Related Research Articles

Pediatrics also spelled paediatrics, is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, pediatrics covers many of their youth until the age of 18. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends people seek pediatric care through the age of 21, but some pediatric subspecialists continue to care for adults up to 25. Worldwide age limits of pediatrics have been trending upward year after year. A medical doctor who specializes in this area is known as a pediatrician, or paediatrician. The word pediatrics and its cognates mean "healer of children", derived from the two Greek words: παῖς and ἰατρός. Pediatricians work in clinics, research centers, universities, general hospitals and children's hospitals, including those who practice pediatric subspecialties.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) is the largest professional association of pediatricians in the United States. It is headquartered in Itasca, Illinois, and maintains an office in Washington, D.C. The AAP has published hundreds of policy statements, ranging from advocacy issues to practice recommendations.

Thomas Berry Brazelton was an American pediatrician, author, and the developer of the Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS). Brazelton hosted the cable television program What Every Baby Knows, and wrote a syndicated newspaper column. He wrote more than two hundred scholarly papers and twenty-four books.
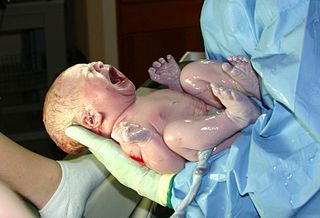
Neonatology is a subspecialty of pediatrics that consists of the medical care of newborn infants, especially the ill or premature newborn. It is a hospital-based specialty and is usually practised in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs). The principal patients of neonatologists are newborn infants who are ill or require special medical care due to prematurity, low birth weight, intrauterine growth restriction, congenital malformations, sepsis, pulmonary hypoplasia, or birth asphyxia.

A neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), also known as an intensive care nursery (ICN), is an intensive care unit (ICU) specializing in the care of ill or premature newborn infants. The NICU is divided into several areas, including a critical care area for babies who require close monitoring and intervention, an intermediate care area for infants who are stable but still require specialized care, and a step down unit where babies who are ready to leave the hospital can receive additional care before being discharged.

Béla Schick was a Hungarian-born American pediatrician. He is the founder of the Schick test. Bela Schick was born in Balatonboglár, Hungary, and brought up in Graz, Austria, where he attended medical school. In 1902, he joined the Medicine Faculty of the University of Vienna where he remained until 1923. Studying problems of immunity, he and Clemens von Pirquet first coined the term 'allergy' as a clinical entity. His discovery of a test for susceptibility to diphtheria made him world famous. From 1923 he directed the Pediatric Department of Mount Sinai Hospital, New York City. From 1936 he was also professor at Columbia University. From 1950 to 1962 Schick headed the Pediatric Department of Beth-El Hospital, Brooklyn, NY. His later interests included the nutrition of the newborn and feeding problems in children.

Mary Ellen Avery, also known as Mel, was an American pediatrician. In the 1950s, Avery's pioneering research efforts helped lead to the discovery of the main cause of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) in premature babies: her identification of surfactant led to the development of replacement therapy for premature infants and has been credited with saving over 830,000 lives. Her childhood, mentors, drive, and education inspired Avery to be the visionary that she was. In 1991 President George H.W. Bush conferred the National Medal of Science on Avery for her work on RDS.

Morgan Stanley Children's Hospital of NewYork-Presbyterian is a women's and children's hospital at 3959 Broadway, near West 165th Street, in the Washington Heights neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. It is a part of NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital and the Columbia University Irving Medical Center. The hospital treats patients aged 0–21 from New York City and around the world. The hospital features a dedicated regional ACS designated pediatric Level 1 Trauma Center and is named after financial firm Morgan Stanley, which largely funded its construction through philanthropy.
Ola Didrik Saugstad is a Norwegian pediatrician, neonatologist and neuroscientist noted for his research on resuscitation of newborn children and his contribution to reduce child mortality. He is a Research Professor at Oslo University Hospital and Professor of Neonatology at Northwestern University's Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago. He is Professor Emeritus of Pediatrics at the University of Oslo and was Director of the Department of Pediatric Research at Oslo University Hospital from 1991 to 2017.
Persistent fetal circulation is a condition caused by a failure in the systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation to convert from the antenatal circulation pattern to the "normal" pattern. Infants experience a high mean arterial pulmonary artery pressure and a high afterload at the right ventricle. This means that the heart is working against higher pressures, which makes it more difficult for the heart to pump blood.
Certified in Neonatal Pediatric Transport (C-NPT) is the designation in the USA for a paramedic, physician, respiratory therapist, neonatal nurse, nurse practitioner, nurse or physician assistant who has earned certification from the National Certification Corporation in neonatal and pediatric transport. This certificate of added qualification was rolled out in 2009. National Certification Corporation utilizes applied measurement professionals to administer its tests.

