
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and to further recognize and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future. Vaccines can be prophylactic, or therapeutic. Some vaccines offer full sterilizing immunity, in which infection is prevented completely.

The MMR vaccine is a vaccine against measles, mumps, and rubella, abbreviated as MMR. The first dose is generally given to children around 9 months to 15 months of age, with a second dose at 15 months to 6 years of age, with at least four weeks between the doses. After two doses, 97% of people are protected against measles, 88% against mumps, and at least 97% against rubella. The vaccine is also recommended for those who do not have evidence of immunity, those with well-controlled HIV/AIDS, and within 72 hours of exposure to measles among those who are incompletely immunized. It is given by injection.
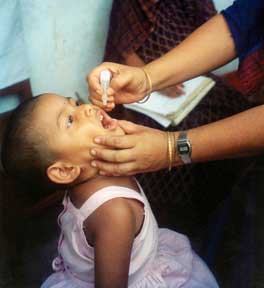
Polio vaccines are vaccines used to prevent poliomyelitis (polio). Two types are used: an inactivated poliovirus given by injection (IPV) and a weakened poliovirus given by mouth (OPV). The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends all children be fully vaccinated against polio. The two vaccines have eliminated polio from most of the world, and reduced the number of cases reported each year from an estimated 350,000 in 1988 to 33 in 2018.

John Franklin Enders was an American biomedical scientist and Nobel Laureate. Enders has been called "The Father of Modern Vaccines."

Albert Bruce Sabin was a Polish-American medical researcher, best known for developing the oral polio vaccine, which has played a key role in nearly eradicating the disease. In 1969–72, he served as the President of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel.
Vaccine hesitancy is a delay in acceptance, or downright refusal, of vaccines despite the availability of vaccine services. The term covers outright refusals to vaccinate, delaying vaccines, accepting vaccines but remaining uncertain about their use, or using certain vaccines but not others. The scientific consensus that vaccines are generally safe and effective is overwhelming. Vaccine hesitancy often results in disease outbreaks and deaths from vaccine-preventable diseases. Therefore, the World Health Organization characterizes vaccine hesitancy as one of the top ten global health threats.
Vaccination and religion have interrelations of varying kinds. No major religion prohibits vaccinations, and some consider it an obligation because of the potential to save lives. However, some people cite religious adherence as a basis for opting to forego vaccinating themselves or their children. Many such objections are pretextual: in Australia, anti-vaccinationists founded the Church of Conscious Living, a "fake church", leading to religious exemptions being removed in that country, and one US pastor was reported to offer vaccine exemptions in exchange for online membership of his church.

Mumps vaccines are vaccines which prevent mumps. When given to a majority of the population they decrease complications at the population level. Effectiveness when 90% of a population is vaccinated is estimated at 85%. Two doses are required for long term prevention. The initial dose is recommended between 12 and 18 months of age. The second dose is then typically given between two years and six years of age. Usage after exposure in those not already immune may be useful.
An attenuated vaccine is a vaccine created by reducing the virulence of a pathogen, but still keeping it viable. Attenuation takes an infectious agent and alters it so that it becomes harmless or less virulent. These vaccines contrast to those produced by "killing" the virus.

Ciro Carlos Araujo de Quadros was a Brazilian leader in the field of Public Health, in particular, the area of vaccines and preventable diseases. He was born in Rio Pardo, Brazil.
The National Institute of Virology in Pune, India is an Indian virology research institute and part of the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). It was previously known as 'Virus Research Centre' and was founded in collaboration with the Rockefeller Foundation. It has been designated as a WHO H5 reference laboratory for SE Asia region.

Measles vaccine protects against becoming infected with measles. Nearly all of those who do not develop immunity after a single dose develop it after a second dose. When rate of vaccination within a population is greater than 92%, outbreaks of measles typically no longer occur; however, they may occur again if the rate of vaccination decrease. The vaccine's effectiveness lasts many years. It is unclear if it becomes less effective over time. The vaccine may also protect against measles if given within a couple of days after exposure to measles.
Samuel L. Katz is an American pediatrician and virologist whose career has been devoted to infectious disease research, focusing principally on vaccine research and development. Katz is currently the Wilburt Cornell Davison Professor and Chairman Emeritus of Pediatrics at Duke University.
Thomas Chalmers Peebles was an American physician who made multiple discoveries in the field of medicine, including being the first to isolate the measles virus. Peebles also did research that led to the development of fluoridated vitamins and did research that showed that tetanus vaccine could be given once every 10 years, rather than annually as had been the widespread practice.
Universal Immunisation Programme (UIP) is a vaccination programme launched by the Government of India in 1985. It became a part of Child Survival and Safe Motherhood Programme in 1992 and is currently one of the key areas under National Rural Health Mission since 2005. The programme now consists of vaccination for 12 diseases- tuberculosis, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, poliomyelitis, measles, hepatitis B, diarrhoea, Japanese encephalitis, rubella, pneumonia and Pneumococcal diseases. Hepatitis B and Pneumococcal diseases were added to the UIP in 2007 and 2017 respectively. The cost of all the vaccines are borne by the state and the government spent ₹3,587 crore (US$450 million) in 2017 to purchase the vaccines to provide them for free.
Pakistan is one of the two remaining countries in the world where poliomyelitis (polio) is still categorized as an endemic viral infection, the other one being Afghanistan. As of August 2022, there has been 14 documented cases in Pakistan in 2022. There was 1 documented case in Pakistan in 2021 and 84 documented cases in Pakistan in 2020. The total count of wild poliovirus cases in Pakistan in 2019 was 147.

The Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute is an Iranian pharmaceutical company. It is located in the Hessarak district in Karaj, Iran. The Institute was built as a national center with the purpose of countering epidemics in domestic animals during Reza Shah era. Further departments were installed, including those dedicated to human medicines. In modern years, the Institute has focused primarily on nanomedicine and biotechnology.
Anna Mitus was a medical researcher best known for her work on the measles vaccine as a part of the John Enders lab. Her most significant contribution to the research was her research on human amnion cells with Dr. Milan V. Milovanovic and how they supported the growth of the measles virus.
Misinformation related to immunization circulates in mass media and social media. Intentional spreading of false information and conspiracy theories have also been propagated by the general public and celebrities. Misinformation related to vaccination fuels vaccine hesitancy and thereby results in disease outbreaks. Although opposition to vaccination has existed for centuries, the internet and social media have recently facilitated the spread of vaccine-related misinformation. Unsubstantiated safety concerns related to vaccines are often presented on the internet as scientific information.

"Measles: A Dangerous Illness" is an open letter written by the children's writer Roald Dahl in 1986 in response to ongoing cases of measles in the United Kingdom at that time, despite the introduction of an effective measles vaccine in 1968.








