Google Developers is Google's site for software development tools and platforms, application programming interfaces (APIs), and technical resources. The site contains documentation on using Google developer tools and APIs—including discussion groups and blogs for developers using Google's developer products.
Android is a mobile operating system based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open-source software, designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Android is developed by a consortium of developers known as the Open Handset Alliance, though its most widely used version is primarily developed by Google. It was unveiled in November 2007, with the first commercial Android device, the HTC Dream, being launched in September 2008.
A mobile operating system is an operating system for smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, smartglasses, or other non-laptop personal mobile computing devices. While computers such as typical/mobile laptops are "mobile", the operating systems used on them are generally not considered mobile ones, as they were originally designed for desktop computers that historically did not have or need specific mobile features. This line distinguishing mobile and other forms has become blurred in recent years, due to the fact that newer devices have become smaller and more mobile unlike hardware of the past. Key notabilities blurring this line are the introduction of tablet computers and light-weight laptops and the hybridization of the two in 2-in-1 PCs.

ChromeOS, sometimes styled as chromeOS and formerly styled as Chrome OS, is a Linux-based operating system developed and designed by Google. It is derived from the open-source ChromiumOS and uses the Google Chrome web browser as its principal user interface.
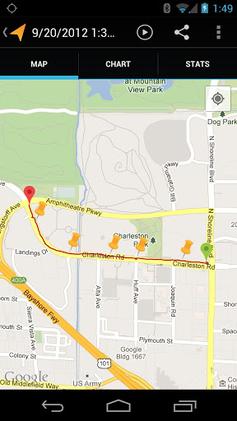
Telenav, Inc. is a wireless location-based services corporation that provides services including Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite navigation, local search, automotive navigation solutions, mobile advertising, enterprise mobility and workflow automation. The company’s headquarters are located in Santa Clara, California in the United States with additional offices in the U.S., Germany, Japan, Romania, China, and Brazil.
The version history of the Android mobile operating system began with the public release of its first beta on November 5, 2007. The first commercial version, Android 1.0, was released on September 23, 2008. The operating system is developed by Google on a yearly cycle since at least 2011. New major releases are announced at Google I/O along with its first public beta to supported Google Pixel devices. The stable version is then released later in the year.

Firefox OS is a discontinued open-source operating system – made for smartphones, tablet computers, smart TVs, and dongles designed by Mozilla and external contributors. It is based on the rendering engine of the Firefox web browser, Gecko, and on the Linux kernel. It was first commercially released in 2014.

Pocket, previously known as Read It Later, is a social bookmarking service for storing, sharing and discovering web bookmarks. Released in 2007, the service was originally only for desktop and laptop computers and is now available for macOS, Windows, iOS, Android, Windows Phone, BlackBerry, Kobo eReaders, and web browsers.

Android Ice Cream Sandwich is the fourth major version of the Android mobile operating system developed by Google. Unveiled on October 19, 2011, Android 4.0 builds upon the significant changes made by the tablet-only release Android Honeycomb, in an effort to create a unified platform for both smartphones and tablets. The first phone with Android Ice Cream Sandwich was Samsung Galaxy Nexus.

OsmAnd is a map and navigation app for Android and iOS. It uses the OpenStreetMap (OSM) map database for its primary displays, but is an independent app not endorsed by the OpenStreetMap Foundation. It is available in both free and paid versions; the latter unlocks the download limit for offline maps and provides access to Wikipedia points of interest (POIs) and their descriptions from within the app. Map data can be stored on the device for offline use. Using the device's GPS capabilities, OsmAnd offers routing, with visual and voice guidance, for car, bike, and pedestrian. All of the main functionalities work both online and offline.

AliOS is a Linux distribution developed by Alibaba Cloud, a subsidiary of Mainland Chinese company Alibaba Group. It is designed for smart cars and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and it had been used as a mobile operating system.
Ubuntu Touch is a mobile version of the Ubuntu operating system, being developed by the UBports community. Its user interface is written in Qt, and is designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers, but the original goal of convergence was intended to bring Ubuntu Touch to laptops, desktops, IOT devices and TVs for a complete unified user experience.

