Arcturus COVID-19 vaccine may also refer to:
Arcturus COVID-19 vaccine may also refer to:
ARCT or Arct may refer to:
Arcturus Therapeutics is an American RNA medicines biotechnology company focused on the discovery, development and commercialization of therapeutics for rare diseases and infectious diseases. Arcturus has developed a novel, potent, and safe RNA therapeutics platform called LUNAR, a proprietary lipid-enabled delivery system for nucleic acid medicines including small interfering RNA (siRNA), messenger RNA (mRNA), gene editing RNA, DNA, antisense oligonucleotides (ASO), and microRNA.

A COVID‑19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19). Prior to the COVID‑19 pandemic, an established body of knowledge existed about the structure and function of coronaviruses causing diseases like severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). This knowledge accelerated the development of various vaccine platforms during early 2020. The initial focus of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines was on preventing symptomatic, often severe illness. On 10 January 2020, the SARS-CoV-2 genetic sequence data was shared through GISAID, and by 19 March, the global pharmaceutical industry announced a major commitment to address COVID-19. The COVID‑19 vaccines are widely credited for their role in reducing the spread, severity, and death caused by COVID-19.

The Moderna COVID‑19 vaccine, codenamed mRNA-1273 and sold under the brand name Spikevax, is a COVID-19 vaccine developed by Moderna, the United States National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) and the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA). It is authorized for use in people aged twelve years and older in some jurisdictions and for people eighteen years and older in other jurisdictions to provide protection against COVID-19 which is caused by infection by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. It is designed to be administered as two or three 0.5 mL doses given by intramuscular injection at an interval of at least 28 days apart.

An immunity passport or vaccine passport, also known as a vaccination IDrecovery certificate, immunity certificate, recovery certificate, health pass or release certificate, is a document, in both paper and digital format, attesting that its bearer is immune to a contagious disease. Similar to quarantine, public certification is an action that governments can take to mitigate an epidemic.

The Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine, codenamed AZD1222, and sold under the brand names Covishield and Vaxzevria among others, is a viral vector vaccine for prevention of COVID-19. Developed by Oxford University and AstraZeneca, it is given by intramuscular injection, using as a vector the modified chimpanzee adenovirus ChAdOx1. Studies carried out in 2020 showed that the efficacy of the vaccine is 76.0% at preventing symptomatic COVID-19 beginning at 22 days following the first dose and 81.3% after the second dose. A study in Scotland found that, for symptomatic COVID-19 infection after the second dose, the vaccine is 81% effective against the Alpha variant, and 61% against the Delta variant.
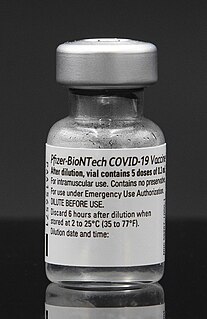
The Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, sold under the brand name Comirnaty, is an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine developed by the German biotechnology company BioNTech. It is authorized for use in people aged twelve years and older in some jurisdictions and for people sixteen years and older in other jurisdictions, to provide protection against COVID-19, caused by infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus. For its development BioNTech collaborated with Pfizer, an American company, for support with clinical trials, logistics, and manufacturing. The vaccine is given by intramuscular injection. It is composed of nucleoside-modified mRNA (modRNA) encoding a mutated form of the full-length spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, which is encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles. Initial advice indicated that vaccination required two doses given 21 days apart, but the interval was later extended to up to 42 days in the US, and up to four months in Canada.

The Sinopharm BIBP COVID-19 vaccine, also known as BBIBP-CorV, the Sinopharm COVID-19 vaccine, or BIBP vaccine, is one of two inactivated virus COVID-19 vaccines developed by Sinopharm's Beijing Institute of Biological Products. It completed Phase III trials in Argentina, Bahrain, Egypt, Morocco, Pakistan, Peru, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) with over 60,000 participants. BBIBP-CorV shares similar technology with CoronaVac and Covaxin, other inactivated virus vaccines for COVID-19. Its product name is SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine, not to be confused with the similar product name of CoronaVac.

The Janssen COVID-19 vaccine or Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine is a COVID-19 vaccine that was developed by Janssen Vaccines in Leiden, Netherlands, and its Belgian parent company Janssen Pharmaceuticals, subsidiary of American company Johnson & Johnson.