Joan Hodgman was a pioneer of neonatology. Her leadership and influence helped develop neonatology as a specialty. She practiced at LAC+USC Medical Center for more than 60 years, holding various positions, including Director of the Divisions of Neonatology. She worked to develop the intensive care unit with guidelines on neonatal care. She later received the AAP Virginia Apgar Award in 1999, the highest award offered in neonatology. She is well known by all practicing neonatologists; Dr. Opas, chief of pediatrics at USC referred to her as one of neonatology's "great sages."

August Reuss was an Austrian pediatrician. He was the son of ophthalmologist August Leopold von Reuss (1841–1924).

A neonatal nurse practitioner (NNP) is an advanced practice registered nurse (APRN) with at least 2 years experience as a bedside registered nurse in a Level III NICU, who is prepared to practice across the continuum, providing primary, acute, chronic, and critical care to neonates, infants, and toddlers through age 2. Primarily working in neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) settings, NNPs select and perform clinically indicated advanced diagnostic and therapeutic invasive procedures. In the United States, a board certified neonatal nurse practitioner (NNP-BC) is an APRN who has acquired Graduate education at the master's or doctoral level and has a board certification in neonatology. The National Association of Neonatal Nurse Practitioners (NANNP) is the national association that represents neonatal nurse practitioners in the United States. Certification is governed by the National Certification Corporation for Obstetrics, Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing Specialties (NCC).
Neelam Kler is an Indian neonatologist, known for her pioneering work on neonatal intensive care and ventilation. She is credited with developing neonatal care to better the survival rate of extremely tiny preterm babies to 90 percent. The Government of India honoured her with the third-highest civilian award, Padmabhushan, in 2014, for her services to the fields of medicine and neonatology.
Roberta A. Ballard is recognized for her contributions to neonatal medicine. In 1965, she graduated from the University of Chicago's medical school and has dedicated much of her life to research on newborn prenatal health. Specifically, Dr. Ballard studies ways to treat and prevent chronic lung disease in premature infants. Some of her research includes the collection of data regarding how inhaled Nitric Oxide can help premature infants who are suffering from lung disease and are undergoing medical ventilation. From her studies she was able to find that Nitric Oxide reduced the risk of death and shortened hospitalization time for infants born prematurely who suffer from lung disease. These contributions have helped to prevent chronic lung disease and brain injury harming infants. Hospitals that Dr. Ballard is associated with include the Hospital of the University of Philadelphia, University of PA Medical Center/Presbyterian, Saint Christopher's Hospital for Children, and Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. Dr. Ballard also served as a Professor of Pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco School of Medicine. Currently, she is Emeritus Professor of Pediatrics and Obstetrics and Gynecology at the University of Pennsylvania. While also being a professor, Dr. Ballard has contributed her knowledge in articles including the New England Journal of Medicine, Pediatrics, Journal of Perinatology, and more. She has served on a number of scientific and medical boards including the American Board of Pediatrics in 1972 and is an author of the book Avery's Diseases of Newborns. The book focuses on the care and treatment of neonates. Dr. Ballard's research and contributions have helped enhance technology and prevent infant death. Her improvements in technology have not only improved the lives of premature infants, but she also seeks to help women who are pregnant to assure they receive proper prenatal attention.

