Related Research Articles

Aung San Suu Kyi, sometimes abbreviated to Suu Kyi, is a Burmese politician, diplomat, author, and a 1991 Nobel Peace Prize laureate who served as State Counsellor of Myanmar and Minister of Foreign Affairs from 2016 to 2021. She has served as the general secretary of the National League for Democracy (NLD) since the party's founding in 1988 and was registered as its chairperson while it was a legal party from 2011 to 2023. She played a vital role in Myanmar's transition from military junta to partial democracy in the 2010s.

Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar, also known as Burma, is a country in Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has a population of about 55 million. It is bordered by Bangladesh and India to its northwest, China to its northeast, Laos and Thailand to its east and southeast, and the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is Naypyidaw, and its largest city is Yangon.

Bagan is an ancient city and a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the Mandalay Region of Myanmar. From the 9th to 13th centuries, the city was the capital of the Pagan Kingdom, the first kingdom that unified the regions that would later constitute Myanmar. During the kingdom's height between the 11th and 13th centuries, more than 10,000 Buddhist temples, pagodas and monasteries were constructed in the Bagan plains alone, of which the remains of over 2200 temples and pagodas survive.
The history of Myanmar covers the period from the time of first-known human settlements 13,000 years ago to the present day. The earliest inhabitants of recorded history were a Tibeto-Burman-speaking people who established the Pyu city-states ranged as far south as Pyay and adopted Theravada Buddhism.

Bago, formerly known as Hanthawaddy, is a city and the capital of the Bago Region in Myanmar. It is located 91 kilometres (57 mi) north-east of Yangon.

The University of Yangon, located in Kamayut, Yangon, is the oldest university in Myanmar's modern education system and the best known university in Myanmar. The university offers mainly undergraduate and postgraduate degrees programs in liberal arts, sciences and law. Full-time bachelor's degrees were not offered at the university's main campus after the student protests of 1996. The bachelor's degree was re-offered from 2014 on. Today degrees in Political Science are offered to undergraduate students, as well as postgraduate diplomas in areas such as social work and geology.

The Pyu city-states were a group of city-states that existed from about the 2nd century BCE to the mid-11th century in present-day Upper Myanmar (Burma). The city-states were founded as part of the southward migration by the Tibeto-Burman-speaking Pyu people, the earliest inhabitants of Burma of whom records are extant. The thousand-year period, often referred to as the Pyu millennium, linked the Bronze Age to the beginning of the classical states period when the Pagan Kingdom emerged in the late 9th century.

British rule in Burma lasted from 1824 to 1948, from the successive three Anglo-Burmese wars through the creation of Burma as a province of British India to the establishment of an independently administered colony, and finally independence. The region under British control was known as British Burma, and officially known as Burma from 1886. Various portions of Burmese territories, including Arakan and Tenasserim, were annexed by the British after their victory in the First Anglo-Burmese War; Lower Burma was annexed in 1852 after the Second Anglo-Burmese War. The annexed territories were designated the minor province of British Burma in 1862.
The cinema of Burma has a long history dating back to the 1910s. The person who created the first silent film was Ohn Maung.
The Kingdom of Pagan was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-day Myanmar. Pagan's 250-year rule over the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery laid the foundation for the ascent of Burmese language and culture, the spread of Bamar ethnicity in Upper Myanmar, and the growth of Theravada Buddhism in Myanmar and in mainland Southeast Asia.

The Ministry of Education is the Myanmar government agency responsible for education in Myanmar.

Insurgencies have been ongoing in Myanmar since 1948, the year the country, then known as Burma, gained independence from the United Kingdom. The conflict has largely been ethnic-based, with several ethnic armed groups fighting Myanmar's armed forces, the Tatmadaw, for self-determination. Despite numerous ceasefires and the creation of autonomous self-administered zones in 2008, many armed groups continue to call for independence, increased autonomy, or the federalisation of the country. The conflict is the world's longest ongoing civil war, having spanned more than seven decades.

