands are bounded by the Anatolian plateau, the Caucasus, the Kura-Aras lowlands, the Iranian Plateau, and Mesopotamia. The highlands are divided into western and eastern regions, defined by the Ararat Valley where Mount Ararat is located. Western Armenia is nowadays referred to as eastern Anatolia, and Eastern Armenia as the Lesser Caucasus or Caucasus Minor, and historically as the Anti-Caucasus, meaning "opposite the Caucasus".

Başkale is a town and district located in south-eastern Turkey in Van Province. There is one municipality in the Başkale district, the town centre, which was established 1937. The neighbourhoods of the town of Başkale are: Tepebaşı, Yeni mahalle, Camii-Kebir, Samandöken, Cevkan, Kale, Hafiziye, Tarım and Yakınyol. In the local elections of March 2019 Erkan Acar from the Peoples' Democratic Party (HDP) was elected mayor.
Vaspurakan was the eighth province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, which later became an independent kingdom during the Middle Ages, centered on Lake Van. Located in what is now called southeastern Turkey and northwestern Iran, the region is considered to be the cradle of Armenian civilization.

The Shaddadids were a Kurdish Sunni Muslim dynasty who ruled in various parts of Armenia and Arran from 951 to 1199 AD. They were established in Dvin. Through their long tenure in Armenia, they often intermarried with the Bagratuni royal family of Armenia.
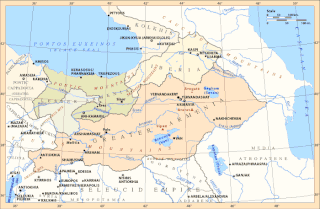
The Satrapy of Armenia, a region controlled by the Orontid dynasty, was one of the satrapies of the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC that later became an independent kingdom. Its capitals were Tushpa and later Erebuni.

Tushpa was the 9th-century BC capital of Urartu, later becoming known as Van which is derived from Biainili the native name of Urartu. The ancient ruins are located just west of Van and east of Lake Van in the Van Province of Turkey. In 2016 it was inscribed in the Tentative list of World Heritage Sites in Turkey.
The Shah-Armens, also known as Ahlatshahs, was a 11th- and 12th-century Turcoman beylik founded after the Battle of Manzikert (1071) and centred in Ahlat on the northwestern shore of the Lake Van. This region comprised most of modern day Bitlis and Van, and parts of Muş provinces.

Karmravank is an abandoned 10th century Armenian monastery in the Vaspurakan province of historic Armenia. It was founded by King Gagik I (908-943) of the Artsruni dynasty. It is located 12 kilometers west-northwest of Akhtamar Island.
Hidarnes I was a King of the Orontid Dynasty of Armenia, reigning in the end of the 6th century BC.
Ancient Armenia refers to the history of Armenia during Antiquity. It follows Prehistoric Armenia and covers a period of approximately one thousand years, beginning at the end of the Iron Age with the events that led to the dissolution of the Kingdom of Urartu, and the emergence of the first geopolitical entity called Armenia in the 6th century BC. Highlights of this period include the rise of ancient Armenia as an important state in Western Asia in the 4th century BC; a briefly held empire under Julius Caesar's contemporary the Great King Tigranes II ; the kingdom's official conversion to Christianity in 301; and the creation of the Armenian alphabet in the year 405. It concludes with the demise of the Armenian kingdom and the country's partition later in the 5th century, marking the beginning of Medieval Armenia.
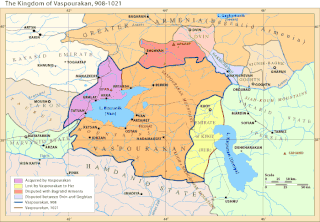
Vaspurakan was the first and biggest province of Greater Armenia, which later became an independent kingdom during the Middle Ages, centered on Lake Van. Located in what is now called eastern Turkey and northwestern Iran, the region is considered to be the cradle of Armenian civilization.

Gaius Julius Sohaemus was a Roman client king of Armenia.
Pacorus, also known as Aurelius Pacorus or Bakur was a Parthian Prince who served as one of the Kings of Armenia in the 2nd century.















