See also
- Archaic (disambiguation), an earlier or ancient period or practice
- Archean, or Archæan, an early geological eon
- "archaeo-" ('ancient'), a commonly used taxonomic affixes
- Arcaea, a rhythm game developed and published by lowiro
Archaea is a domain of single-celled organisms.
Archaea or archea may also refer to:
Drachma may refer to:
Greek may refer to:
Substance may refer to:
Thebes or Thebae may refer to one of the following places:

In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla.

In biological taxonomy, a domain, also dominion, superkingdom, realm, or empire, is the highest taxonomic rank of all organisms taken together. It was introduced in the three-domain system of taxonomy devised by Carl Woese, Otto Kandler and Mark Wheelis in 1990.
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
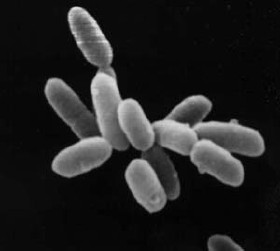
Euryarchaeota is a kingdom of archaea. Euryarchaeota are highly diverse and include methanogens, which produce methane and are often found in intestines; halobacteria, which survive extreme concentrations of salt; and some extremely thermophilic aerobes and anaerobes, which generally live at temperatures between 41 and 122 °C. They are separated from the other archaeans based mainly on rRNA sequences and their unique DNA polymerase.
Macedonia most commonly refers to:
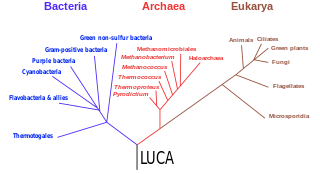
The last universal common ancestor (LUCA) is the hypothesized common ancestral cell from which the three domains of life, the Bacteria, the Archaea, and the Eukarya originated. The cell had a lipid bilayer; it possessed the genetic code and ribosomes which translated from DNA or RNA to proteins. The LUCA probably existed at latest 3.6 billion years ago, and possibly as early as 4.3 billion years ago or earlier. The nature of this point or stage of divergence remains a topic of research.
Translocation may refer to:
Archaic may refer to:
Archaean may refer to:
Achaea is a subdivision of Greece.

A prokaryote is a single-cell organism whose cell lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word prokaryote comes from the Ancient Greek πρό (pró), meaning 'before', and κάρυον (káruon), meaning 'nut' or 'kernel'. In the two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard Chatton, prokaryotes were classified within the empire Prokaryota. However in the three-domain system, based upon molecular analysis, prokaryotes are divided into two domains: Bacteria and Archaea. Organisms with nuclei are placed in a third domain: Eukaryota.

Archaea is a domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its prokaryotic members, but this sense has been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are now known to have evolved from archaea. Even though the domain Archaea includes eukaryotes, the term "archaea" in English still generally refers specifically to prokaryotic members of Archaea. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria, but this term has fallen out of use.
Celer may refer to:
Israeli may refer to:
Geba may mean: