This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2016) |
The Anticancer Fund (ACF) is a Belgian private not-for-profit foundation that provides evidence-based information for patients about cancers and therapies.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2016) |
The Anticancer Fund (ACF) is a Belgian private not-for-profit foundation that provides evidence-based information for patients about cancers and therapies.
Officially established in 2013, the foundation has grown from Reliable Cancer Therapies (RCT), a non-profit organization established in 2009. RCT is still operational today, but the foundation has taken over many of its tasks as well as the goals. [1]
The vision of the ACF is to expand the amount of possible treatment options for cancer. The mission of the Anticancer Fund is to cure all people who suffer from cancer. This is done on two levels: information and research.
One of the main activities of the anticancer Fund is providing the public with scientifically accurate information regarding cancer and treatments. [2] This includes information on the different types of cancer, treatments (both conventional and non-conventional) and other information related to cancer and therapies. The Anticancer Fund holds a HON-certificate for the information that can be found on its website. [3]
Part of ACF's activities in the information section focus on exposing false and potentially lethal information. This fits in with the goal of providing evidence-based information concerning cancer and cancer treatments. An example of this is the drug GcMAF, which has been promoted as a miracle cure for several illnesses including cancer, but for which those results were never confirmed by independent study.
Dr Pan Pantziarka is the organisation's spokesman in the United Kingdom. [4]
In terms of research, the ACF develops promising treatment options for patients, which is done on an international scale. The ACF collaborates with other researchers across the European continent to advance the development of cures. The ACF also funds promising research projects financially. For example, the ACF is partaking in the CUSP9 trials, which focuses on the re-purposing of drugs for the treatment of cancer. It has formed a partnership called the Repurposing Drugs in Oncology project with the American GlobalCures to investigate the use of existing medicines with novel uses. It has identified Diclofenac, a common painkiller, as having significant anti-cancer properties. [5] It is also investigating the use of nitroglycerin. [6]
ACF’s funding comes from a private fund, as well donations from individuals who wish to support the cause of the Anticancer Fund.
Alternative medicine is any practice that aims to achieve the healing effects of medicine despite lacking biological plausibility, testability, repeatability or evidence of effectiveness. Unlike modern medicine, which employs the scientific method to test plausible therapies by way of responsible and ethical clinical trials, producing repeatable evidence of either effect or of no effect, alternative therapies reside outside of medical science and do not originate from using the scientific method, but instead rely on testimonials, anecdotes, religion, tradition, superstition, belief in supernatural "energies", pseudoscience, errors in reasoning, propaganda, fraud, or other unscientific sources. Frequently used terms for relevant practices are New Age medicine, pseudo-medicine, unorthodox medicine, holistic medicine, fringe medicine, and unconventional medicine, with little distinction from quackery.

A randomized controlled trial is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical techniques, medical devices, diagnostic procedures or other medical treatments.
Essiac is a herbal tea promoted as an alternative treatment for cancer and other illnesses. There is no evidence it is beneficial to health. In a number of studies Essiac either showed no action against cancer cells, or actually increased the rate of cancer growth.

The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society (LLS), a 501(c)(3) charitable organization founded in 1949, is the largest voluntary health organization dedicated to fighting blood cancer in the world. The LLS's mission is to cure leukemia, lymphoma, Hodgkin's lymphoma and myeloma, and improve the quality of life of patients and their families.

Max Gerson was a German-born American physician who developed the Gerson Therapy, a dietary-based alternative cancer treatment that he claimed could cure cancer and most chronic, degenerative diseases.
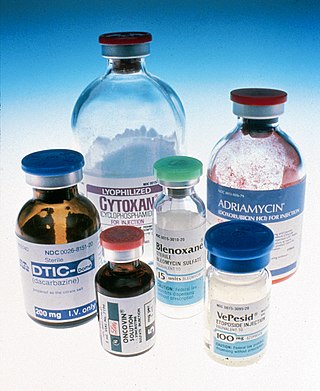
The era of cancer chemotherapy began in the 1940s with the first use of nitrogen mustards and folic acid antagonist drugs. The targeted therapy revolution has arrived, but many of the principles and limitations of chemotherapy discovered by the early researchers still apply.

The Children's Tumor Foundation (CTF) is a 501(c)(3) foundation dedicated to improving the health and well-being of individuals and families affected by NF, a group of genetic conditions known as neurofibromatosis or schwannomatosis. Their four-part mission includes propelling drug research and development through a series of strategic investments, strengthening patient support, increasing public awareness of NF and establishing best practices in clinical care for affected individuals. The Foundation is incorporated in all 50 states with active chapters and affiliates in 37 states. CTF is the largest private funder of all forms of NF research.
Hoxsey Therapy or Hoxsey Method is an alternative medical treatment promoted as a cure for cancer. The treatment consists of a caustic herbal paste for external cancers or a herbal mixture for "internal" cancers, combined with laxatives, douches, vitamin supplements, and dietary changes. Reviews by major medical bodies, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the National Cancer Institute, the American Cancer Society, M. D. Anderson Cancer Center, and Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, have found no evidence that Hoxsey Therapy is an effective treatment for cancer. The sale or marketing of the Hoxsey Method was banned in the United States by the FDA on September 21, 1960 as a "worthless and discredited" remedy and a form of quackery.

