
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of 27 member states that are located primarily in Europe. The Union has a total area of 4,233,255 km2 (1,634,469 sq mi) and an estimated total population of over 448 million. The EU has often been described as a sui generis political entity combining the characteristics of both a federation and a confederation.

The euro is the official currency of 20 of the 27 member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the euro area or, more commonly, the eurozone. The euro is divided into 100 euro cents.

The economy of Greece is the 54th largest in the world, with a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of $250.276 billion per annum. In terms of purchasing power parity, Greece is the world's 55th largest economy, at $430.125 billion per annum. As of 2023, Greece is the sixteenth largest economy in the European Union and eleventh largest in the eurozone. According to the International Monetary Fund's figures for 2024, Greece's GDP per capita is $23,966 at nominal value and $41,188 at purchasing power parity. Among OECD nations, Greece has a highly efficient and strong social security system; social expenditure stood at roughly 24.1% of GDP.

The economy of Libya depends primarily on revenues from the petroleum sector, which represents over 95% of export earnings and 60% of GDP. These oil revenues and a small population have given Libya one of the highest nominal per capita GDP in Africa.
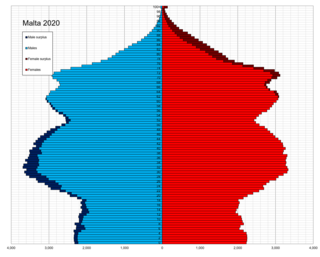
Demographic features of the population of Malta include population density, ethnicity, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

Muammar Muhammad Abu Minyar al-Gaddafi was a Libyan revolutionary, politician and political theorist who ruled Libya from 1969 until his assassination by rebel forces in 2011. He first served as Revolutionary Chairman of the Libyan Arab Republic from 1969 to 1977 and then as the Brotherly Leader of the Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya from 1977 to 2011. Initially ideologically committed to Arab nationalism and Arab socialism, Gaddafi later ruled according to his own Third International Theory.
The National Bank of Greece is a global banking and financial services company with its headquarters in Athens, Greece. It is the largest Greek bank by total assets.

Piraeus Bank is a Greek multinational financial services company with its headquarters in Athens, Greece. Piraeus Bank's shares have been listed on the Athens Stock Exchange (ATHEX) since January 1918.

The Aegean dispute is a set of interrelated controversies between Greece and Turkey over sovereignty and related rights in the region of the Aegean Sea. This set of conflicts has strongly affected Greek-Turkish relations since the 1970s, and has twice led to crises coming close to the outbreak of military hostilities, in 1987 and in early 1996. The issues in the Aegean fall into several categories:

Antonis Samaras is a Greek politician who served as 14th Prime Minister of Greece from 2012 to 2015. A member of the New Democracy party, he was its president from 2009 until 2015. Samaras started his national political career as Minister of Finance in 1989; he served as Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1989 to 1992 and Minister of Culture in 2009.
The Sahara Bank is a Libyan commercial bank, established in 1964. The bank performs retail and corporate banking operations and its head office is located in Tripoli.
The mass media in Greece refers to mass media outlets based in the Hellenic Republic. Television, magazines, and newspapers are all operated by both state-owned and for-profit corporations which depend on advertising, subscription, and other sales-related revenues. The Constitution of Greece guarantees freedom of speech.
The international reactions to the Libyan Civil War were the responses to the series of protests and military confrontations occurring in Libya against the government of Libya and its de facto head of state Muammar Gaddafi.

The Arab National Bank (anb) is a major bank based in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia and listed on the Saudi Stock Exchange. It is among the top ten largest banks in the Middle East and has received an 'A' rank from Standard and Poor's. It has 156 branches in Saudi Arabia. Its largest shareholder is Arab Bank, holding 40% of the fund.

During 2015, there was a period of significantly increased movement of refugees and migrants into Europe. 1.3 million people came to the continent to request asylum, the most in a single year since World War II. They were mostly Syrians, but also included significant numbers from Afghanistan, Nigeria, Pakistan, Iraq, Eritrea, and the Balkans. The increase in asylum seekers has been attributed to factors such as the escalation of various wars in the Middle East and ISIL's territorial and military dominance in the region due to the Arab Winter, as well as Lebanon, Jordan, and Egypt ceasing to accept Syrian asylum seekers.

United Arab Emirates corporate law regulates the governance, finance and power of corporations in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) through UAE law. Every emirate has its own basic corporate code.
Immigration to Malta has increased significantly over the past decade. In 2011, immigration contributed to 4.9% of the total population of the Maltese islands in 2011, i.e. 20,289 persons of non-Maltese citizenship, of whom 643 were born in Malta. In 2011, most of migrants in Malta were EU citizens, predominantly from the United Kingdom.

In 2020, Turkey militarily intervened in support of the United Nations-recognized Government of National Accord (GNA) of Libya in the 2014–2020 Libyan civil war. Military intervention was approved by the Grand National Assembly of Turkey on 2 January 2020, which passed a one-year mandate to deploy troops to Libya. Turkish military deployments to Libya began on 5 January.

Fish for finance is a possible trade-off that has been considered by both sides in the trade negotiations between the United Kingdom and the European Union (EU) over their future relationship following Brexit in January 2020. The Brexit withdrawal agreement between the two parties called for an agreement on fisheries to be concluded by June 2020, followed by an agreement on financial services at the end of July, deadlines which were both missed. Both were expected to be part of the final EU–UK trade agreement reached by the end of 2020, the end of the Brexit transition period. The final agreement had some broad outlines for a future fishing deal, primarily gradual EU concessions of fishing quota in UK waters, but was largely silent on finance.













