
The Dorset and Somerset Canal was a proposed canal in southwestern England. The main line was intended to link Poole, Dorset with the Kennet and Avon Canal near Bradford on Avon, Wiltshire. A branch was to go from the main line at Frome to the southern reaches of the Somerset coalfield at Nettlebridge. Construction of the branch started in 1786, using boat lifts rather than locks to cope with changes of level, but the company ran out of money and the canal was abandoned in 1803, never to be completed.

The Pont du Gard is an ancient Roman aqueduct bridge built in the first century AD to carry water over 50 km (31 mi) to the Roman colony of Nemausus (Nîmes). It crosses the river Gardon near the town of Vers-Pont-du-Gard in southern France. The Pont du Gard is one of the best preserved Roman aqueduct bridges. It was added to UNESCO's list of World Heritage sites in 1985 because of its exceptional preservation, historical importance, and architectural ingenuity.

Piazza del Campo is the main public space of the historic center of Siena, a city in Tuscany, Italy, Its name comes from the Italian word campanilismo, which translates to "local pride" and campanile "bell tower." The campo is regarded as one of Europe's greatest medieval squares. It is renowned worldwide for its beauty and architectural integrity. The Palazzo Pubblico and its Torre del Mangia, as well as various palazzi signorili, surround the scallop shell-shaped piazza. At the northwest edge is the Fonte Gaia.
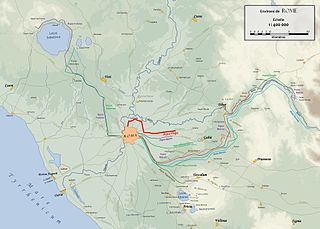
The Aqua Virgo was one of the eleven Roman aqueducts that supplied the city of ancient Rome. It was completed in 19 BC by Marcus Agrippa, during the reign of the emperor Augustus and was built mainly to supply the contemporaneous Baths of Agrippa in the Campus Martius.

The Romans constructed aqueducts throughout their Republic and later Empire, to bring water from outside sources into cities and towns. Aqueduct water supplied public baths, latrines, fountains, and private households; it also supported mining operations, milling, farms, and gardens.

Capannori is an Italian town and comune in the province of Lucca, in northern Tuscany.

The Acqua Felice is one of the aqueducts of Rome, completed in 1586 by Pope Sixtus V, whose birth name, which he never fully abandoned, was Felice Peretti. The first new aqueduct of early modern Rome, its source is at the springs at Pantano Borghese, off Via Casilina. Its length is fifteen miles (24 km), running underground for eight miles (13 km) from its source, first in the channel of Aqua Alexandrina, then alternating on the arches of the Aqua Claudia and the Aqua Marcia for seven miles (11 km) to its terminus at the Fontana dell'Acqua Felice on the Quirinal Hill, standing to one side of the Strada Pia, so as to form a piazza in this still new part of Rome. The engineer was Giovanni Fontana, brother of Sixtus' engineer-architect Domenico Fontana, who recorded that the very day the new pope entered the Lateran, he decided that he would bring water once again to the hills of Rome, which had remained waterless and sparsely inhabited, largely by monasteries, since the original ancient aqueducts had been destroyed in the sixth century. From the source, which Sixtus purchased, there was only a very small fall, and the work required an underground conduit as well as an aqueduct carried on arches.
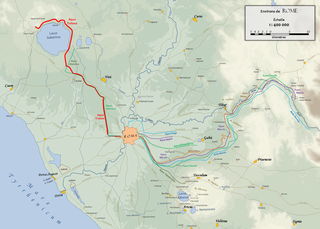
The Aqua Traiana was a 1st-century Roman aqueduct built by Emperor Trajan and inaugurated in 109 AD. It channelled water from sources around Lake Bracciano, 40 km (25 mi) north-west of Rome, to ancient Rome. It joined the earlier Aqua Alsietina to share a common lower route into Rome.
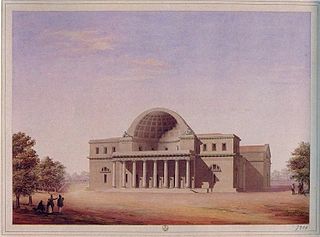
The Cisternoni of Livorno are a series of three large buildings in the neoclassical style at Livorno, in Tuscany, Italy. They were constructed between 1829 and 1848 as part of a complex of purification plants and storage tanks to the Leopoldino aqueduct; a fourth cisternone planned at Castellaccia was never built. The cisternoni, literally "great cisterns", provided Livorno — a city that is still today one of the principal ports of the Mediterranean — with fresh and, more importantly, clean water throughout the 19th and 20th centuries.

The Villa Marlia or Villa Reale di Marlia is a late-Renaissance palazzo or villa, and its estate's property that includes renowned gardens and adjacent villas and follies within the compound. It is located in Capannori, in the Province of Lucca, west of Florence, in the northern Tuscany region of Italy.

The AqueductofValens was a Roman aqueduct system built in the late 4th century AD, to supply Constantinople – the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire. Construction of the aqueduct began during the reign of the Roman emperor Constantius II and was completed in 373 by the Emperor Valens. The aqueduct remained in use for many centuries. It was extended and maintained by the Byzantines and the Ottomans.

The Fontana dell'Acqua Paola, also known as Il Fontanone or Mostra dell'Acqua Paola, is a monumental fountain located on the Janiculum Hill, near the church of San Pietro in Montorio, in Rome, Italy. It was built in 1612 to mark the end of the Acqua Paola aqueduct, restored by Pope Paul V, and took its name from him. It was the first major fountain on the right bank of the River Tiber.

Neher water system provided clean water for the people of Aurangabad and its suburbs. It was created by Malik Ambar who founded the town under the name Khadki and was later expanded by Aurangzeb to facilitate the military activity that became prevalent under Mughal rule during the 17th century.

The Wignacourt Aqueduct is a 17th-century aqueduct in Malta, which was built by the Order of Saint John to carry water from springs in Dingli and Rabat to the newly built capital city Valletta. The aqueduct carried water through underground pipes and over arched viaducts across depressions in the ground.

The Zaghouan Aqueduct or Aqueduct of Carthage is an ancient Roman aqueduct, which supplied the city of Carthage, Tunisia with water. From its source in Zaghouan it flows a total of 132 km, making it among the longest aqueducts in the Roman Empire.

The Fountain of San Maurizio, also called Samoreci, is a medieval public fountain located at the intersection of Via di Pantaneto and Via San Girolamo in Siena, region of Tuscany, Italy. It is located just outside one set of medieval city walls and the Arco di San Maurizio.
Lorenzo Nottolini was an architect and engineer of the Neoclassic style in Lucca, Italy.
The Specola Di Lucca is a Neoclassic-style former astronomical observatory built during the early 19th century near the Royal Villa at Marlia, near Lucca, region of Tuscany, Italy. The architect Lorenzo Nottolini was commissioned in 1819 to build the structure by Duchess Maria Luisa di Borbone.

The Caldaccoli Aqueduct was an ancient Roman aqueduct dating to the 1st century. It carried water from the thermal springs at the resort of Caldaccoli, then known as the calidae acquae,, near the present-day San Giuliano Terme, to the Roman baths at Pisa.

Fountain Green Hydroelectric Plant Historic District, located northwest of Fountain Green, Utah, was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1989. The listing included three contributing buildings and a contributing structure.




