The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research is dedicated to finding a cure for Parkinson's disease (PD) established in 2000 by Michael J. Fox. It concentrates on funding research and ensuring the development of improved therapies for people with Parkinson's.

Alternative cancer treatment describes any cancer treatment or practice that is not part of the conventional standard of cancer care. These include special diets and exercises, chemicals, herbs, devices, and manual procedures. Most alternative cancer treatments do not have high-quality evidence supporting their use and many have been described as fundamentally pseudoscientific. Concerns have been raised about the safety of some purported treatments and some have been found unsafe in clinical trials. Despite this, many untested and disproven treatments are used around the world. Promoting or marketing such treatments is illegal in most of the developed world.
The "war on cancer" is the effort to find a cure for cancer by increased research to improve the understanding of cancer biology and the development of more effective cancer treatments, such as targeted drug therapies. The aim of such efforts is to eradicate cancer as a major cause of death. The signing of the National Cancer Act of 1971 by United States president Richard Nixon is generally viewed as the beginning of this effort, though it was not described as a "war" in the legislation itself.

The mission of the Foundation Fighting Blindness is to fund research that will lead to the prevention, treatment and cures for the entire spectrum of retinal degenerative diseases, including retinitis pigmentosa, macular degeneration, Usher syndrome, Stargardt disease and related conditions. These diseases, which affect more than 10 million Americans and millions more throughout the world, often lead to severe vision loss or complete blindness.

The Prostate Cancer Foundation (PCF), headquartered in Santa Monica, California, funds research into the prevention and cure of prostate cancer.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a professional organization representing physicians of all oncology sub-specialties who care for people with cancer. Founded in 1964 by Fred Ansfield, Harry Bisel, Herman Freckman, Arnoldus Goudsmit, Robert Talley, William Wilson, and Jane C. Wright, it has nearly 45,000 members worldwide.

Genta Incorporated was a biopharmaceutical company started in La Jolla, California, which discovered and developed innovative drugs for the treatment of patients with cancer. Founded in 1989 by a highly skilled entrepreneur, the company focused on a novel technology known as antisense, which targets gene products that are associated with the onset and progression of serious diseases. At that time, only Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. was conducting significant research with this technology. Antisense is a short span of oligonucleotides – modified DNA structures ranging from about 12-24 bases that selectively bind to specific RNA. The intent is to block expression of an aberrant protein that contributes to the disease of interest. Genta in-licensed three different antisense molecules that blocked Bcl-2, a fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and the gene c-myb, respectively.

Diffuse midline glioma (DMG), H3K27 altered, previously called diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) is a fatal tumour that arises in the brainstem; most commonly in the pons or thalamus. DMG is believed to be caused by genetic mutations that cause epigenetic changes in cells of the developing nervous system, resulting in a failure of the cells to properly differentiate. Currently, the standard of care is fractionated external beam radiotherapy, as the tumour location precludes surgery, and chemotherapy has shown to be ineffective; however, the estimated survival post-diagnosis remains only 9–15 months.
The Castleman Disease Collaborative Network (CDCN) is an organization focused on research and awareness of Castleman disease. It was founded in 2012 and has used a collaborative network approach to advance several research studies on Castleman disease.
Personalized onco-genomics (POG) is the field of oncology and genomics that is focused on using whole genome analysis to make personalized clinical treatment decisions. The program was devised at British Columbia's BC Cancer Agency and is currently being led by Marco Marra and Janessa Laskin. Genome instability has been identified as one of the underlying hallmarks of cancer. The genetic diversity of cancer cells promotes multiple other cancer hallmark functions that help them survive in their microenvironment and eventually metastasise. The pronounced genomic heterogeneity of tumours has led researchers to develop an approach that assesses each individual's cancer to identify targeted therapies that can halt cancer growth. Identification of these "drivers" and corresponding medications used to possibly halt these pathways are important in cancer treatment.

The Shake It Up Australia Foundation (SIUAF) is an Australian non-for-profit foundation founded in 2011 by Clyde and Greg Campbell. It is partnered with the Michael J. Fox Foundation (MJFF) to achieve the foundations primary aims of “promoting and funding Parkinson’s disease research in Australia to slow, stop and cure the disease”. Together MJFF and SIUAF are the largest non-government funders of Parkinson's research across multiple institutes in Australia. Since its founding, the foundation has co-founded 38 Parkinson's research projects across 12 institutes to the value of over $10.8 million. The foundation's funding model ensures that 100% of proceeds goes towards Parkinson's research in Australia. This is possible due to the founding directors covering all overhead costs and expenses. In January 2019, Shake It Up are one of the partner organisation in the Australian Parkinson's Mission which was awarded a $30 million-dollar grant to test repurposed drugs in clinical trials.