
The X Window System is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems.

Wine is a free and open-source compatibility layer that aims to allow application software and computer games developed for Microsoft Windows to run on Unix-like operating systems. Wine also provides a software library, named Winelib, against which developers can compile Windows applications to help port them to Unix-like systems.

KDE Display Manager (KDM) is a display manager developed by KDE for the windowing systems X11.
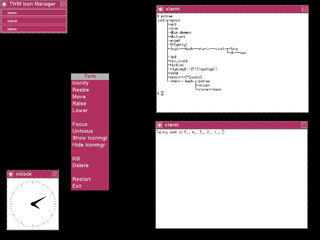
twm is a window manager for the X Window System. Started in 1987 by Tom LaStrange, it has been the standard window manager for the X Window System since version X11R4. The name originally stood for Tom's Window Manager, but the software was renamed Tab Window Manager by the X Consortium when they adopted it in 1989. twm is a stacking window manager that provides title bars, shaped windows and icon management. It is highly configurable and extensible.

The F Virtual Window Manager is a virtual window manager for the X Window System. Originally a twm derivative, FVWM has evolved into a powerful and highly configurable environment for Unix-like systems.
PuTTY is a free and open-source terminal emulator, serial console and network file transfer application. It supports several network protocols, including SCP, SSH, Telnet, rlogin, and raw socket connection. It can also connect to a serial port. The name "PuTTY" has no official meaning.
In computing, the Inter-Client Communication Conventions Manual is a standard protocol for the X Window System. It specifies conventions for clients of a common X server about selections and cut buffers, communication with the window manager and session manager, manipulation of shared resources, and color characterization.
Microsoft Configuration Manager, formerly Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager, System Center Configuration Manager and Systems Management Server (SMS) is a systems management software product developed by Microsoft for managing large groups of computers providing remote control, patch management, software distribution, operating system deployment, and hardware and software inventory. Configuration Manager supports the Microsoft Windows and Windows Embedded operating systems. Previous versions also supported macOS, Linux or UNIX, as well as Windows Phone, Symbian, iOS and Android mobile operating systems.
PHIGS is an application programming interface (API) standard for rendering 3D computer graphics, considered to be the 3D graphics standard for the 1980s through the early 1990s. Subsequently, a combination of features and power led to the rise of OpenGL, which became the most popular professional 3D API of the mid to late 1990s.
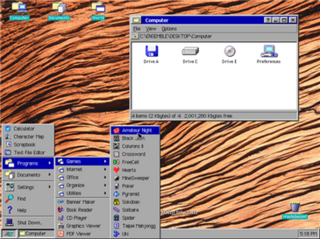
GEOS is a computer operating environment, graphical user interface (GUI), and suite of application software. Originally released as PC/GEOS, it runs on DOS-based, IBM PC compatible computers. Versions for some handheld platforms were also released and licensed to some companies.

X Toolkit Intrinsics is a library that implements an API to facilitate the development of programs with a graphical user interface (GUI) for the X Window System. It can be used in the C or C++ languages.

OpenWindows is a discontinued desktop environment for Sun Microsystems workstations which combined SunView, NeWS, and X Window System protocols. OpenWindows was included in later releases of the SunOS 4 and Solaris operating systems, until its removal in Solaris 9 in favor of Common Desktop Environment (CDE) and GNOME 2.0.

The Ultrix Window Manager (uwm) is a historic standard window manager software for the X Window System from X11R1 through X11R3 releases. In fact, it was the only X11-compatible window manager as of X11R1.
swm is an X Window System window manager developed by Tom LaStrange at Solbourne Computer in 1990. The most important innovation of swm was the introduction of the virtual desktop. It also introduced a primitive form of session management to X.

Linux is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy.
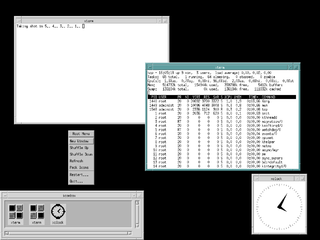
In computing, the Motif Window Manager (MWM) is an X window manager based on the Motif toolkit.
Stardent Computer, Inc. was a manufacturer of graphics supercomputer workstations in the late 1980s. The company was formed in 1989 when Ardent Computer Corporation and Stellar Computer Inc. merged.
X386 was an implementation of the X Window System for IBM PC compatible computers. It ran on systems with Intel 386 or later processors, running Unix System V-based operating systems, and supported a variety of VGA-compatible graphics cards. X386 was created by Thomas Roell while at Technische Universität München and first released in 1991. X386 1.2 was incorporated in the X11R5 release later the same year.

antiX is a Linux distribution based on Debian Stable.












