Related Research Articles
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of all pregnancies. When deliberate steps are taken to end a pregnancy, it is called an induced abortion, or less frequently "induced miscarriage". The unmodified word abortion generally refers to an induced abortion. The most common reasons women give for having an abortion are for birth-timing and limiting family size. Other reasons reported include maternal health, an inability to afford a child, domestic violence, lack of support, feeling they are too young, wishing to complete education or advance a career, and not being able or willing to raise a child conceived as a result of rape or incest.

Laura Lane Bush is an American educator who was the first lady of the United States from 2001 to 2009 as the wife of George W. Bush, the 43rd president of the United States. Bush was previously the first lady of Texas from 1995 to 2000 when her husband was governor.

The combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP), often referred to as the birth control pill or colloquially as "the pill", is a type of birth control that is designed to be taken orally by women. It is the oral form of combined hormonal contraception. The pill contains two important hormones: a progestin and estrogen. When taken correctly, it alters the menstrual cycle to eliminate ovulation and prevent pregnancy.

Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin.
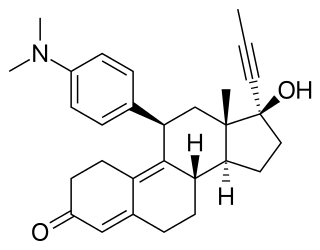
Mifepristone, also known by its developmental code name RU-486, is a medication typically used in combination with misoprostol to bring about a medical abortion during pregnancy and manage early miscarriage. This combination is 97% effective during the first 63 days of pregnancy. It is also effective in the second trimester of pregnancy. It is taken by mouth.
Women's health differs from that of men's health in many unique ways. Women's health is an example of population health, where health is defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity". Often treated as simply women's reproductive health, many groups argue for a broader definition pertaining to the overall health of women, better expressed as "The health of women". These differences are further exacerbated in developing countries where women, whose health includes both their risks and experiences, are further disadvantaged.
The abortion–breast cancer hypothesis posits that having an induced abortion can increase the risk of getting breast cancer. This hypothesis is at odds with mainstream scientific opinion and is rejected by major medical professional organizations; despite this, it continues to be widely propagated as pseudoscience, typically in service of an anti-abortion agenda.
Joel Lewis Brind is a professor of human biology and endocrinology at Baruch College, City University of New York and a leading advocate of the abortion-breast cancer hypothesis, which posits that abortion increases the risk of breast cancer. This idea is rejected by mainstream medical professional organizations and there is overwhelming evidence in the peer-reviewed medical literature debunking it. Brind is openly contemptuous of mainstream medical professional organizations and journals, accusing them of conducting a deliberate cover-up with the goal of "protecting the abortion industry."

Voice for Life, formerly known as the Society for the Protection of the Unborn Child (SPUC), is a New Zealand anti-abortion advocacy group. It has also lobbied against infanticide, embryonic stem cell research, cloning and euthanasia. In recent years, it has strongly campaigned against the decriminalisation of euthanasia in New Zealand as well as abortion, but was unsuccessful in preventing the decriminalisation of either in 2020.

Else "Els" Borst-Eilers was a Dutch politician of the Democrats 66 (D66) party and physician. She was granted the honorary title of Minister of State on 21 December 2012.
The National Women's Health Network (NWHN) is a non-profit women's health advocacy organization located in Washington, D.C. It was founded in 1975 by Barbara Seaman, Alice Wolfson, Belita Cowan, Mary Howell, and Phyllis Chesler. The stated mission of the organization is to give women a greater voice within the healthcare system. The NWHN researches and lobbies federal agencies on such issues as AIDS, reproductive rights, breast cancer, older women's health, and new contraceptive technologies. The Women's Health Voice, the NWHN's health information program, provides independent research on a variety of women's health topics.

Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unintended pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth control only became available in the 20th century. Planning, making available, and using human birth control is called family planning. Some cultures limit or discourage access to birth control because they consider it to be morally, religiously, or politically undesirable.
The Family Planning Services and Population Research Act of 1970 is the only federal grant program dedicated to providing individuals with comprehensive family planning and related preventive health services. It was signed into law under President Richard Nixon on December 24, 1970.

The Princess Grace Hospital is a private hospital in Marylebone, London, and is part of the international division of HCA, which is the world's largest private healthcare company.

Endeavour Forum is a conservative political organisation describing itself as "a Christian, pro-life, pro-family organisation that was founded to counter feminism, to defend the right to life of the unborn, and to support marriage and the natural family." It was founded in 1979 by the late Babette Francis AM (1930-2024) and has links to similar groups, such as the Australian Family Association and the World Congress of Families. It exerted strong influence on the Fraser government of the seventies and eighties and the Queensland state government led by Sir Joh Bjelke-Petersen (1911-2005) until it fell due to internal government corruption in the late eighties.

Angela Hartley Brodie was a British biochemist who pioneered development of steroidal aromatase inhibitors in cancer research. Born in Lancashire, Brodie studied chemical pathology to a doctoral level in Sheffield and was awarded a fellowship sponsored by National Institutes of Health. After 17 years of working in Shrewsbury, Massachusetts on oral contraceptives with Harry Brodie, whom she married, she switched focus to the effects of the oestrogen-producing enzyme, aromatase, on breast cancer.
Charlotte Ellertson was a sociologist and public health researcher activist who specialized in emergency contraception and medication abortion. She founded Ibis Reproductive Health, an organization that advocates for sexual and reproductive health education and access. The organization, and Ellertson's work in it, is recognized as instrumental in the FDA approval of the abortion inducing pill RU-486. In 2013, HuffPost named Ellertson one of 50 most influential people in women's health.

Combined hormonal contraception (CHC), or combined birth control, is a form of hormonal contraception which combines both an estrogen and a progestogen in varying formulations.
The women's health movementin the United States refers to the aspect of the American feminist movement that works to improve all aspects of women's health and healthcare. It began during the second wave of feminism as a sub-movement of the women's liberation movement. WHM activism involves increasing women's knowledge and control of their own bodies on a variety of subjects, such as fertility control and home remedies, as well as challenging traditional doctor-patient relationships, the medicalization of childbirth, misogyny in the health care system, and ensuring drug safety.

Xiaohong Rose Yang is an American biomedical scientist researching the genetics of dysplastic nevus syndrome and chordoma, and etiologic heterogeneity of breast cancer. She is a senior investigator at the National Cancer Institute. Yang leads breast cancer studies in mainland China, Hong Kong, and Malaysia.
References
- ↑ "Angela Lanfranchi". Library of Congress Name Authority File. Library of Congress. Retrieved 4 June 2017.
- ↑ "History". Breast Cancer Prevention Institute. Archived from the original on 29 May 2017. Retrieved 4 June 2017.
- ↑ Aston, Heath (25 July 2014). "Ministers to join pro-lifer who believes the 'pill kills' at World Congress of Families". Sydney Morning-Herald. Retrieved 4 June 2017.
- ↑ Davey, Melissa (30 August 2014). "Angela Lanfranchi, who links abortion and cancer, stars at families congress". The Guardian. Retrieved 4 June 2017.