India began administration of COVID-19 vaccines on 16 January 2021. As of 11 September 2021, India has administered over 738 million doses overall, including first and second doses of the currently-approved vaccines.

As of 1 September 2021, 5.34 billion COVID-19 vaccine doses had been administered worldwide, with 39.6 per cent of the global population having received at least one dose. While 40.5 million vaccines were then being administered daily, only 1.8 per cent of people in low-income countries had received at least a first vaccine by September 2021, according to official reports from national health agencies, which is collated by Our World in Data.
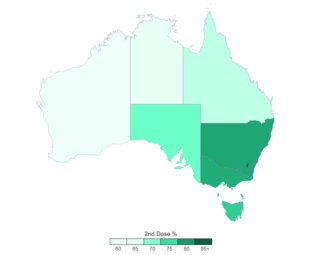
The general COVID-19 vaccination in Australia programme began on 22 February 2021 in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, and will continue with the goal of vaccinating all willing Australians before 2022. Front-line workers and aged care staff and residents will be the first Australians to be inoculated, before a gradual phased release to less-vulnerable and lower-risk population groups throughout 2021. The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) approved four vaccines for Australian use: the Pfizer–BioNTech vaccine on 25 January, Janssen vaccine on 25 June 2021, Moderna vaccine on 9 August and Oxford–AstraZeneca vaccine on 16 February. The fourth vaccine approved for Australia is the Janssen vaccine but it is not included in the vaccination program.

ARCT-021, also known as LUNAR-COV19, is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Arcturus Therapeutics.
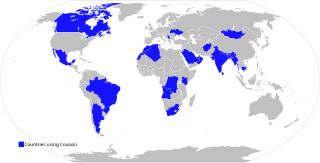
Vaccine Maitri is a humanitarian initiative undertaken by the Indian government to provide COVID-19 vaccines to countries around the world. The government started providing vaccines from 20 January 2021. As of 9 May 2021, India had delivered around 66.3 million doses of vaccines to 95 countries. Of these, 10.7 million doses were gifted to 47 countries by the Government of India. The remaining 54 million were supplied by the Serum Institute of India under its commercial and COVAX obligations. In late March 2021, the Government of India temporarily froze exports of the Covishield, citing India's own COVID crisis and the domestic need for these vaccines.

Post-vaccination embolic and thrombotic events, also termed vaccine-induced prothrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT), vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT), or thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) are rare types of blood clotting syndromes that were initially observed in a very small number of people who had previously received the Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine (AZD1222) during the COVID-19 pandemic. It was subsequently also described in the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine leading to suspension of its use until its safety had been reassessed.

The COVID-19 vaccination in Vietnam is an ongoing immunization campaign against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), in response to the ongoing pandemic in the country. Following the approval of the Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine on 30 January 2021, vaccinations commenced on 8 March 2021, and will continue throughout the year with the goal of vaccinating 80% of the population by June 2022. The Sputnik V was later approved for use on 23 March 2021. Sinopharm COVID-19 vaccine was approved for emergency use on 4 June 2021, while Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, Moderna COVID-19 vaccine and Janssen COVID-19 vaccine were approved on 12 June 2021, 29 June 2021, and 15 July 2021, respectively.

A COVID-19 vaccine card is a record often given to those who have received a COVID-19 vaccine showing information such as the date(s) one has received the shot(s) and the brand of vaccine one has received, sometimes including the lot number. The card also contains information identifying the recipient and the location where the shot was given. Depending on the country, it could serve as an official document verifying one has received the shot, which could be required by some institutions, such as a school or workplace, when boarding a cruise ship, or when crossing an international border, as proof that one has been vaccinated.

ARCT-154, also known as VBC-COV19-154 in Vietnam, is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Arcturus Therapeutics. For its development, Arcturus collaborated with Vinbiocare, a Vietnamese company, for support with clinical trials and manufacturing.

COVID-19 vaccine clinical research is the clinical research on COVID-19 vaccines, including their efficacy, effectiveness and safety. There are 22 vaccines authorized for use by national governments, with six vaccines being approved for emergency or full use by at least one WHO-recognised stringent regulatory authority; and five of them are in Phase IV. 204 vaccines under clinical trials that have not yet been authorized. There are also nine clinical trials on heterologous vaccination courses.