F-Droid is an app store and software repository for Android, serving a similar function to the Google Play store. The main repository, hosted by the project, contains only free and open source apps. Applications can be browsed, downloaded and installed from the F-Droid website or client app without the need to register for an account. "Anti-features" such as advertising, user tracking, or dependence on non-free software are flagged in app descriptions.
Avare is a free open source "moving map" aviation GPS, A/FD and EFB app for phones or tablets using the Android Operating System. The app uses any internal Android or compatible external GPS receiver to determine location, allowing real-time display of location, heading, speed, distance, time, and altitude on free U.S. FAA IFR or VFR aviation charts; or on select topographic charts. Included are 3D, ADSB-In and other advanced options. The user can access all relevant static current FAA official data and some non-FAA maps and data in flight without data connection, once data has been downloaded to the device. With an aircraft ADSB-Out transmitter and inexpensive ADSB-In receiver Avare can also display any available FAA live ADSB data in flight. Some advanced users also interface Avare with an auto-pilot or flight simulator.
Fire OS is a mobile operating system based on the Android Open Source Project (AOSP). It is developed by Amazon for their devices. Fire OS includes proprietary software, a customized user interface primarily centered on content consumption, and heavy ties to content available from Amazon's storefronts and services.
This article contains a list with gratis satellite navigation software for a range of devices. Some of the free software mentioned here does not have detailed maps or the ability to follow streets or type in street names. However, in many cases, it is also that which makes the program free, avoid the need of an Internet connection, and make it very lightweight. Very basic programs like this may not be suitable for road navigation in cars, but serve their purpose for navigation while walking or trekking, and for use at sea. To determine the GPS coordinates of a destination, one can use sites such as GPScoordinates.eu and GPS visualizer.
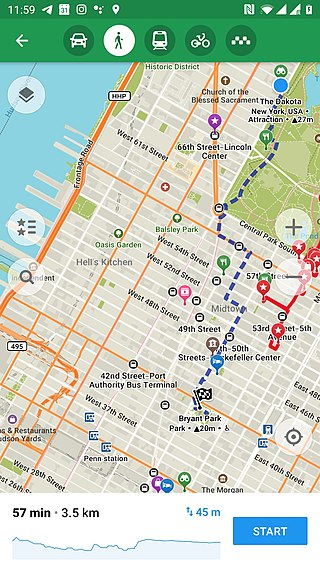
Maps.me is a mobile app for Android, iOS and BlackBerry that provides offline maps using OpenStreetMap data. It was formerly known as MapsWithMe. In November 2014, it was acquired by Mail.Ru Group and became part of its My.com brand. In September 2015, the app was open sourced and a free and open-source software version was additionally made available on F-droid until the application was sold to the payment processor Daegu Limited, part of Parity.com, which changed the application user interface and content, which led Alexander Borsuk and Viktor Govako to release an open source ad-and tracker-free fork called 'Organic Maps' in response.

Android Lollipop is the fifth major version of the Android mobile operating system developed by Google and the 12th version of Android, spanning versions between 5.0 and 5.1.1. Unveiled on June 25, 2014 at the Google I/O 2014 conference, it became available through official over-the-air (OTA) updates on November 12, 2014, for select devices that run distributions of Android serviced by Google. Its source code was made available on November 3, 2014. The first phone with Android Lollipop was the Nexus 6.

MicroG is a free and open-source implementation of proprietary Google libraries that serves as a replacement for Google Play Services on the Android operating system. It is maintained by German developer Marvin Wißfeld. In a presentation, Wißfeld described microG as "the framework to create a fully-compatible Android distribution without any proprietary Google components".

Conversations is a free software, instant messaging client application software for Android. It is largely based on recognized open standards such as the Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) and Transport Layer Security (TLS).