Related Research Articles

The government of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) conducts its own foreign relations. Since independence in 1986, the FSM has established diplomatic relations with 92 countries, including all of its Pacific neighbors.

Tuvalu, formerly known as the Ellice Islands, is an island country in the Polynesian subregion of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean, about midway between Hawaii and Australia. It lies east-northeast of the Santa Cruz Islands, northeast of Vanuatu, southeast of Nauru, south of Kiribati, west of Tokelau, northwest of Samoa and Wallis and Futuna, and north of Fiji.

Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place. Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both in freshwater waterbodies and the oceans. About 500 million people worldwide are economically dependent on fisheries. 171 million tonnes of fish were produced in 2016, but overfishing is an increasing problem, causing declines in some populations.

The Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) is an inter-governmental organization that aims to enhance cooperation among countries and territories of Oceania, including formation of a trade bloc and regional peacekeeping operations. It was founded in 1971 as the South Pacific Forum (SPF), and changed its name in 1999 to "Pacific Islands Forum", so as to be more inclusive of the Forum's Oceania-spanning membership of both north and south Pacific island countries, including Australia. It is a United Nations General Assembly observer.
From 1916 to 1975, Tuvalu was part of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands colony of the United Kingdom. A referendum was held in 1974 to determine whether the Gilbert Islands and Ellice Islands should each have their own administration. As a consequence of the referendum, the separate British colonies of Kiribati and Tuvalu were formed. Tuvalu became fully independent as a sovereign state within the Commonwealth on 1 October 1978. On 5 September 2000, Tuvalu became the 189th member of the United Nations.

Marine shrimp farming is an aquaculture business for the cultivation of marine shrimp or prawns for human consumption. Although traditional shrimp farming has been carried out in Asia for centuries, large-scale commercial shrimp farming began in the 1970s, and production grew steeply, particularly to match the market demands of the United States, Japan and Western Europe. The total global production of farmed shrimp reached more than 1.6 million tonnes in 2003, representing a value of nearly 9 billion U.S. dollars. About 75% of farmed shrimp is produced in Asia, in particular in China and Thailand. The other 25% is produced mainly in Latin America, where Brazil, Ecuador, and Mexico are the largest producers. The largest exporting nation is India.

Fishing in India is a major sector within the economy of India contributing 1.07% of its total GDP. The fishing sector in India supports the livelihood of over 28 million people in the country, especially within the marginalized and vulnerable communities. India is the third largest fish producing country in the world accounting for 7.96% of the global production and second largest producer of fish through aquaculture, after China. The total fish production during the FY 2020-21 is estimated at 14.73 million metric tonnes. According to the National Fisheries Development Board the Fisheries Industry generates an export earnings of Rs 334.41 billion. Centrally sponsored schemes will increase exports by Rs 1 lakh crore in FY25. 65,000 fishermen have been trained under these schemes from 2017 to 2020. Freshwater fishing consists of 55% of total fish production.

China has one-fifth of the world's population and accounts for one-third of the world's reported fish production as well as two-thirds of the world's reported aquaculture production. It is also a major importer of seafood and the country's seafood market is estimated to grow to a market size worth US$53.5 Billion by 2027.

As with other countries, the 200 nautical miles (370 km) exclusive economic zone (EEZ) off the coast of the United States gives its fishing industry special fishing rights. It covers 11.4 million square kilometres, which is the second largest zone in the world, exceeding the land area of the United States.
Aquaculture in Vanuatu exists on a small scale, both commercially and privately. Several aquacultural efforts have been made in the country, including attempts to raise Pacific oyster, rabbitfish, Malaysian prawn, and tilapia. Experiments with Kappaphycus alvarezii and three species of giant clam were carried out by the Fisheries Department in 1999. The official Fisheries Department records state that $1165 US of cultured coral was exported from the country in 2000, with 275 pieces in total. The cultivation of Macrobrachium lar in taro terraces is practiced for subsistence purposes, and Macrobrachium rosenbergii has been identified by the Vanuatu government as a high-priority species.
Aquaculture in Palau is not well-developed commercially, contributing little to the country's economy. The Palau government has recognized that a great potential for aquacultural pursuits in the area, and released an Aquaculture and Fisheries Action Plan in June 2008 in order to suggest how this potential might be realized. Belau Aquaculture is the only company in the region cultivating ornamental sponges.
Aquaculture in Samoa is hampered because of the limited number of sizable freshwater bodies in the country, although numerous aquaculture projects are underway. There have been several attempts to introduce tilapia cultivation, however these have generally been unsuccessful due to flooding as well as the difficulty of catching adult tilapia. The Samoa National Aquaculture Workshop, a workshop intended to develop a national industry plan by seeking out partnerships with stakeholders, convened in December 2004.
Aquaculture in Tonga has been the responsibility of the Ministry of Fisheries since the early 1970s. The main centre for this is the Sopu Mariculture Centre on the main island of Tongatapu, which is operated by the Ministry of Fisheries and was established with the assistance of the Government of Japan. A serious setback was experienced in 1982 as a result of damage caused by Cyclone Isaac.

