
Devanagari is an Indic script used in the Indian subcontinent. Also simply called Nāgari, it is a left-to-right abugida, based on the ancient Brāhmi script. It is one of the official scripts of the Republic of India and Nepal. It was developed and in regular use by the 8th century CE and achieved its modern form by 1000 CE. The Devanāgari script, composed of 48 primary characters, including 14 vowels and 34 consonants, is the fourth most widely adopted writing system in the world, being used for over 120 languages.

Mojibake is the garbled or gibberish text that is the result of text being decoded using an unintended character encoding. The result is a systematic replacement of symbols with completely unrelated ones, often from a different writing system.
Devanagari is an Indic script used for many Indo-Aryan languages of North India and Nepal, including Hindi, Marathi and Nepali, which was the script used to write Classical Sanskrit. There are several somewhat similar methods of transliteration from Devanagari to the Roman script, including the influential and lossless IAST notation. Romanised Devanagari is also called Romanagari.
The National Library at Kolkata romanisation is a widely used transliteration scheme in dictionaries and grammars of Indic languages. This transliteration scheme is also known as (American) Library of Congress and is nearly identical to one of the possible ISO 15919 variants. The scheme is an extension of the IAST scheme that is used for transliteration of Sanskrit.

An input method is an operating system component or program that enables users to generate characters not natively available on their input devices by using sequences of characters that are available to them. Using an input method is usually necessary for languages that have more graphemes than there are keys on the keyboard.
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that emerged during the 19th century from suggestions by Charles Trevelyan, William Jones, Monier Monier-Williams and other scholars, and formalised by the Transliteration Committee of the Geneva Oriental Congress, in September 1894. IAST makes it possible for the reader to read the Indic text unambiguously, exactly as if it were in the original Indic script. It is this faithfulness to the original scripts that accounts for its continuing popularity amongst scholars.
ISO 15919 is an international standard for the romanization of Brahmic and Nastaliq scripts. Published in 2001, it is part of a series of international standards by the International Organization for Standardization.

There are Unicode typefaces which are open-source and designed to contain glyphs of all Unicode characters, or at least a broad selection of Unicode scripts. There are also numerous projects aimed at providing only a certain script, such as the Arabeyes Arabic font. The advantage of targeting only some scripts with a font was that certain Unicode characters should be rendered differently depending on which language they are used in, and that a font that only includes the characters a certain user needs will be much smaller in file size compared to one with many glyphs. Unicode fonts in modern formats such as OpenType can in theory cover multiple languages by including multiple glyphs per character, though very few actually cover more than one language's forms of the unified Han characters.
The "Indian languages TRANSliteration" (ITRANS) is an ASCII transliteration scheme for Indic scripts, particularly for the Devanagari script.

The pinyin method refers to a family of input methods based on the pinyin method of romanization.
Google Pinyin IME is a discontinued input method developed by Google China Labs. The tool was made publicly available on April 4, 2007. Aside from Pinyin input, it also includes stroke count method input. As of March 2019, Google Pinyin has been discontinued and the download page tools.google.com/pinyin/ has been deleted. However, Google Pinyin IME can still be obtained from https://dl.google.com/pinyin/v2/GooglePinyinInstaller.exe.
Indic Computing means "computing in Indic", i.e., Indian Scripts and Languages. It involves developing software in Indic Scripts/languages, Input methods, Localization of computer applications, web development, Database Management, Spell checkers, Speech to Text and Text to Speech applications and OCR in Indian languages.

Microsoft Translator or Bing Translator is a multilingual machine translation cloud service provided by Microsoft. Microsoft Translator is a part of Microsoft Cognitive Services and integrated across multiple consumer, developer, and enterprise products, including Bing, Microsoft Office, SharePoint, Microsoft Edge, Microsoft Lync, Yammer, Skype Translator, Visual Studio, and Microsoft Translator apps for Windows, Windows Phone, iPhone and Apple Watch, and Android phone and Android Wear.
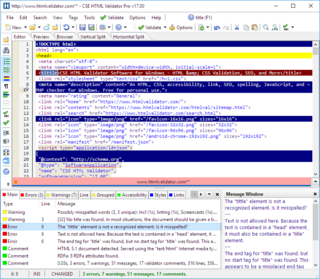
CSS HTML Validator is an HTML editor and CSS editor for Windows that helps web developers create syntactically correct and accessible HTML/HTML5, XHTML, and CSS documents by locating errors, potential problems like browser compatibility issues, and common mistakes. It is also able to check links, check spelling, suggest improvements, alert developers to deprecated, obsolete, or proprietary tags, attributes, and CSS properties, and find issues that can affect search engine optimization.
Microsoft Indic Language Input Tool is a typing tool for languages written in Indic scripts. It is a virtual keyboard which allows to type Indic text directly in any application without the hassle of copying and pasting. It is available for both, online and offline use. It was released in December 2009.
The Indian blogosphere is the online predominantly community of Indian weblogs that is part of the larger blogosphere.
Bengali input methods refer to different systems developed to type the characters of the Bengali script for Bengali language and others, using a typewriter or a computer keyboard.

Azhagi is a freeware transliteration tool, which enables its users to type in a number of regional Indian languages, including Tamil, Hindi, and others, using an English keyboard. In 2002, The Hindu dubbed Azhagi as a tool that "stand[s] out" among various similar software "emerg[ing] nearly every other day". Since year 2000, Azhagi has provided support for Tamil transliteration; this was later expanded to nearly 13 Indian languages, featuring 16 total built-in languages as of the day of writing.

The Tamil keyboard is used in computers and mobile devices to input text in the Tamil script.

Yandex Translate is a web service provided by Yandex, intended for the translation of web pages into another language.









