Doctor of Medicine is a medical degree, the meaning of which varies between different jurisdictions. In the United States, and some other countries, the M.D. denotes a professional degree. This generally arose because many in 18th-century medical professions trained in Scotland, which used the M.D. degree nomenclature. In England, however, Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery was used and eventually in the 19th century became the standard in Scotland too. Thus, in the United Kingdom, Ireland and other countries, the M.D. is a research doctorate, honorary doctorate or applied clinical degree restricted to those who already hold a professional degree (Bachelor's/Master's/Doctoral) in medicine. In those countries, the equivalent professional degree to the North American, and some others' usage of M.D. is still typically titled Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (M.B.B.S.).
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, professional school, or forms a part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery, Master of Medicine, Doctor of Medicine (MD), or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO). Many medical schools offer additional degrees, such as a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), master's degree (MSc) or other post-secondary education.
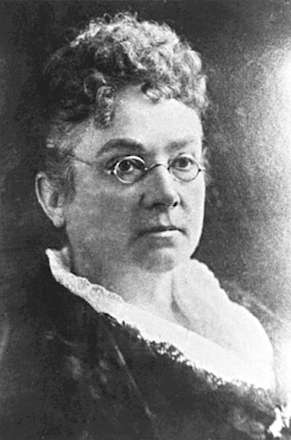
Emily Howard Stowe was a Canadian physician who was the first female physician to practise in Canada, the second licensed female physician in Canada and an activist for women's rights and suffrage. Stowe helped found the women's suffrage movement in Canada and campaigned for the country's first medical college for women.

Susannah Lattin was an American woman who died of a postpartum infection at an illegal maternity clinic at 6 Amity Place in New York City, operated by Henry Dyer Grindle. Her death led to an investigation which resulted in regulation of maternity clinics and adoptions in New York City in 1868.

Strong Medicine is an American medical drama with a focus on feminist politics, health issues and class conflict that aired on the Lifetime network from 2000 to 2006. It was created and produced in part by Whoopi Goldberg, who made cameos on the series, and by Tammy Ader. It starred Rosa Blasi, Janine Turner, and Patricia Richardson. It was the highest-rated original drama on basic cable in 2001.

Baruj Benacerraf was a Venezuelan-American immunologist, who shared the 1980 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the "discovery of the major histocompatibility complex genes which encode cell surface protein molecules important for the immune system's distinction between self and non-self." His colleagues and shared recipients were Jean Dausset and George Davis Snell.

Rebecca Lee Crumpler, born Rebecca Davis,, was an American physician, nurse and author. After studying at the New England Female Medical College, in 1864 she became the first African American woman to become a doctor of medicine in the United States. Crumpler was also one of the first female physician authors in the nineteenth century. In 1883, she published A Book of Medical Discourses. The book has two parts that cover the prevention and cure of infantile bowel complaints, and the life and growth of human beings. Dedicated to nurses and mothers, it focuses on maternal and pediatric medical care and was among the first publications written by an African American on the subject of medicine.

Emily Blackwell was the second woman to earn a medical degree at what is now Case Western Reserve University, after Nancy Talbot Clark. In 1993, she was inducted into the National Women's Hall of Fame.

Bernard N. Nathanson was an American medical doctor and co-founder, in 1969, of the National Association for the Repeal of Abortion Laws (NARAL), later renamed National Abortion Rights Action League. He was also the former director of New York City's Center for Reproductive and Sexual Health, but later became an anti-abortion activist. He was the narrator for the controversial 1984 anti-abortion film The Silent Scream.

Allen Richard Selzer was an American surgeon and author.

Dr. Mary Steichen Calderone was an American physician, author, public speaker, and public health advocate for reproductive rights and sex education. Known as the "mother of sex education" as well as the "grande dame of sex education", Dr. Calderone was an instrumental figure in the advancement of reproductive rights and sex education in the United States. Among her most notable feats include playing a key role in pushing forward a movement to reexamine and reform abortion laws in the U.S., helping to move birth control into the mainstream of American medicine, and transforming sex education from "a series of vague moral lessons focused on disease and reproduction" to a scientifically informed, comprehensive framework.
Henry Dyer Grindle was a Manhattan physician and abortion provider in the 1870s who worked under the name H.D. Grindle.

The University of Santo Tomas Faculty of Medicine and Surgery (USTFMS) is the medical school of the University of Santo Tomas, the oldest and largest Catholic university in Manila, Philippines.

Dorothy Lavinia Brown, also known as "Dr. D.", was an African-American surgeon, legislator, and teacher. She was the first female surgeon of African-American ancestry from the Southeastern United States. She was also the first African American female to serve in the Tennessee General Assembly as she was elected to the Tennessee House of Representatives. While serving in the House of Representatives, Brown fought for women's rights and for the rights of people of color.

Margaret Dorothea Craighill was born October 16, 1898, in Southport, North Carolina. She was the daughter of Colonel William E. Craighill and Mrs. Mary Craighill. Craighill was a third generation officer following in the footsteps of her grandfather, Brigadier General William Price Craighill, and her father. Both men graduated from the United States Military Academy, commonly referred to as West Point, in West Point, New York. On May 28, 1943, she became the first woman commissioned officer in the United States Army Medical Corps. Major Craighill served through World War II and afterward worked with the Veterans Administration. She died on July 20, 1977, in Southbury, Connecticut.
William Floyd Nathaniel Harrison was an American obstetrician who delivered 6,000 babies and then switched to abortions, performing the procedure an estimated 20,000 times in his career. He became one of the only doctors in Northwest Arkansas to provide this service to women, as other physicians stopped offering to perform abortions. His Fayetteville Women's Clinic was frequently picketed and blocked by anti-abortion protesters.

Kermit Barron Gosnell is an American former physician and serial killer. He provided abortions at his clinic in West Philadelphia. Gosnell was convicted of the murders of three infants who were born alive after using drugs to induce birth, was convicted of manslaughter in connection with the death of one woman during an abortion procedure, and was convicted of several other medically related crimes.

Blake Colburn Wilbur was a surgeon and one of the co-founders of the Palo Alto Medical Clinic.

Charles DeWitt Watts was an African-American surgeon and activist for the poor. Watts was the first surgeon of African-American ancestry in North Carolina. Earning his medical degree in 1943 from Howard University College, he was the first African-American board-certified surgeon to serve in North Carolina. After surgical training at Freedman's Hospital in Washington, D.C., in 1949, he moved to Durham, North Carolina, in 1950 and established a clinic to provide access to medical services for the poor. Breaking the social customs of racial obstacles, he advocated for certification of African-American medical students. He also became a member of many professional colleges including the National Academy of Science's Institute of Medicine and the American College of Surgeons. He served as chief of surgery at Durham's Lincoln Hospital and was later one of the key figures in converting it to the Lincoln Community Health Center, a low-priced clinic for the poor.

Eliza Anna Grier (1864–1902) was an American physician and the first African American woman licensed to practice medicine in the U.S. state of Georgia.