China, with one-fifth of the world's population, accounts for two-thirds of the world's reported aquaculture production.
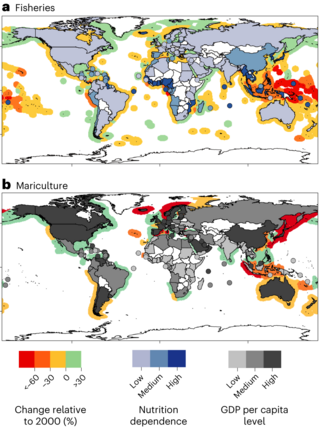
Fisheries are affected by climate change in many ways: marine aquatic ecosystems are being affected by rising ocean temperatures, ocean acidification and ocean deoxygenation, while freshwater ecosystems are being impacted by changes in water temperature, water flow, and fish habitat loss. These effects vary in the context of each fishery. Climate change is modifying fish distributions and the productivity of marine and freshwater species. Climate change is expected to lead to significant changes in the availability and trade of fish products. The geopolitical and economic consequences will be significant, especially for the countries most dependent on the sector. The biggest decreases in maximum catch potential can be expected in the tropics, mostly in the South Pacific regions.
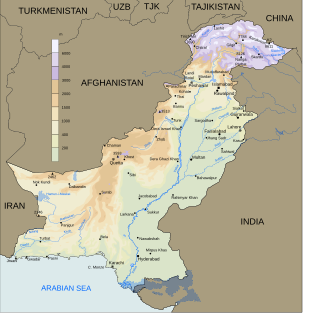
The fishing industry plays a significant part in the national economy of Pakistan. With a coastline of about 1,120 km, Pakistan has enough fishery resources that remain to be developed. Most of the population of the coastal areas of Sindh and Balochistan depends on fisheries for livelihood. It is also a major source of export earning.

South Korea is a major center of aquaculture production, and the world's third largest producer of farmed algae as of 2020.
Aquaculture in Madagascar started to take off in the 1980s. The industry includes the cultivation of sea cucumbers, seaweed, fish and shrimp and is being used to stimulate the country's economy, increase the wages of fishermen and women, and improve the regions ocean water quality. Coastal regions of Madagascar are reliant on the Indian Ocean's marine resources as a source of food, income, and cultural identity.

Cormorant culling is the intentional killing of cormorants by humans for the purposes of wildlife management. It has been practiced for centuries, with supporters of culling generally arising from the angling community. Culling techniques may involve the killing of birds, the destruction of eggs, or both. Historically, culls have occurred to protect the interests of recreational and commercial fishermen who perceive the animals to be competing with them for their intended catch or for the prey of their intended catch. Since the 1960s, the growing aquaculture industry has undertaken cormorant culls to protect its farmed fish and crustacean stocks. Opponents of cormorant culling include conservation groups such as the National Audubon Society, Cormorant Defenders International and Sea Shepherd.

Minute Alapati Taupo OBE was a Tuvaluan politician, diplomat, economist and accountant. Taupo was elected to the Parliament of Tuvalu in the 2019 Tuvaluan general election to represent the Nanumanga electorate. He was appointed Deputy Prime Minister & Minister for Fisheries and Trade in the Natano Ministry.
References
- ↑ Richard A. Herr (1990). The Forum Fisheries Agency. Institute of Pacific Studies of the University of the South Pacific. p. 137. ISBN 982-02-0057-1.
- ↑ "Fishery and Aquaculture Country Profile: Tuvalu". Food and Agriculture Organization. Archived from the original on 26 March 2009. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ↑ "Twenty-Sixth Regional Technical Meeting on Fisheries: Country Profile: Tuvalu" (PDF). Secretariat of the Pacific Community. July 30, 1996. Retrieved 2009-05-02.