
A revolver is a repeating handgun with at least one barrel and a revolving cylinder containing multiple chambers for firing. Because most revolver models hold up to six cartridges, before needing to be reloaded, revolvers are commonly called six shooters or sixguns. Due to their rotating cylinder mechanism, they may also be called wheel guns.

A cartridge, also known as a round, is a type of pre-assembled firearm ammunition packaging a projectile, a propellant substance and an ignition device (primer) within a metallic, paper, or plastic case that is precisely made to fit within the barrel chamber of a breechloading gun, for convenient transportation and handling during shooting. Although in popular usage the term "bullet" is often used to refer to a complete cartridge, the correct usage only refers to the projectile.

A derringer or deringer is a small handgun that is neither a revolver, semi-automatic pistol, nor machine pistol. It is not to be confused with mini-revolvers or pocket pistols, although some later derringers were manufactured with the pepperbox configuration. The modern derringer is often multi barreled, and is generally the smallest usable handgun of any given caliber and barrel length due to the lack of a moving action, which takes up more space behind the barrel. It is frequently used by women because it is easily concealable in a purse or a stocking.

The pepper-box revolver or simply pepperbox is a multiple-barrel firearm, mostly in the form of a handgun, that has three or more gun barrels in a revolving mechanism. Each barrel holds a single shot, and the shooter can manually rotate the whole barrel assembly to sequentially index each barrel into alignment with the lock or hammer, similar to rotation of a revolver's cylinder.

Ethan Allen was a major American arms maker from Massachusetts. He is unrelated to the revolutionary Ethan Allen. His first firearm, the "Pocket rifle" was developed in 1836, and his first patent was granted in 1837.
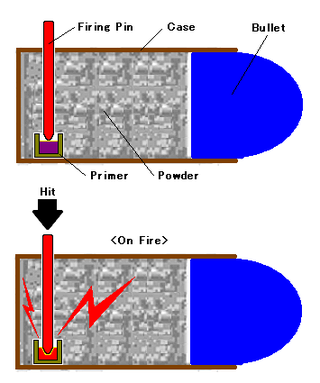
The pin-fire is an obsolete type of metallic cartridge used in firearms, where the priming compound is ignited by striking a small pin that protrudes radially from above the base of the cartridge. Invented by Frenchman Casimir Lefaucheux in 1832, but not patented until 1835, it was one of the earliest practical designs of a metallic cartridge to hasten the loading and firing process of a firearm. Its history is closely associated with the development of the breechloader, which would eventually replace all muzzle-loading firearms.

A pistol sword is a sword with a pistol or revolver attached, usually alongside the blade. It differs from a rifle with a bayonet attached, in that the weapon is designed primarily for use as a sword, and the firearm component is typically considered a secondary weapon designed to be an addition to the blade, rather than the sword being a secondary addition to the pistol. In addition, the two components of these weapons typically cannot be separated, unlike most bayonets mounted on rifles.

The LeMat revolver was a .42 or .36 caliber cap & ball black powder revolver invented by Jean Alexandre LeMat of France, which featured an unusual secondary 16 to 20 gauge smooth-bore barrel capable of firing buckshot. It saw service with the armed forces of the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War of 1861–1865 and the Army of the Government of National Defense during the Franco-Prussian War.

The Type 26 or Model 26 "hammerless" revolver was the first modern revolver adopted by the Imperial Japanese Army. It was developed at the Koishikawa Arsenal and is named for its year of adoption in the Japanese dating system. The revolver saw action in conflicts including the Russo-Japanese War, World War I and World War II.

In American English, a pocket pistol is any small, pocket-sized semi-automatic pistol, and is suitable for concealed carry in a pocket or a similar small space.

North American Arms is a United States company, headquartered in Provo, Utah, that manufactures pocket pistols and mini-revolvers, also called mouse guns. The company was originally named Rocky Mountain Arms when it was founded in 1972. In 1974 it was bought by new owners who renamed the company North American Manufacturing (NAM) and then North American Arms (NAA).

A snubnosed revolver is a small, medium, or large frame revolver with a short barrel, generally less than 3 inches in length. Smaller such revolvers are often made with "bobbed" or "shrouded" hammers and there are also "hammerless" models ; the point is to allow the gun to be drawn with little risk of it snagging on clothing. Since the external movement of the mechanism is minimal or nil, shrouded and hammerless models may be fired from within clothing. The design of these revolvers compromises range and accuracy at a distance in favor of maneuverability and ease of carry and concealment.

A handgun is a firearm designed to be usable with only one hand. It is distinguished from a long barreled gun which typically is intended to be held by both hands and braced against the shoulder. Handguns have shorter effective ranges compared to long guns, and are much harder to shoot accurately. While most early handguns are single-shot pistols, the two most common types of handguns used in modern times are revolvers and semi-automatic pistols.

A pistol is a type of handgun, characterised by a barrel with an integral chamber. The word "pistol" derives from the Middle French pistolet, meaning a small gun or knife, and first appeared in the English language c. 1570 when early handguns were produced in Europe. In colloquial usage, the word "pistol" is often used as a generic term to describe any type of handgun, inclusive of revolvers and the pocket-sized derringers.

In firearms, the cylinder is the cylindrical, rotating part of a revolver containing multiple chambers, each of which is capable of holding a single cartridge. The cylinder rotates (revolves) around a central axis in the revolver's action to sequentially align each individual chamber with the barrel bore for repeated firing. Each time the gun is cocked, the cylinder indexes by one chamber. Serving the same function as a rotary magazine, the cylinder stores ammunitions within the revolver and allows it to fire multiple times, before needing to be reloaded.

The Colt Paterson revolver was the first commercial repeating firearm employing a revolving cylinder with multiple chambers aligned with a single, stationary barrel. Its design was patented by Samuel Colt on February 25, 1836, in the United States, England and France, and it derived its name from being produced in Paterson, New Jersey. The revolutionary design inspired the popular phrase of the time, "God created men, Col. Colt made them equal". Initially this 5 shot revolver was produced in .28 caliber, with a .36 caliber model following a year later. As originally designed and produced, no loading lever was included with the revolver; a user had to partially disassemble the revolver to re-load it. Starting in 1839, however, a reloading lever and a capping window were incorporated into the design, allowing reloading without disassembly. This loading lever and capping window design change was also incorporated after the fact into most Colt Paterson revolvers that had been produced from 1836 until 1839. Unlike later revolvers, a folding trigger was incorporated into the Colt Paterson. The trigger became visible only upon cocking the hammer.
The following are terms related to firearms and ammunition topics.

Merwin, Hulbert, and Co. or Merwin Hulbert was an American firearms designer and marketer based in New York City which produced revolvers and rifles from 1874 to 1896. The firearms were manufactured by a subsidiary company, Hopkins & Allen of Norwich, Connecticut. Merwin Hulbert's designs had influenced other gunmakers of the time, such as Meriden Firearms Co., Harrington & Richardson, Forehand & Wadsworth, and Iver Johnson.

The Colt Model 1871–72 Open Top is a metallic cartridge rear-loading .44-caliber revolver introduced in 1872 by the Colt's Patent Fire Arms Manufacturing Company. The handgun was developed following two patents, the first in 1871 and the second in 1872, and is estimated to have been produced primarily between February 1872 and June 1873. This has led to some confusion in its name. Both Colt Model 1871 and Colt Model 1872 have been used, but currently the most commonly accepted names are Colt Model 1871–72 Open Top, Colt Model 1871–72 or Colt Open Top.

A repeating firearm or repeater is any firearm that is designed for multiple, repeated firings before the gun has to be reloaded with new ammunition.




















