Related Research Articles

Bohemia is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohemian kings, including Moravia and Czech Silesia, in which case the smaller region is referred to as Bohemia proper as a means of distinction.

The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages and lasted for almost 1,000 years until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.

The House of Habsburg, also known as the House of Austria, is one of the most prominent and important dynasties in European history.

The 15th century was the century which spans the Julian dates from 1 January 1401 to 31 December 1500 (MD).

Albert the Magnanimous KG, elected King of the Romans as Albert II was king of the Holy Roman Empire and a member of the House of Habsburg. By inheritance he became Albert V, Duke of Austria. Through his wife he also became King of Hungary, Croatia, Bohemia, and inherited a claim to the Duchy of Luxembourg.

Sigismund of Luxembourg was Holy Roman Emperor from 1433 until his death in 1437. He was elected King of Germany in 1410, and was also King of Bohemia from 1419, as well as prince-elector of Brandenburg. As the husband of Mary, Queen of Hungary, he was also King of Hungary and Croatia from 1387. He was the last male member of the House of Luxembourg.

Charles IV, also known as Charles of Luxembourg, born Wenceslaus, was Holy Roman Emperor from 1355 until his death in 1378. He was elected King of Germany in 1346 and became King of Bohemia that same year. He was a member of the House of Luxembourg from his father's side and the Bohemian House of Přemyslid from his mother's side; he emphasized the latter due to his lifelong affinity for the Bohemian side of his inheritance, and also because his direct ancestors in the Přemyslid line included two saints.

Carniola is a historical region that comprised parts of present-day Slovenia. Although as a whole it does not exist anymore, Slovenes living within the former borders of the region still tend to identify with its traditional parts Upper Carniola, Lower Carniola, and to a lesser degree with Inner Carniola. In 1991, 47% of the population of Slovenia lived within the borders of the former Duchy of Carniola.

The history of the Czech lands – an area roughly corresponding to the present-day Czech Republic – starts approximately 800,000 years BCE. A simple chopper from that age was discovered at the Red Hill archeological site in Brno. Many different primitive cultures left their traces throughout the Stone Age, which lasted approximately until 2000 BCE. The most widely known culture present in the Czech lands during the pre-historical era is the Únětice Culture, leaving traces for about five centuries from the end of the Stone Age to the start of the Bronze Age. Celts – who came during the 5th century BCE – are the first people known by name. One of the Celtic tribes were the Boii (plural), who gave the Czech lands their first name Boiohaemum – Latin for the Land of Boii. Before the beginning of the Common Era the Celts were mostly pushed out by Germanic tribes. The most notable of those tribes were the Marcomanni and traces of their wars with the Roman Empire were left in south Moravia.

Early modern Europe, also referred to as the post-medieval period, is the period of European history between the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, roughly the mid 15th century to the late 18th century. Historians variously mark the beginning of the early modern period with the invention of moveable type printing in the 1450s, the Fall of Constantinople and end of the Hundred Years' War in 1453, the end of the Wars of the Roses in 1485, the beginning of the High Renaissance in Italy in the 1490s, the end of the Reconquista and subsequent voyages of Christopher Columbus to the Americas in 1492, or the start of the Protestant Reformation in 1517. The precise dates of its end point also vary and are usually linked with either the start of the French Revolution in 1789 or with the more vaguely defined beginning of the Industrial Revolution in late 18th century England.

Ferdinand I was Holy Roman Emperor from 1556, King of Bohemia, Hungary, and Croatia from 1526, and Archduke of Austria from 1521 until his death in 1564. Before his accession as emperor, he ruled the Austrian hereditary lands of the House of Habsburg in the name of his elder brother, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. Also, he often served as Charles' representative in the Holy Roman Empire and developed encouraging relationships with German princes. In addition, Ferdinand also developed valuable relationships with the German banking house of Jakob Fugger and the Catalan bank, Banca Palenzuela Levi Kahana.

Frederick V was the Elector Palatine of the Rhine in the Holy Roman Empire from 1610 to 1623, and reigned as King of Bohemia from 1619 to 1620. He was forced to abdicate both roles, and the brevity of his reign in Bohemia earned him the derisive sobriquet "the Winter King".

A psaltery is a fretboard-less box zither and is considered the archetype of the zither and dulcimer. Plucked keyboard instruments such as the harpsichord were also inspired by it. Its resonance box is usually trapezoidal, rectangular or in the form of a "pig's head" and often richly decorated.

Bohemianism is a social and cultural movement that has, at its core, a way of life away from society's conventional norms and expectations. The term originates from the French bohème and spread to the English-speaking world. It was used to describe mid-19th-century non-traditional lifestyles, especially of artists, writers, journalists, musicians, and actors in major European cities.
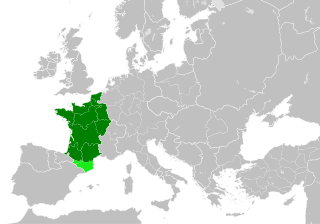
The Kingdom of France in the Middle Ages was marked by the fragmentation of the Carolingian Empire and West Francia (843–987); the expansion of royal control by the House of Capet (987–1328), including their struggles with the virtually independent principalities, and the creation and extension of administrative/state control in the 13th century; and the rise of the House of Valois (1328–1589), including the protracted dynastic crisis against the House of Plantagenet and their Angevin Empire, culminating in the Hundred Years' War (1337–1453), which laid the seeds for a more centralized and expanded state in the early modern period and the creation of a sense of French identity.

The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a successor state of the Byzantine Empire that existed during the 13th through to the 15th century. The empire consisted of the Pontus, or far northeastern corner of Anatolia, and portions of southern Crimea.

The Kingdom of Bohemia, sometimes referenced in English literature as the Czech Kingdom, was a medieval and early modern monarchy in Central Europe. It was the predecessor of the modern Czech Republic.

The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period.

Archduke Louis, Prince Royal of Hungary and Bohemia and Prince of Tuscany, was the 15th child of Holy Roman Emperor Leopold II, King of Hungary and Bohemia, Grand Duke of Tuscany, and Infanta Maria Luisa of Spain.
A queen mother is a former queen, often a queen dowager, who is the mother of the reigning monarch. The term has been used in English since the early 1560s. It arises in hereditary monarchies in Europe and is also used to describe a number of similar yet distinct monarchical concepts in non-European cultures around the world. The rank does not go to all mothers of monarchs though. A mother of a ruling monarch may only be referred to as Queen Mother if she was a Queen Consort as opposed to a Princess Consort.
References
- ↑ Heikki Mikkeli, Europe as an Idea and an Identity (London, 1998) p. 35