This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations .(February 2020) |
The Annals of Duiske is an Irish annal, created from 1513.
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations .(February 2020) |
The Annals of Duiske is an Irish annal, created from 1513.
Domhnall Riabhach Mac Murchadha Caomhánach, a son of Gerald mac Murchadha Caomhánach, became Kings of Leinster during 1478. In 1475, he had "granted eight pence annually from every plough in his territory to the abbey of Duiske." [1] One of Domhnall's sons, Cathal Mac Murchadha Caomhánach (anglicised Charles Kavanagh), became its abbot in 1501 and in 1513 he directed one of his monks to compile the annals of Ireland. This book was known as the "Annals of Duiske" or "The Ancient Book of Graig" but it was lost. [1] However, surviving fragments were published by Kenneth Nicholls in Peritia in 1983.
Diarmait Mac Murchada, was King of Leinster in Ireland from 1127 to 1171. In 1167, he was deposed by the High King of Ireland, Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair. To recover his kingdom, Mac Murchada solicited help from King Henry II of England. His issue unresolved, he gained the military support of the Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke, thus initiating the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland.

Art Óg Mac Murchadha Caomhánach was an Irish king who is generally regarded as the most formidable of the later kings of Leinster. He revived not only the royal family's prerogatives, but also their lands and power. During his 42-year reign, he dominated the Anglo-Norman settlers of Leinster. His dominance of the province and its inhabitants, both Gaelic and Hiberno-Norman, was deemed sufficiently detrimental to the colony that Richard II of England spent much of the years 1394 and 1395 sparring with him. While MacMurrough-Kavanagh did eventually submit to Richard, he renounced this fealty on Richard's departure and made much of his kingdom a death trap for any invading English or Anglo-Irish forces. The Crown accordingly dealt with him cautiously and he was granted an amnesty in 1409.
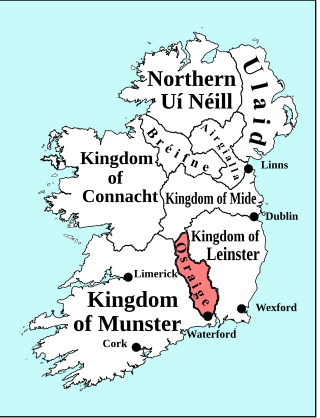
The kings of Osraige reigned over the medieval Irish kingdom of Osraige from the first or second century AD until the late twelfth century. Osraige was a semi-provincial kingdom in south-east Ireland which disappeared following the Norman Invasion of Ireland. A number of important royal Ossorian genealogies are preserved, particularly MS Rawlinson B502, which traces the medieval Mac Giolla Phádraig dynasty back through Óengus Osrithe, who supposedly flourished in the first or second century. and one in the Book of Leinster. Recent analysis of ninth and tenth century regnal succession in Osraige has suggested that in peaceful times, kingship passed primarily from eldest to youngest brother, before crossing generations and passing to sons and nephews.
The Uí Ceinselaig, from the Old Irish "grandsons of Cennsalach", are an Irish dynasty of Leinster who trace their descent from Énnae Cennsalach, a supposed contemporary of Niall of the Nine Hostages. Énda was said to be a grandson of Bressal Bélach and a first cousin of Dúnlaing mac Énda Niada, eponymous ancestor of the rival Uí Dúnlainge.
Events from the year 1171 in Ireland.

Kavanagh or Kavanaugh is a surname of Irish origin, Caomhánach in Irish. It is one of the few Irish surnames that does not traditionally have an O or a Mac in either English or Irish.

Caomhánach is an Irish-language surname first assumed by Domhnall Caomhánach, eldest son of the 12th-century Diarmait Mac Murchada, king of Leinster. A considerable number of anglicised variations of Caomhánach exist; some of the most common are Kavanagh, Cavanagh, Kavanaugh and Cavanaugh.

Domhnall mac Raghnaill was a Hebridean noble in the late 12th and early 13th centuries. He is the eponymous progenitor of Clan Donald. For this reason some traditions accumulated around him in the later Middle Ages and early modern period. His vast impact on culture and in the centuries remains today. Despite his role as the historical figurehead of one of the world's most famous kindreds and surnames, there is almost no contemporary evidence yielding certain information about his life.
Amlaíb Ua Donnubáin is the last member of the O'Donovan family to be styled king of Uí Chairpre Áebda in the Irish annals, and in fact the very last known king of this people.
An Crom Ua Donnubáin or Crom O'Donovan is the individual characterized as the ancestor of O'Donovans later found in Carbery in County Cork, and later still in distant County Wexford in Leinster. Nothing is known for sure of his life but his progeny, and the circumstances of his slaying and further events which followed. He was the son of Máel Ruanaid,, son of Aneislis, son of Murchad, son of Amlaíb, son of Cathal, son of Donnubán,, son of Cathal. An uncle or near relation was Amlaíb Ua Donnubáin, last known king of Uí Chairpre Áebda, slain in 1201.

Ó Coileáin is a Modern Irish surname generally belonging to the descendants of the last leading family of the Uí Chonaill Gabra, a sept and small but notable overkingdom of medieval and ancient Ireland, based in western County Limerick. Throughout much of their history the Uí Chonaill Gabra were in turn the leading sept of the greater regional overkingdom of the Uí Fidgenti, considered among the highest ranked princes or flatha in all the Province of Munster. Ó Coileáin/Ua Cuiléin is most commonly anglicized O'Collins and O'Cullane. The surname has also long been found in County Cork, believed largely due to the migration there, probably in the late 12th or early 13th century, of a junior branch of the County Limerick dynasty.
The Kings of Umaill were rulers of Umaill, a kingdom or territory located in the west of what is now County Mayo, Ireland.
Domhnall Ó Cobhthaigh was an Irish poet.
Tadhg na Mainistreach Mac Carthaigh Mór reigned as King of Desmond from 1390/2 to his death in 1428. He was the son of the previous king Domhnall Óg Mac Carthaigh Mór. According to the Annals of Inisfallen Tadhg Mac Carthaigh had the reputation as the greatest wine-drinker in Ireland when he died, but was still "a son worthy of his father". He was married to one Sebán, a daughter of "Garret the earl". This is likely a form of 'Siobhán' which translates as 'Joan,' so Sebán is probably a reference to Joan, a daughter of Gerald FitzGerald, 3rd Earl of Desmond.
Domhnall Spáinneach Mac Murchadha Caomhánach was the last King of Leinster.
Domhnall Caomhánach is the ancestor of the Caomhánach line of the Uí Ceinnselaig dynasty and was King of Leinster from 1171 to 1175. Domhnall was the eldest son of the 12th century King of Leinster, Diarmait Mac Murchada in Ireland.
Gerald Kavanagh, known as Gerald of Ferns, was King of Leinster from 1518 to 1522, when his son Morogh succeeded him. His father was Art Óg mac Murchadha Caomhánach, who was a king of Ireland and King of Leinster.
Cathal Mac Murchadha Caomhánach, fl. 1450 - c. 1550, Abbot of Duiske.
Donnchad mac Murchada was a King of Leinster from 1098 until 1115 when he died in battle while fighting Domnall Gerrlámhach, the King of Dublin. A near contemporary account by Gerald of Wales, suggests that the King of Dublin lured him to Dublin under false pretence of peace, killed him and then buried him with a dog as an insult.