Related Research Articles

In computing, BIOS is firmware used to perform hardware initialization during the booting process, and to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs. The BIOS firmware comes pre-installed on a personal computer's system board, and it is the first software to run when powered on. The name originates from the Basic Input/Output System used in the CP/M operating system in 1975. The BIOS originally proprietary to the IBM PC has been reverse engineered by some companies looking to create compatible systems. The interface of that original system serves as a de facto standard.

A Java virtual machine (JVM) is a virtual machine that enables a computer to run Java programs as well as programs written in other languages that are also compiled to Java bytecode. The JVM is detailed by a specification that formally describes what is required in a JVM implementation. Having a specification ensures interoperability of Java programs across different implementations so that program authors using the Java Development Kit (JDK) need not worry about idiosyncrasies of the underlying hardware platform.

SPARC is a reduced instruction set computing (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) originally developed by Sun Microsystems. Its design was strongly influenced by the experimental Berkeley RISC system developed in the early 1980s. First developed in 1986 and released in 1987, SPARC was one of the most successful early commercial RISC systems, and its success led to the introduction of similar RISC designs from a number of vendors through the 1980s and 90s.

Jakarta EE, formerly Java Platform, Enterprise Edition and Java 2 Platform, Enterprise Edition (J2EE) is a set of specifications, extending Java SE with specifications for enterprise features such as distributed computing and web services. Jakarta EE applications are run on reference runtimes, that can be microservices or application servers, which handle transactions, security, scalability, concurrency and management of the components it is deploying.

Solaris is a proprietary Unix operating system originally developed by Sun Microsystems. It superseded the company's earlier SunOS in 1993. In 2010, after the Sun acquisition by Oracle, it was renamed Oracle Solaris.
InfiniBand (IB) is a computer networking communications standard used in high-performance computing that features very high throughput and very low latency. It is used for data interconnect both among and within computers. InfiniBand is also used as either a direct or switched interconnect between servers and storage systems, as well as an interconnect between storage systems. It is designed to be scalable and uses a switched fabric network topology.
In computing, Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a standard application programming interface (API) for accessing database management systems (DBMS). The designers of ODBC aimed to make it independent of database systems and operating systems. An application written using ODBC can be ported to other platforms, both on the client and server side, with few changes to the data access code.

Windows-1252 or CP-1252 is a single-byte character encoding of the Latin alphabet, used by default in the legacy components of Microsoft Windows for English and many European languages including Spanish, French, and German.

pax is an archiving utility available for various operating systems and defined since 1995. Rather than sort out the incompatible options that have crept up between tar and cpio, along with their implementations across various versions of Unix, the IEEE designed a new archive utility that could support various archive formats with useful options from both archivers. The pax command is available on Unix and Unix-like operating systems and on IBM i, Microsoft Windows NT, and Windows 2000.
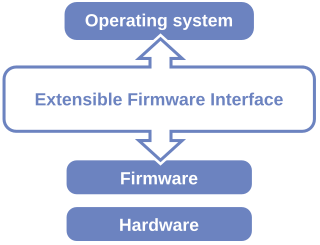
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a specification that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware. UEFI replaces the legacy Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) firmware interface originally present in all IBM PC-compatible personal computers, with most UEFI firmware implementations providing support for legacy BIOS services. UEFI can support remote diagnostics and repair of computers, even with no operating system installed.
In computing, the X Window System is a network-transparent windowing system for bitmap displays. This article details the protocols and technical structure of X11.
uim is a multilingual input method framework. Applications can use it through so-called bridges.
The Base One Foundation Component Library (BFC) is a rapid application development toolkit for building secure, fault-tolerant, database applications on Windows and ASP.NET. In conjunction with Microsoft's Visual Studio integrated development environment, BFC provides a general-purpose web application framework for working with databases from Microsoft, Oracle, IBM, Sybase, and MySQL, running under Windows, Linux/Unix, or IBM iSeries or z/OS. BFC also includes facilities for distributed computing, batch processing, queuing, and database command scripting, and these run under Windows or Linux with Wine.
In computing, software engineering, and software testing, a test oracle is a mechanism for determining whether a test has passed or failed. The use of oracles involves comparing the output(s) of the system under test, for a given test-case input, to the output(s) that the oracle determines that product should have. The term "test oracle" was first introduced in a paper by William E. Howden. Additional work on different kinds of oracles was explored by Elaine Weyuker.

The Intelligent Input Bus is an input method (IM) framework for multilingual input in Unix-like operating-systems. The name "Bus" comes from its bus-like architecture.
The Java Development Kit (JDK) is an implementation of either one of the Java Platform, Standard Edition, Java Platform, Enterprise Edition, or Java Platform, Micro Edition platforms released by Oracle Corporation in the form of a binary product aimed at Java developers on Solaris, Linux, macOS or Windows. The JDK includes a private JVM and a few other resources to finish the development of a Java application. Since the introduction of the Java platform, it has been by far the most widely used Software Development Kit (SDK).
The Linear Tape File System (LTFS) is a file system that allows files stored on magnetic tape to be accessed in a similar fashion to those on disk or removable flash drives. It requires both a specific format of data on the tape media and software to provide a file system interface to the data.

Fcitx is an input method framework with extension support for the X Window System that supports multiple input method engines including Pinyin transcription, table-based input methods, fcitx-chewing for Traditional Chinese, fcitx-keyboard for layout-based ones, fcitx-mozc for Japanese, fcitx-hangul for Korean.

XQuery API for Java (XQJ) refers to the common Java API for the W3C XQuery 1.0 specification.
PL/SQL is Oracle Corporation's procedural extension for SQL and the Oracle relational database. PL/SQL is available in Oracle Database, Times Ten in-memory database, and IBM DB 2. Oracle Corporation usually extends PL/SQL functionality with each successive release of the Oracle Database.
References
- ↑ Nye, Adrian (June 1994). XLIB Programming Manual. O'Reilly. ISBN 9780596806187.
- ↑ "XIM specification". Archived from the original on 2012-02-28. Retrieved 2011-09-01.
- ↑ IBM Knowledge Center: X Input Method (XIM) and Input Method Editors (IME) and encodings
- ↑ Oracle Asian Application Developer's Guide: Overview of the X Window System Input Method (XIM)
