Related Research Articles

The International Olympic Committee is the international, non-governmental, sports governing body of the modern Olympic Games. Founded in 1894 by Pierre de Coubertin and Demetrios Vikelas, it is based in Lausanne, Switzerland. The IOC is the authority responsible for organizing the Summer, Winter, and Youth Olympics. The IOC also is the governing body of the National Olympic Committees (NOCs) and of the worldwide Olympic Movement, the IOC's term for all entities and individuals involved in the Olympic Games. As of 2020, 206 NOCs officially were recognized by the IOC. The IOC president has been Thomas Bach since 2013.
World Athletics, formerly known as the International Amateur Athletic Federation and International Association of Athletics Federations and formerly abbreviated as the IAAF, is the international governing body for the sport of athletics, covering track and field, cross country running, road running, race walking, mountain running, and ultra running. Included in its charge is the standardization of rules and regulations for the sports, certification of athletic facilities, recognition and management of world records, and the organisation and sanctioning of athletics competitions, including the World Athletics Championships. The organisation's president is Sebastian Coe of the United Kingdom, who was elected to the four-year position in 2015 and re-elected in 2019 for a second four-year term, and then again in 2023 for a third four-year term.

The United States Anti-Doping Agency is a non-profit, non-governmental 501(c)(3) organization and the national anti-doping organization (NADO) for the United States. To protect clean competition and the integrity of sport and prevent doping in the United States with a performance-enhancing substance, the USADA provides education, leads scientific initiatives, conducts testing, and oversees the results management process. Headquartered in Colorado Springs, Colorado, USADA is a signatory to the World Anti-Doping Code, which harmonizes anti-doping practices around the world, and is widely considered the basis for the strongest and strictest anti-doping programs to prevent doping in sport.

The World Anti-Doping Agency is an international organization co-founded by the governments of over 140 nations along with the International Olympic Committee based in Canada to promote, coordinate, and monitor the fight against drugs in sports. The agency's key activities include scientific research, education, development of anti-doping capacities, and monitoring of the World Anti-Doping Code, whose provisions are enforced by the UNESCO International Convention Against Doping in Sport. The aims of the Council of Europe Anti-Doping Convention and the United States Anti-Doping Agency are also closely aligned with those of WADA.

Pavel Anatolyevich Kolobkov is a Russian retired épée fencer. He won one gold, two silver and three bronze medals at five Olympic Games from 1988 to 2004. Kolobkov served as Russia's representative to the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) until 2015 when WADA declared the Russian Anti-Doping Agency to be non-compliant, and he was barred from serving as a representative to WADA. He served as the Russian Minister of Sport from 2016 to 2020, when he was dismissed from the position by President Putin. He also previously served as the Russian Deputy Minister of Sport as well as the Russian Deputy Minister of Sport, Tourism and Youth Policy.

The Miss Norway is a national beauty pageant in Norway The pageant was founded in 1950, where the winners were sent to Miss Universe.
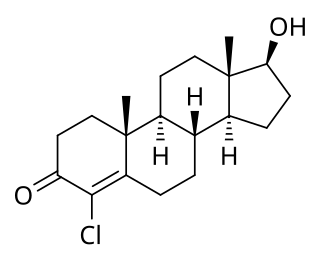
Clostebol usually as the ester clostebol acetate, is a synthetic anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS). Clostebol is the 4-chloro derivative of the natural hormone testosterone. The chlorination prevents conversion to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) while also rendering the chemical incapable of conversion to estrogen. Although usually used as an ester including clostebol acetate, clostebol caproate (Macrobin-Depot), or clostebol propionate (Yonchlon), unmodified/non-esterified clostebol is also reported to be marketed, under the brand name Trofodermin-S in Mexico.
Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESA) are medications which stimulate the bone marrow to make red blood cells. They are used to treat anemia due to end stage kidney disease, chemotherapy, major surgery, or certain treatments in HIV/AIDS. In these situations they decrease the need for blood transfusions. The different agents are more or less equivalent. They are given by injection.

Linda Cathrine Hofstad Helleland is a Norwegian politician for the Conservative Party. She held several ministerial positions in Erna Solberg's government between 2015 and 2021, with a break between 2019 and 2021. She also served as Vice President of the World Anti-Doping Association from 2016 to 2019. In parliament, she has represented Sør-Trøndelag since 2009, and been a deputy representative between 2001 and 2009.
Randi Heggemsnes Gustad is a Norwegian team handball player. She played for the club Nordstrand IF and for the Norwegian national team.

Anstein Birger Gjengedal is a former Norwegian police chief.
The Russian Anti-Doping Agency, established in January 2008, is the Russian National Anti-Doping Organisation (NADO), affiliated with the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).
Fancy Bear is a Russian cyber espionage group. Cybersecurity firm CrowdStrike has said with a medium level of confidence that it is associated with the Russian military intelligence agency GRU. The UK's Foreign and Commonwealth Office as well as security firms SecureWorks, ThreatConnect, and Mandiant, have also said the group is sponsored by the Russian government. In 2018, an indictment by the United States Special Counsel identified Fancy Bear as GRU Unit 26165. This refers to its unified Military Unit Number of the Russian army regiments. The headquarters of Fancy Bear and the entire military unit, which reportedly specializes in state-sponsored cyberattacks and decryption of hacked data, were targeted by Ukrainian drones on July 24, 2023, the rooftop on an adjacent building collapsed as a result of the explosion.
The Estonian Athletic Association is the governing body for the sport of athletics in Estonia.

The International Federation of Cerebral Palsy Football (IFCPF) is the world governing body for cerebral palsy football. It was founded in January 2015, when the governance of the sport transferred from the Cerebral Palsy International Sports and Recreation Association (CPISRA) to the IFCPF. It is a member organization, with members from five different continental zones. The IFCPF has relationships with other international association football sporting bodies. It organizes tournaments for the sport, and is in charge of Paralympic Games inclusion and participation. The IFCPF is a World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) signatory, and international footballers may be subject to out-of-competition doping controls.
Some racing drivers have used doping in auto racing to enhance their performance. Deemed unsafe and illegal by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile. Appendix A to the International Sporting Code determines which substances are banned and mandates penalties.
Systematic doping of Russian athletes has resulted in 51 Olympic medals stripped from Russia, four times the number of the next highest, and more than 30% of the global total. Russia has the most competitors who have been caught doping at the Olympic Games in the world, with more than 150.

Norway sent competitors to the 2018 Winter Paralympics in Pyeongchang, South Korea. People competed in para-alpine skiing, para-Nordic skiing, para-snowboarding, sledge hockey and wheelchair curling.

The International Testing Agency, often referred to by the acronym ITA, is an independent organisation constituted as a non-profit foundation which implements anti-doping programs for international sports federations, major event organizers or any other anti-doping organisation requiring support. The organisation was created in 2018 under the supervision of the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) and the International Olympic Committee (IOC) to promote independence, expertise and transparency in the global fight against doping. Its headquarters are located in the city of Lausanne in Switzerland.
References
- ↑ "About Anti-Doping Norway". Anti-Doping Norway.
- ↑ "Code Signatories". World Anti-Doping Agency. Retrieved 21 January 2016.
- ↑ "Ansatte". Antidoping Norge. Retrieved 2019-09-08.
- ↑ "ÅRSRAPPORT 2018" (PDF).
- ↑ "Stiftelsen Antidoping Norge – Store norske leksikon" . Retrieved 19 October 2016.
- ↑ "Dette betyr statsbudsjettet for idretten" . Retrieved 19 October 2016.