In user interface design, a pie menu or radial menu is a circular context menu where selection depends on direction. It is a graphical control element. A pie menu is made of several "pie slices" around an inactive center and works best with stylus input, and well with a mouse. Pie slices are drawn with a hole in the middle for an easy way to exit the menu.
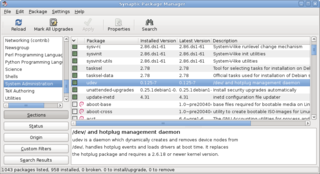
A package manager or package-management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner.

Ultrix is the brand name of Digital Equipment Corporation's (DEC) discontinued native Unix operating systems for the PDP-11, VAX, MicroVAX and DECstations.

The Unix philosophy, originated by Ken Thompson, is a set of cultural norms and philosophical approaches to minimalist, modular software development. It is based on the experience of leading developers of the Unix operating system. Early Unix developers were important in bringing the concepts of modularity and reusability into software engineering practice, spawning a "software tools" movement. Over time, the leading developers of Unix established a set of cultural norms for developing software; these norms became as important and influential as the technology of Unix itself, and have been termed the "Unix philosophy."

SQLite is a database engine written in the C programming language. It is not a standalone app; rather, it is a library that software developers embed in their apps. As such, it belongs to the family of embedded databases. It is the most widely deployed database engine, as it is used by several of the top web browsers, operating systems, mobile phones, and other embedded systems.
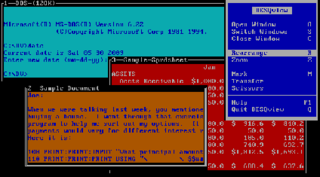
DESQview (DV) is a text mode multitasking operating environment developed by Quarterdeck Office Systems which enjoyed modest popularity in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Running on top of DOS, it allows users to run multiple programs concurrently in multiple windows.
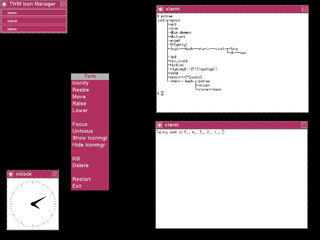
twm is a window manager for the X Window System. Started in 1987 by Tom LaStrange, it has been the standard window manager for the X Window System since version X11R4. The name originally stood for Tom's Window Manager, but the software was renamed Tab Window Manager by the X Consortium when they adopted it in 1989. twm is a stacking window manager that provides title bars, shaped windows and icon management. It is highly configurable and extensible.

Multi-booting is the act of installing multiple operating systems on a single computer, and being able to choose which one to boot. The term dual-booting refers to the common configuration of specifically two operating systems. Multi-booting may require a custom boot loader.

In computing, text-based user interfaces (TUI), is a retronym describing a type of user interface (UI) common as an early form of human–computer interaction, before the advent of bitmapped displays and modern conventional graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Like modern GUIs, they can use the entire screen area and may accept mouse and other inputs. They may also use color and often structure the display using box-drawing characters such as ┌ and ╣. The modern context of use is usually a terminal emulator.

A window manager is system software that controls the placement and appearance of windows within a windowing system in a graphical user interface. Most window managers are designed to help provide a desktop environment. They work in conjunction with the underlying graphical system that provides required functionality—support for graphics hardware, pointing devices, and a keyboard—and are often written and created using a widget toolkit.
The Unix Desktop Environment (UDE) is a desktop environment for the X Window System. Given its efficient and lightweight design it can be used on almost any Unix-like operating system, mostly without any porting effort.

In computing, a virtual desktop is a term used with respect to user interfaces, usually within the WIMP paradigm, to describe ways in which the virtual space of a computer's desktop environment is expanded beyond the physical limits of the screen's display area through the use of software. This compensates limits of the desktop area and is helpful in reducing clutter of running graphical applications.

Lazarus is a cross-platform, integrated development environment (IDE) for rapid application development (RAD) using the Free Pascal compiler. Its goal is to provide an easy-to-use development environment for developing with the Object Pascal language, which is as close as possible to Delphi. It is free and open-source software with different parts released under different software licenses.

dwm is a minimalist dynamic window manager for the X Window System developed by Suckless that has influenced the development of several other X window managers, including xmonad and awesome. It is externally similar to wmii, but internally much simpler. dwm is written purely in C for performance and lacks any configuration interface besides editing the source code. One of the project's guidelines is that the source code is intended never to exceed 2000 SLOC, and options meant to be user-configurable are all contained in a single header file.
A software repository, or repo for short, is a storage location for software packages. Often a table of contents is also stored, along with metadata. A software repository is typically managed by source or version control, or repository managers. Package managers allow automatically installing and updating repositories, sometimes called "packages".

GNU Emacs is a text editor and suite of free software tools. Its development began in 1984 by GNU Project founder Richard Stallman, based on the Emacs editor developed for Unix operating systems. GNU Emacs has been a central component of the GNU project and a flagship project of the free software movement.

Raspberry Pi OS is a Unix-like operating system based on the Debian Linux distribution for the Raspberry Pi family of compact single-board computers. Raspbian was developed independently in 2012, became the primary operating system for these boards since 2013, was originally optimized for the Raspberry Pi 1 and distributed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation. In 2020, the Raspberry Pi Foundation renamed Raspbian to Raspberry Pi OS.
Microsoft, a tech company historically known for its opposition to the open source software paradigm, turned to embrace the approach in the 2010s. From the 1970s through 2000s under CEOs Bill Gates and Steve Ballmer, Microsoft viewed the community creation and sharing of communal code, later to be known as free and open source software, as a threat to its business, and both executives spoke negatively against it. In the 2010s, as the industry turned towards cloud, embedded, and mobile computing—technologies powered by open source advances—CEO Satya Nadella led Microsoft towards open source adoption although Microsoft's traditional Windows business continued to grow throughout this period generating revenues of 26.8 billion in the third quarter of 2018, while Microsoft's Azure cloud revenues nearly doubled.
Comparison of user features of operating systems refers to a comparison of the general user features of major operating systems in a narrative format. It does not encompass a full exhaustive comparison or description of all technical details of all operating systems. It is a comparison of basic roles and the most prominent features. It also includes the most important features of the operating system's origins, historical development, and role.















