Haskovo Cove is a 2.1 km wide cove indenting for 1 km the northern coast of Greenwich Island between Aprilov Point and Miletich Point in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Situated next east of Crutch Peaks, southwest of Ongley Island and northwest of Sevtopolis Peak. Shape enhanced as a result of Teteven Glacier’s retreat in the late 20th and early 21st century. The cove is named after the city of Haskovo in Southeastern Bulgaria.

Murgash Glacier is the 3.4 km long and 3.2 km wide glacier on Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica situated southeast of Yakoruda Glacier, south of Teteven Glacier, southwest of Traub Glacier and west-northwest of Bravo Glacier. It is bounded by Lloyd Hill on the northwest, Tile Ridge on the east and Hebrizelm Hill on the southeast, and drains southwards into Kramolin Cove in McFarlane Strait between Yovkov Point and Kaspichan Point.

Musala Glacier on Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica is situated northeast of Targovishte Glacier, east-northeast of Zheravna Glacier and southeast of Fuerza Aérea Glacier. It is bounded by St. Kiprian Peak to the south, Vratsa Peak to the southwest, central Breznik Heights to the west, and Ilarion Ridge bordering Hardy Cove to the northeast, extends 2 nautical miles in east-west direction and 1.2 nautical miles in north-south direction, and drains eastwards into Bransfield Strait north of Fort Point.

Pomorie Point is a point on the coast of McFarlane Strait forming the north side of the entrance to Lister Cove, Varna Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica.
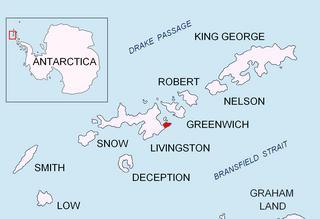
Rila Point is a low, ice-free point on the south coast of Moon Bay, projecting 330 m west-northwestwards from Burgas Peninsula on Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, and forming the east side of the entrance to Bruix Cove. The point is named after Rila Mountain, Bulgaria.

Skaptopara Cove is a 2 km wide cove indenting for 900 m the north coast of Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica east of Aprilov Point and west of Terimer Point. Situated northeast of Sevtopolis Peak, southeast of Ongley Island and northwest of Mount Plymouth. Shape enhanced as a result of Teteven Glacier’s retreat in the late 20th and early 21st century.

Avitohol Point is a point on the north coast of Livingston Island, Antarctica projecting 1.15 km into Hero Bay to form the west side of the entrance to Skravena Cove and the southeast side of the entrance to Prisoe Cove. The point is named after the legendary Khan Avitohol listed in the 8th Century ‘Nominalia of the Bulgarian Khans’, who laid the foundations of the Bulgarian statehood in Europe in 165 AD.

Yovkov Point is a point on the southwest coast of Greenwich Island, Antarctica projecting 150 m southwards into McFarlane Strait, forming the northwest side of the entrance to Kramolin Cove. Formed as a result of Murgash Glacier's retreat in the late 20th and early 21st century. The feature is named after the famous Bulgarian writer Yordan Yovkov (1880–1937).

Kaspichan Point is a point on the southeast side of the entrance to Kramolin Cove on the southwest coast of Greenwich Island, Antarctica. Situated next west of Hebrizelm Hill, 1.4 km northwest of Triangle Point, 2 km south-southwest of Tile Ridge, and 2 km southeast of Yovkov Point. Shape enhanced by recent glacier retreat northwest of the point. Bulgarian topographic survey Tangra 2004/05. Named after the town of Kaspichan in northeastern Bulgaria.

Zahari Point is an ice-free point on the southwest coast of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica forming the northwest side of the entrance to Micalvi Cove. Ice-free surface area 21 hectares. The feature is named after the Bulgarian writer and historiographer Zahari Stoyanov (1850–1889).

Gela Point is a point on the west side of the entrance to Chavei Cove on the southeast coast of Rozhen Peninsula on Livingston Island, Antarctica formed by an offshoot of Yambol Peak. Situated on the coast of Bransfield Strait 5.1 km east-northeast of Botev Point, 700 m east-southeast of Yambol Peak, and 4.1 km west-southwest of Samuel Point. Formed as a result of recent retreat of the adjacent Prespa Glacier to the northeast. Bulgarian topographic survey Tangra 2004/05. Named after the settlement of Gela in the central Rhodope Mountains, Bulgaria.

Perelik Point is a point on the north side of the entrance to Kozloduy Cove and the southeast side of the entrance to Garnya Cove on the east coast of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica.

Lukovit Point is an ice-free point on the coast of Hero Bay, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica forming the west side of the entrance to Maleshevo Cove. Situated 2.74 km west-southwest of Siddins Point, 3.27 km east by north of Atanasova Point and 5.6 km east of Kuklen Point. Shape enhanced as a result of the retreat of Tundzha Glacier in the late 20th and early 21st centuries. Spanish mapping in 1991, Bulgarian in 2005 and 2009. Named after the town of Lukovit in northern Bulgaria.

Miletich Point is the rocky point forming the west side of the entrance to Haskovo Cove on Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands in Antarctica. Stuated 800 m north of the summit of Crutch Peaks, 200 m southeast of Kabile Island, 1.55 km east of Pavlikeni Point, and 2.1 km west of Aprilov Point.

Herring Point is a point on the north coast of Rugged Island off the west coast of Byers Peninsula of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica forming the east side of the entrance to Hersilia Cove.

Yana Point is the point forming the west side of the entrance to Bruix Cove in eastern Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The point separates the glacier termini of Huron Glacier to the northwest and Iskar Glacier to the southeast. The feature is named after the settlement of Yana in western Bulgaria.

Agüedo Point is the point forming the north extremity of Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica and the west side of the entrance to Guayaquil Bay. The adjacent ice-free area of Flamingo Beach on the west covers 80 hectares, and ends in Terimer Point, the east entrance point of Skaptopara Cove.

Yasen Point is the sharp, rocky point on the south coast of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, forming the west side of the entrance to Mateev Cove. Situated on the east side of the small ice-free promontory ending in Hannah Point to the west.

Brusen Point is the narrow rocky point projecting 200 m in north-northwest direction and forming the north extremity of Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica.

Terimer Point is the low, rounded and ice-free tipped east entrance point of Skaptopara Cove, forming the west extremity of Flamingo Beach on the north coast of Greenwich Island in Antarctica. It is named after the medieval settlement of Terimer in Western Bulgaria.