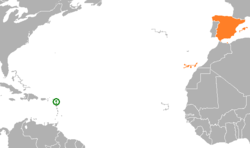
Montenegro–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe, and of the NATO. Montenegro has an embassy in Madrid. Spain is accredited to Montenegro from its embassy in Belgrade, Serbia.

Bilateral and diplomatic relations exist between The Bahamas and Spain. The Spanish embassy in Kingston, Jamaica, is accredited for Bahamas.

Saint Kitts and Nevis–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Saint Kitts and Nevis does not have embassy in Spain, but its embassy in United Kingdom is accredited for Spain. Spain also has no embassy on the islands, but its embassy in Kingston, Jamaica, is accredited to them.

Spain–Trinidad and Tobago relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Spain has an embassy in Port of Spain, which is also accredited for Spanish consulates in other small nations of the Caribbean. Trinidad and Tobago does not have embassies or consulates in Spain.

Marshall Islands–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. The Spanish embassy in Manila, Philippines, is accredited for the Marshall Islands, plus Spain has an honorary consulate in Majuro. The Marshall Islands have an embassy in Madrid and a consulate in Barcelona.

Cambodia and Spain share bilateral and diplomatic relations. Cambodia does not have embassy in Spain, but the embassy in Paris is accredited for this country. There is no diplomatic delegation from Spain in Cambodia. The Spanish Embassy is located in Bangkok, Thailand.

Jordan–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Jordan has an embassy in Madrid and two consulates in Barcelona and Bilbao. Spain has an embassy in Amman.

Nepal–Spain relations are the bilateral relations between Nepal and Spain. Nepal has an embassy in Madrid. Spain is accredited to Nepal from its embassy in New Delhi, India.

Singapore–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Singapore is accredited to Spain through its embassy in Paris, France and has two honorary consulates in Barcelona and Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Singapore.

Spain–Syria relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Syria has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Damascus. Both countries are charter members of the Union for the Mediterranean, although Syria suspended its membership in 2011.

Spain–Thailand relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Thailand has an embassy in Madrid and two honorary consulates in Barcelona and Santa Cruz de Tenerife. Spain has an embassy in Bangkok.

Spain–Uzbekistan relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Uzbekistan has an embassy in Madrid and honorary consulates in Madrid and Barcelona. The Spanish embassy in Moscow, Russia is also accredited for Uzbekistan. The Uzbek ambassador, Rakhmatulla Nurimbetov, declared that relations between the two countries have a "great potential not used", especially in agricultural, tourism and scientific matters, so he has invited the Spanish businessmen to "invest and contribute to the development of the country", such as companies Talgo and Marsans, and has expressed his desire that Spain open an Embassy in Tashkent "In the near future".
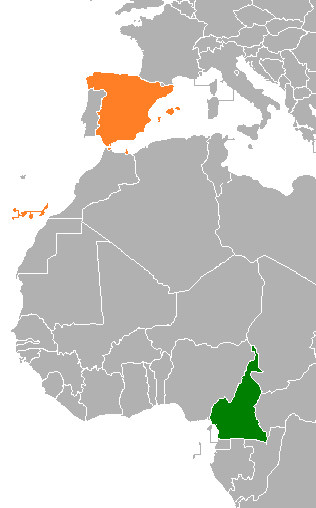
Cameroon–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Cameroon has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Yaoundé.
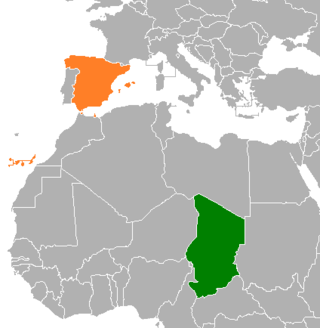
Chad–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Chad is accredited to Spain from its embassy in Paris, France. Spain is accredited to Chad from its embassy in Yaoundé, Cameroon and maintains an embassy office in N'Djamena.

Democratic Republic of the Congo–Spain relations are the bilateral relations between the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and Spain. The Democratic Republic of the Congo has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Kinshasa.

Gabon–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Gabon has an embassy in Madrid and consulates in Barcelona and Bilbao. Spain has an embassy in Libreville.
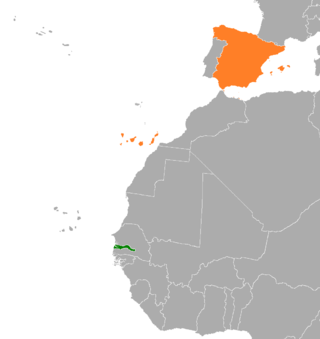
Gambia–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Gambia has an embassy in Madrid and honorary consulates in Almería, Barcelona, Gerona, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Madrid and Zaragoza. Spain has an embassy office in Banjul.

Namibia–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Namibia is accredited to Spain from its embassy in Paris, France. Spain has an embassy in Windhoek.

Antigua and Barbuda and Mexico are members of the Association of Caribbean States, Organization of American States and the United Nations.