
The Common Desktop Environment (CDE) is a desktop environment for Unix and OpenVMS, based on the Motif widget toolkit. It was part of the UNIX 98 Workstation Product Standard, and was for a long time the Unix desktop associated with commercial Unix workstations. It helped to influence early implementations of successor projects such as KDE and GNOME desktop environment, which largely replaced CDE following the turn of the century.
In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system that share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphical shell. The desktop environment was seen mostly on personal computers until the rise of mobile computing. Desktop GUIs help the user to easily access and edit files, while they usually do not provide access to all of the features found in the underlying operating system. Instead, the traditional command-line interface (CLI) is still used when full control over the operating system is required.

The GNU Project is a free software, mass collaboration project announced by Richard Stallman on September 27, 1983. Its goal is to give computer users freedom and control in their use of their computers and computing devices by collaboratively developing and publishing software that gives everyone the rights to freely run the software, copy and distribute it, study it, and modify it. GNU software grants these rights in its license.

The ROX Desktop is a graphical desktop environment for the X Window System. It is based on the ROX-Filer which is a drag and drop spatial file manager. It is free software released under the GNU General Public License. The environment was inspired by the user interface of RISC OS. The name "ROX" comes from "RISC OS on X". Programs can be installed or removed easily using Zero Install.

Scanner Access Now Easy (SANE) is an open-source application programming interface (API) that provides standardized access to any raster image scanner hardware. The SANE API is public domain. It is commonly used on Linux.
GNU Parted is a free partition editor, used for creating and deleting partitions. This is useful for creating space for new operating systems, reorganising hard disk usage, copying data between hard disks, and disk imaging. It was written by Andrew Clausen and Lennert Buytenhek.

gPhoto is a set of software applications and libraries for use in digital photography. gPhoto supports not just retrieving of images from camera devices, but also upload and remote controlled configuration and capture, depending on whether the camera supports those features.

openSUSE is a free and open source RPM-based Linux distribution developed by the openSUSE project.

Linux is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the use and importance of GNU software in many distributions, causing some controversy.
HAL is a software subsystem for UNIX-like operating systems providing hardware abstraction.
A desktop environment is a collection of software designed to give functionality and a certain look and feel to an operating system.

In the 1950s and 1960s, computer operating software and compilers were delivered as a part of hardware purchases without separate fees. At the time, source code, the human-readable form of software, was generally distributed with the software providing the ability to fix bugs or add new functions. Universities were early adopters of computing technology. Many of the modifications developed by universities were openly shared, in keeping with the academic principles of sharing knowledge, and organizations sprung up to facilitate sharing. As large-scale operating systems matured, fewer organizations allowed modifications to the operating software, and eventually such operating systems were closed to modification. However, utilities and other added-function applications are still shared and new organizations have been formed to promote the sharing of software.

Trisquel is a computer operating system, a Linux distribution, derived from another distribution, Ubuntu. The project aims for a fully free software system without proprietary software or firmware and uses a version of Ubuntu's modified kernel, with the non-free code removed. Trisquel relies on user donations. Its logo is a triskelion, a Celtic symbol. Trisquel is listed by the Free Software Foundation as a distribution that contains only free software.
Linux began in 1991 as a personal project by Finnish student Linus Torvalds: to create a new free operating system kernel. The resulting Linux kernel has been marked by constant growth throughout its history. Since the initial release of its source code in 1991, it has grown from a small number of C files under a license prohibiting commercial distribution to the 4.15 version in 2018 with more than 23.3 million lines of source code, not counting comments, under the GNU General Public License v2.
Chih-Wei Huang is a developer and promoter of free software who lives in Taiwan. He is famous for his work in the VoIP and internationalization and localization fields in Greater China. The user name he usually uses is cwhuang.

GNOME, originally an acronym for GNU Network Object Model Environment, is a free and open-source desktop environment for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems.

MATE is a desktop environment composed of free and open-source software that runs on Linux, BSD, and illumos operating systems.
GNOME Project is a community behind the GNOME desktop environment and the software platform upon which it is based. It consists of all the software developers, artists, writers, translators, other contributors, and active users of GNOME. It is no longer part of the GNU Project.
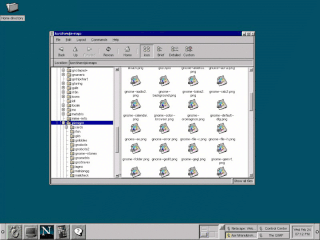
GNOME 1 is the first major release of the GNOME desktop environment. Its primary goal was to provide a consistent user-friendly environment in conjunction with the X Window System. It was also a modern and free and open source software alternative to older desktop environments such as the Common Desktop Environment (CDE), but also to the K Desktop Environment (KDE). Each desktop environment was built-upon then proprietary-licensed widget toolkits, whereas GNOME's goal from the onset, was to be freely-licensed, and utilize the GTK toolkit instead.












