Cygwin is a Unix-like environment and command-line interface for Microsoft Windows.
The Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. Its most notable applications are remote login and command-line execution.

The X Window System is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems.

rsync is a utility for transferring and synchronizing files between a computer and a storage drive and across networked computers by comparing the modification times and sizes of files. It is commonly found on Unix-like operating systems and is under the GPL-3.0-or-later license.

In computing, a windowing system is a software suite that manages separately different parts of display screens. It is a type of graphical user interface (GUI) which implements the WIMP paradigm for a user interface.

Gambas is the name of an object-oriented dialect of the BASIC programming language, as well as the integrated development environment that accompanies it. Designed to run on Linux and other Unix-like computer operating systems, its name is a recursive acronym for Gambas Almost Means Basic. Gambas is also the word for prawns in the Spanish, French, and Portuguese languages, from which the project's logos are derived.
Cygwin/X is an implementation of the X Window System that runs under Microsoft Windows. It is part of the Cygwin project, and is installed using Cygwin's standard setup system. Cygwin/X is free software, licensed under the X11 License.
In computing, X-Win32 is a proprietary implementation of the X Window System for Microsoft Windows, produced by StarNet Communications. It is based on X11R7.4.
X.Org Server is the free and open-source implementation of the X Window System (X11) display server stewarded by the X.Org Foundation.

Cooperative Linux, abbreviated as coLinux, is software which allows Microsoft Windows and the Linux kernel to run simultaneously in parallel on the same machine.
PuTTY is a free and open-source terminal emulator, serial console and network file transfer application. It supports several network protocols, including SCP, SSH, Telnet, rlogin, and raw socket connection. It can also connect to a serial port. The name "PuTTY" has no official meaning.
NX technology, commonly known as NX or NoMachine, is a remote access and remote control computer software, allowing remote desktop access and maintenance of computers. It is developed by the Luxembourg-based company NoMachine S.à r.l.. NoMachine is proprietary software and is free-of-charge for non-commercial use.

WinSCP is a free and open-source file manager, SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), File Transfer Protocol (FTP), WebDAV, Amazon S3, and secure copy protocol (SCP) client for Microsoft Windows.
An SSH client is a software program which uses the secure shell protocol to connect to a remote computer. This article compares a selection of notable clients.
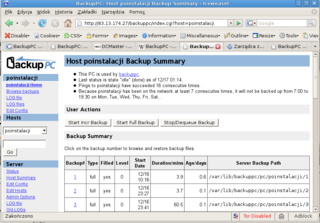
BackupPC is a free disk-to-disk backup software suite with a web-based frontend. The cross-platform server will run on any Linux, Solaris, or UNIX-based server. No client is necessary, as the server is itself a client for several protocols that are handled by other services native to the client OS. In 2007, BackupPC was mentioned as one of the three most well known open-source backup software, even though it is one of the tools that are "so amazing, but unfortunately, if no one ever talks about them, many folks never hear of them".
MKS X/Server, a commercial X server developed by MKS Inc., allows users to access Unix/Linux systems from a PC computers which run a Microsoft Windows operating system. The product offers both a full 32-bit X server and a native 64-bit X server that operate on various versions of Microsoft Windows.
This page is a comparison of notable remote desktop software available for various platforms.

mintty is a free and open source terminal emulator for Cygwin, the Unix-like environment for Windows. It features a native Windows user interface and does not require a display server; its terminal emulation is aimed to be compatible with xterm.

Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a feature of Windows that allows developers to run a Linux environment without the need for a separate virtual machine or dual booting. There are two versions of WSL: WSL 1 and WSL 2. WSL 1 was first released on August 2, 2016, and acts as a compatibility layer for running Linux binary executables by implementing Linux system calls on the Windows kernel. It is available on Windows 10, Windows 10 LTSB/LTSC, Windows 11, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server 2022.