The Communist Party of Burma (CPB), also known as the Burma Communist Party (BCP), is a clandestine communist party in Myanmar (Burma). It is the oldest existing political party in the country.
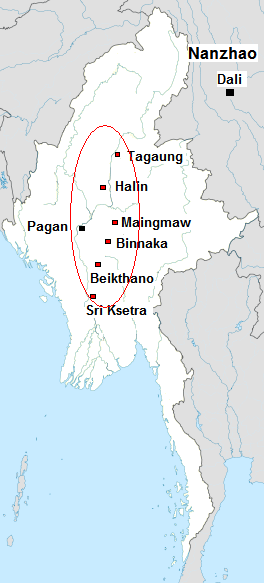
Sri Ksetra, located along the Irrawaddy River at present-day Hmawza, was once a prominent Pyu settlement. The Pyu occupied several sites across Upper Myanmar, with Sri Ksetra recorded as the largest, the city wall enclosing an area of 1,477 hectares, although a recent survey found it enclosed 1,857 hectares within its monumental brick walls, with an extramural area of a similar size, being the largest Southeast Asian city before Angkor times. Issues surrounding the dating of this site has meant the majority of material is dated between the seventh and ninth centuries AD, however recent scholarship suggests Pyu culture at Sri Ksetra was active centuries before this.
The royal chronicles of Myanmar are detailed and continuous chronicles of the monarchy of Myanmar (Burma). The chronicles were written on different media such as parabaik paper, palm leaf, and stone; they were composed in different literary styles such as prose, verse, and chronograms. Palm-leaf manuscripts written in prose are those that are commonly referred to as the chronicles. Other royal records include administrative treatises and precedents, legal treatises and precedents, and censuses.

Hmannan Maha Yazawindawgyi is the first official chronicle of Konbaung Dynasty of Burma (Myanmar). It was compiled by the Royal Historical Commission between 1829 and 1832. The compilation was based on several existing chronicles and local histories, and the inscriptions collected on the orders of King Bodawpaya, as well as several types of poetry describing epics of kings. Although the compilers disputed some of the earlier accounts, they by and large retained the accounts given Maha Yazawin, the standard chronicle of Toungoo Dynasty.

Min Aung Hlaing is a Burmese army general who has ruled Myanmar as the chairman of the State Administration Council since seizing power in the February 2021 coup d'état. He additionally appointed himself Prime Minister in August 2021. He has led the Tatmadaw, an independent branch of government, as the commander-in-chief of Defence Services since March 2011, when he was handpicked to succeed longtime military ruler Than Shwe, who transferred leadership over the country to a civilian government upon retiring. Before assuming leadership over the Tatmadaw, Min Aung Hlaing served as Joint Chief of Staff from 2010 to 2011.
The Journal of the Burma Research Society was an academic journal covering Burma studies that was published by the Burma Research Society between 1911 and 1980. When it began publication in 1911, the journal became the first peer-reviewed academic journal focused on Burma studies. Over the 69-year period, the journal published 59 volumes and 132 issues, including over 1,300 articles. It was published twice a year at the Rangoon University Estate in both English and Burmese.

A coup d'état in Myanmar began on the morning of 1 February 2021, when democratically elected members of the country's ruling party, the National League for Democracy (NLD), were deposed by the Tatmadaw — Myanmar's military — which then vested power in a military junta. Acting President of Myanmar Myint Swe proclaimed a year-long state of emergency and declared power had been transferred to Commander-in-Chief of Defence Services Senior General Min Aung Hlaing. It declared the results of the November 2020 general election invalid and stated its intent to hold a new election at the end of the state of emergency. The coup d'état occurred the day before the Parliament of Myanmar was to swear in the members elected in the 2020 election, thereby preventing this from occurring. President Win Myint and State Counsellor Aung San Suu Kyi were detained, along with ministers, their deputies, and members of Parliament.
References
- 1 2 AUNG-THWIN, MICHAEL (1982). "Burma Before Pagan: The Status of Archaeology Today". Asian Perspectives. 25 (2): 1–21. JSTOR 42928082.
- ↑ Morris, Jennifer A. (Fall 2015). "Rebuilding a Troubled Nation, One Brick at a Time: Cultural Heritage and the Law in Myanmar" (PDF). Marshall-Wythe School of Law College of William & Mary.