Related Research Articles

A sculpin is a type of fish that belongs to the superfamily Cottoidea in the order Scorpaeniformes. As of 2006, this superfamily contains 11 families, 149 genera, and 756 species.

Benthos, also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone. This community lives in or near marine or freshwater sedimentary environments, from tidal pools along the foreshore, out to the continental shelf, and then down to the abyssal depths.

Igloolik is an Inuit hamlet in Foxe Basin, Qikiqtaaluk Region in Nunavut, northern Canada. Because its location on Igloolik Island is close to Melville Peninsula, it is often mistakenly thought to be on the peninsula. The name "Igloolik" means "there is a house here". It derives from iglu, meaning house or building, and refers to the sod houses that were originally in the area, not to snow igloos. In Inuktitut the residents are called Iglulingmiut.
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean, and can be further divided into regions by depth. The word pelagic is derived from Ancient Greek πέλαγος (pélagos) 'open sea'. The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the surface of the sea and the bottom. Conditions in the water column change with depth: pressure increases; temperature and light decrease; salinity, oxygen, micronutrients all change.

The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths." Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud.

An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3,000 metres (9,800 ft) and 6,000 metres (20,000 ft). Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth's surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest, and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains are key geologic elements of oceanic basins.

The seabed is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.

Kaikō was a remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROV) built by the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC) for exploration of the deep sea. Kaikō was the second of only five vessels ever to reach the bottom of the Challenger Deep, as of 2019. Between 1995 and 2003, this 10.6 ton unmanned submersible conducted more than 250 dives, collecting 350 biological species, some of which could prove to be useful in medical and industrial applications. On 29 May 2003, Kaikō was lost at sea off the coast of Shikoku Island during Typhoon Chan-Hom, when a secondary cable connecting it to its launcher at the ocean surface broke.

Pelagic fish live in the pelagic zone of ocean or lake waters – being neither close to the bottom nor near the shore – in contrast with demersal fish that do live on or near the bottom, and reef fish that are associated with coral reefs.

Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes. They occupy the sea floors and lake beds, which usually consist of mud, sand, gravel or rocks. In coastal waters they are found on or near the continental shelf, and in deep waters they are found on or near the continental slope or along the continental rise. They are not generally found in the deepest waters, such as abyssal depths or on the abyssal plain, but they can be found around seamounts and islands. The word demersal comes from the Latin demergere, which means to sink.
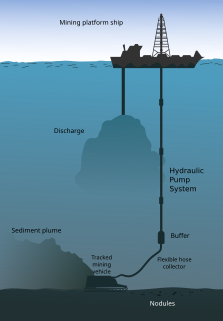
Deep sea mining is a growing subfield of experimental seabed mining that involves the retrieval of minerals and deposits from the ocean floor found at depths of 200 meters or greater. As of 2021, the majority of marine mining efforts are limited to shallow coastal waters only, where sand, tin and diamonds are more readily accessible. There are three types of deep sea mining that have generated great interest: polymetallic nodule mining, polymetallic sulphide mining, and the mining of cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts. The majority of proposed deep sea mining sites are near of polymetallic nodules or active and extinct hydrothermal vents at 1,400 to 3,700 metres below the ocean’s surface. The vents create globular or massive sulfide deposits, which contain valuable metals such as silver, gold, copper, manganese, cobalt, and zinc. The deposits are mined using either hydraulic pumps or bucket systems that take ore to the surface to be processed.
The Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA), formerly the Interim Marine and Coastal Regionalisation for Australia, is a biogeographic regionalisation of the oceanic waters of Australia's exclusive economic zone (EEZ). As of 2008, the most recent version is IMCRA Version 4.0.

The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes. They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence comes from symbiotic bacteria, which are thought to be acquired from seawater, that dwell in and around the sea.

Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas (HERMIONE) is an international multidisciplinary project, started in April 2009, that studies deep-sea ecosystems. HERMIONE scientists study the distribution of hotspot ecosystems, how they function and how they interconnect, partially in the context of how these ecosystems are being affected by climate change and impacted by humans through overfishing, resource extraction, seabed installations and pollution. Major aims of the project are to understand how humans are affecting the deep-sea environment and to provide policy makers with accurate scientific information, enabling effective management strategies to protect deep sea ecosystems. The HERMIONE project is funded by the European Commission's Seventh Framework Programme, and is the successor to the HERMES project, which concluded in March 2009.
ABISMO is a remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROV) built by the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC) for exploration of the deep sea. It is the only remaining ROV rated to 11,000-meters, ABISMO is intended to be the permanent replacement for Kaikō, a ROV that was lost at sea in 2003.
The benthic comb jelly is a comb jelly living in the Ryukyu Trench near Japan. Found at a depth of 7,217 metres (23,700 ft), it is the deepest dwelling ctenophore discovered.
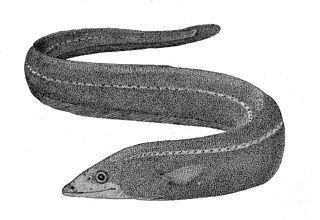
The shortdorsal cutthroat eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1887. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific and western central Atlantic Ocean, including Zanzibar, Maldives, Australia, Japan, Suriname, and the Gulf of Mexico. It dwells at a depth range of 900 to 3,000 metres, most often between 1,000 to 2,500 metres, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 111 centimetres (44 in).
Chinese oceanographic research ship Zhang Jian is a Chinese research ship designed by Shanghai Ocean University and built by the civilian owned Zhejiang TianShi Shipbuilding Co., Ltd. (浙江天时造船有限公司) in Wenling, instead of government-owned enterprise, as in most cases of the ships in Chinese service.
The Rainbowfish class bathyscaphe is a Chinese deep submergence vehicle under development in 2015 and originally scheduled to enter service in 2019, but has since been postponed after 2020.

Angelika Brandt is the world leader in Antarctic deep-sea biodiversity and has developed, organised and led several oceanographic expeditions to Antarctica, notably the series of ANDEEP cruises, which have contributed significantly to Antarctica and deep-sea biology. Brandt was the senior scientist of ANDEEP which was devoted entirely to benthic research in the Antarctic abyss.
References
- ↑ "Cedamar.org - Welcome to the deep sea! - ANDEEP". Archived from the original on 2009-02-13. Retrieved 2008-11-11.
- ↑ "ANDEEP — samswebsite". Archived from the original on 2008-10-23. Retrieved 2008-11-11.