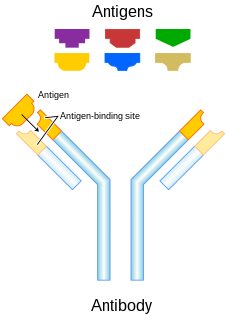
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term antigen originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides, polysaccharides, lipids, or nucleic acids.

The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions.
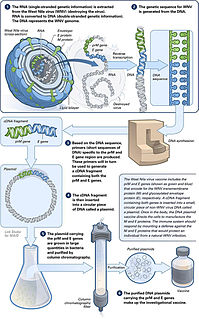
A DNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that transfects a specific antigen-coding DNA sequence into the cells of an organism as a mechanism to induce an immune response.
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which could cause serious problems to the health of the host organism if not cleared from the body. There are two distinct aspects of the immune response, the innate and the adaptive, which work together to protect against pathogens. The innate branch—the body's first reaction to an invader—is known to be a non-specific and quick response to any sort of pathogen. Components of the innate immune response include physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes, immune cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, and monocytes, and soluble factors including cytokines and complement. On the other hand, the adaptive branch is the body's immune response which is catered against specific antigens and thus, it takes longer to activate the components involved. The adaptive branch include cells such as dendritic cells, T cell, and B cells as well as antibodies—also known as immunoglobulins—which directly interact with antigen and are a very important component for a strong response against an invader.

Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system that belong to the rapidly expanding family of innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and represent 5–20% of all circulating lymphocytes in humans. The role of NK cells is analogous to that of cytotoxic T cells in the vertebrate adaptive immune response. NK cells provide rapid responses to virus-infected cell and other intracellular pathogens acting at around 3 days after infection, and respond to tumor formation. Typically, immune cells detect the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) presented on infected cell surfaces, triggering cytokine release, causing the death of the infected cell by lysis or apoptosis. NK cells are unique, however, as they have the ability to recognize and kill stressed cells in the absence of antibodies and MHC, allowing for a much faster immune reaction. They were named "natural killers" because of the notion that they do not require activation to kill cells that are missing "self" markers of MHC class 1. This role is especially important because harmful cells that are missing MHC I markers cannot be detected and destroyed by other immune cells, such as T lymphocyte cells.

Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules - including secreted antibodies, complement proteins, and certain antimicrobial peptides - located in extracellular fluids. Humoral immunity is named so because it involves substances found in the humors, or body fluids. It contrasts with cell-mediated immunity. Humoral immunity is also referred to as antibody-mediated immunity.
Opsonins are extracellular proteins that, when bound to substances or cells, induce phagocytes to phagocytose the substances or cells with the opsonins bound. Thus, opsonins act as tags to label things in the body that should be phagocytosed by phagocytes. Different types of things ("targets") can be tagged by opsonins for phagocytosis, including: pathogens, cancer cells, aged cells, dead or dying cells, excess synapses, or protein aggregates. Opsonins help clear pathogens, as well as dead, dying and diseased cells.
Cancer immunotherapy is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving on the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the fundamental research of cancer immunology and a growing subspeciality of oncology.

The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates.
An immunogen is a substance that induces immune response. All immunogens are antigens, and the term antigen arises from its ability to induce generation of antibodies. All antigens are recognized by specific lymphocytes or by antibodies, but not every antigen can evoke an immune response. Those antigens that are capable of inducing an immune response are said to be immunogenic and are called immunogens.

An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a cell that displays antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize these complexes using their T cell receptors (TCRs). APCs process antigens and present them to T-cells.
Immunogenicity is the ability of a foreign substance, such as an antigen, to provoke an immune response in the body of a human or other animal. It may be wanted or unwanted:

An immune complex, sometimes called an antigen-antibody complex or antigen-bound antibody, is a molecule formed from the binding of multiple antigens to antibodies. The bound antigen and antibody act as a unitary object, effectively an antigen of its own with a specific epitope. After an antigen-antibody reaction, the immune complexes can be subject to any of a number of responses, including complement deposition, opsonization, phagocytosis, or processing by proteases. Red blood cells carrying CR1-receptors on their surface may bind C3b-coated immune complexes and transport them to phagocytes, mostly in liver and spleen, and return to the general circulation.
Co-stimulation is a secondary signal which immune cells rely on to activate an immune response in the presence of an antigen-presenting cell. In the case of T cells, two stimuli are required to fully activate their immune response. During the activation of lymphocytes, co-stimulation is often crucial to the development of an effective immune response. Co-stimulation is required in addition to the antigen-specific signal from their antigen receptors.
Anti-idiotypic vaccines comprise of antibodies that have three-dimensional immunogenic regions, termed idiotopes, that consist of protein sequences that bind to cell receptors. Idiotopes are aggregated into idiotypes specific to their target antigen. An example of an anti-idiotype antibody is Racotumomab.
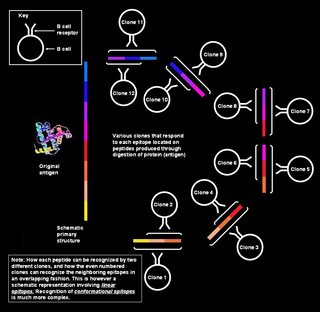
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.

Minor histocompatibility antigen are receptors on the cellular surface of donated organs that are known to give an immunological response in some organ transplants. They cause problems of rejection less frequently than those of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). Minor histocompatibility antigens (MiHAs) are diverse, short segments of proteins and are referred to as peptides. These peptides are normally around 9-12 amino acids in length and are bound to both the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II proteins. Peptide sequences can differ among individuals and these differences arise from SNPs in the coding region of genes, gene deletions, frameshift mutations, or insertions. About a third of the characterized MiHAs come from the Y chromosome. The proteins are composed of a single immunogenic HLA allele. Prior to becoming a short peptide sequence, the proteins expressed by these polymorphic or diverse genes need to be digested in the proteasome into shorter peptides. These endogenous or self peptides are then transported into the endoplasmic reticulum with a peptide transporter pump called TAP where they encounter and bind to the MHC class I molecule. This contrasts with MHC class II molecules's antigens which are peptides derived from phagocytosis/endocytosis and molecular degradation of non-self entities' proteins, usually by antigen-presenting cells. MiHA antigens are either ubiquitously expressed in most tissue like skin and intestines or restrictively expressed in the immune cells.
In immunology, an adjuvant is a substance that increases or modulates the immune response to a vaccine. The word "adjuvant" comes from the Latin word adiuvare, meaning to help or aid. "An immunologic adjuvant is defined as any substance that acts to accelerate, prolong, or enhance antigen-specific immune responses when used in combination with specific vaccine antigens."
Immunogenic cell death is any type of cell death eliciting an immune response. Both accidental cell death and regulated cell death can result in immune response. Immunogenic cell death contrasts to forms of cell death that do not elicit any response or even mediate immune tolerance.