Gerhard Jorch is a German pediatrician. He is Professor for general pediatrics and neonatology at the Otto-von-Guericke University of Magdeburg and director of the University children's hospital.
Angela Okolo is a Nigerian professor of pediatrics and child health, neonatologist in the department of Pediatrics, Federal Medical Center, Asaba and President of the Nigerian Society of Neonatal Medicine (NISONM).
Samuel Zachary Levine was an American pediatrician who was a professor of pediatrics at Cornell University Medical College. His research focused on neonatology, particularly physiology of premature infants. He served as president of both th Society for Pediatric Research and served the American Pediatric Society.
Jerold Francis Lucey was an American pediatrician and journal editor. He specialized in the field of neonatology, and introduced several therapies to mainstream use in the United States, including phototherapy for neonatal jaundice, transcutaneous oxygen monitoring, and pulmonary surfactant use.
References
- 1 2 3 "Anne Ormisson". www.kliinikum.ee. Archived from the original on 2023-02-01. Retrieved 2023-02-01.
- 1 2 Mikelsaar, Raik-Hiio (2002). "Anne Ormisson 60". Eesti Arst. doi:10.15157/ea.v0i0.9392. Archived from the original on 2023-02-01. Retrieved 2023-02-01.
- ↑ "Anne Ormisson | MD; PhD | Department of Pediatrics (ARLA)". Archived from the original on 2023-02-01. Retrieved 2023-02-01.
- ↑ Nucci, Anita M.; Virtanen, Suvi M.; Sorkio, Susa; Bärlund, Sonja; Cuthbertson, David; Uusitalo, Ulla; Lawson, Margaret L.; Salonen, Marja; Berseth, Carol L.; Ormisson, Anne; Lehtonen, Eveliina; Savilahti, Erkki; Becker, Dorothy J.; Dupré, John; Krischer, Jeffrey P. (July 2017). "Regional differences in milk and complementary feeding patterns in infants participating in an international nutritional type 1 diabetes prevention trial". Maternal & Child Nutrition. 13 (3): e12354. doi:10.1111/mcn.12354. ISSN 1740-8709. PMC 5384884 . PMID 27714970.
- ↑ Lehtonen, Eveliina; Ormisson, Anne; Nucci, Anita; Cuthbertson, David; Sorkio, Susa; Hyytinen, Mila; Alahuhta, Kirsi; Berseth, Carol; Salonen, Marja; Taback, Shayne; Franciscus, Margaret; González-Frutos, Teba; Korhonen, Tuuli E.; Lawson, Margaret L.; Becker, Dorothy J. (April 2014). "Use of vitamin D supplements during infancy in an international feeding trial". Public Health Nutrition. 17 (4): 810–822. doi:10.1017/S1368980013001122. ISSN 1475-2727. PMC 4225543 . PMID 23795865.
- ↑ Mustonen, Neea; Siljander, Heli; Peet, Aleksandr; Tillmann, Vallo; Härkönen, Taina; Ilonen, Jorma; Hyöty, Heikki; Knip, Mikael; the DIABIMMUNE Study Group; Koski, Katriina; Koski, Matti; Ryhänen, Samppa; Hämäläinen, Anu‐Maaria; Ormisson, Anne; Ulich, Valentina (November 2019). "Early childhood infections and the use of antibiotics and antipyretic‐analgesics in Finland, Estonia and Russian Karelia". Acta Paediatrica. 108 (11): 2075–2082. doi:10.1111/apa.14874. ISSN 0803-5253. PMID 31132164. S2CID 167207123. Archived from the original on 2023-02-01. Retrieved 2023-02-01.
- 1 2 Kallionpää, Henna; Laajala, Essi; Öling, Viveka; Härkönen, Taina; Tillmann, Vallo; Dorshakova, Natalya V.; Ilonen, Jorma; Lähdesmäki, Harri; Knip, Mikael; Lahesmaa, Riitta; Koski, Katriina; Koski, Matti; Ryhänen, Samppa; Siljander, Heli; Hämäläinen, Anu-Maaria (2014-11-01). "Standard of hygiene and immune adaptation in newborn infants" (PDF). Clinical Immunology. 155 (1): 136–147. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2014.09.009 . ISSN 1521-6616. PMID 25245264. S2CID 34105125 . Retrieved 2023-02-01.
- ↑ Nutrition, Immunity, and Infection in Infants and Children. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. 2001. ISBN 978-0-7817-3079-2. Archived from the original on 2023-03-25. Retrieved 2023-02-22.
- ↑ "Lehekülge ei leitud" (PDF).
- ↑ Virtanen, Suvi M.; Cuthbertson, David; Nucci, Anita M.; Hyytinen, Mila; Ormisson, Anne; Salonen, Marja; Turrini, Tania; Cummings, Elizabeth A.; Bradley, Brenda; Tanner‐Blasiar, Marilyn; Becker, Dorothy J.; Åkerblom, Hans K.; Savilahti, Erkki; Krischer, Jeffrey P.; Knip, Mikael (August 2021). "Dietary compliance in a randomized double‐blind infant feeding trial during infancy aiming at prevention of type 1 diabetes". Food Science & Nutrition. 9 (8): 4221–4231. doi:10.1002/fsn3.2389. ISSN 2048-7177. PMC 8358383 . PMID 34401073.
- ↑ "Koolitused | Eesti Perinatoloogia Selts" (in Estonian). Archived from the original on 2023-02-01. Retrieved 2023-02-01.
- ↑ Publishers, Estonian Academy (1995). Proceedings of the Estonian Academy of Sciences, Geology. Estonian Academy Publishers. Archived from the original on 2023-03-25. Retrieved 2023-02-22.
- ↑ "Anne Ormisson | Tartu". www.tartu.ee (in Russian). 19 November 1942. Archived from the original on 2023-02-01. Retrieved 2023-02-01.
- ↑ "WHO | Previous Winners". 2005-07-25. Archived from the original on 2005-07-25. Retrieved 2022-12-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ↑ "Tartu tänas auväärseid tartlasi". Uudised (in Estonian). 2014-02-24. Archived from the original on 2023-02-01. Retrieved 2023-02-01.
- ↑ "Linnavalitsus ootab ettepanekuid aukodanike ja Tartu Tähe kavaleride valimiseks". Tartu Postimees (in Estonian). 2022-11-15. Archived from the original on 2023-02-01. Retrieved 2023-02-01.
- ↑ "President of Estonia to bestow state decorations on 166 individuals". err.ee. 2018-02-05. Archived from the original on 2023-02-01. Retrieved 2023-02-01.
- ↑ Reiljan, Kaire (2018-02-05). "Presidendi auraha saavad Anneli Aken, Mirje Sims ja Janek Vipre". Lääne Elu (in Estonian). Archived from the original on 2023-02-01. Retrieved 2023-02-01.