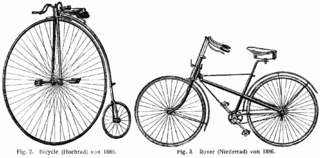
In business theory, disruptive innovation is innovation that creates a new market and value network or enters at the bottom of an existing market and eventually displaces established market-leading firms, products, and alliances. The term, "disruptive innovation" was popularized by the American academic Clayton Christensen and his collaborators beginning in 1995, but the concept had been previously described in Richard N. Foster's book "Innovation: The Attacker's Advantage" and in the paper Strategic Responses to Technological Threats.

A business model describes how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value, in economic, social, cultural or other contexts. The model describes the specific way in which the business conducts itself, spends, and earns money in a way that generates profit. The process of business model construction and modification is also called business model innovation and forms a part of business strategy.

Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entity, realizing or redistributing value". Others have different definitions; a common element in the definitions is a focus on newness, improvement, and spread of ideas or technologies.
Positioning refers to the place that a brand occupies in the minds of the customers and how it is distinguished from the products of the competitors. It is different from the concept of brand awareness. In order to position products or brands, companies may emphasize the distinguishing features of their brand or they may try to create a suitable image through the marketing mix. Once a brand has achieved a strong position, it can become difficult to reposition it. To effectively position a brand and create a lasting brand memory, brands need to be able to connect to consumers in an authentic way, creating a brand persona usually helps build this sort of connection.

In the field of management, strategic management involves the formulation and implementation of the major goals and initiatives taken by an organization's managers on behalf of stakeholders, based on consideration of resources and an assessment of the internal and external environments in which the organization operates. Strategic management provides overall direction to an enterprise and involves specifying the organization's objectives, developing policies and plans to achieve those objectives, and then allocating resources to implement the plans. Academics and practicing managers have developed numerous models and frameworks to assist in strategic decision-making in the context of complex environments and competitive dynamics. Strategic management is not static in nature; the models can include a feedback loop to monitor execution and to inform the next round of planning.
In business, a competitive advantage is an attribute that allows an organization to outperform its competitors.

Crossing the Chasm: Marketing and Selling High-Tech Products to Mainstream Customers or simply Crossing the Chasm, is a marketing book by Geoffrey A. Moore that examines the market dynamics faced by innovative new products, with a particular focus on the "chasm" or adoption gap that lies between early and mainstream markets.

In statistics and business, a long tail of some distributions of numbers is the portion of the distribution having many occurrences far from the "head" or central part of the distribution. The distribution could involve popularities, random numbers of occurrences of events with various probabilities, etc. The term is often used loosely, with no definition or an arbitrary definition, but precise definitions are possible.

Blue Ocean Strategy is a book published in 2005 written by W. Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne, professors at INSEAD, and the name of the marketing theory detailed on the book.

Workforce productivity is the amount of goods and services that a group of workers produce in a given amount of time. It is one of several types of productivity that economists measure. Workforce productivity, often referred to as labor productivity, is a measure for an organisation or company, a process, an industry, or a country.
A core product or flagship product is a company's primary promotion, service or product that can be purchased by a consumer. Core products may be integrated into end products, either by the company producing the core product or by other companies to which the core product is sold.
Marketing effectiveness is the measure of how effective a given marketer's go to market strategy is toward meeting the goal of maximizing their spending to achieve positive results in both the short- and long-term. It is also related to marketing ROI and return on marketing investment (ROMI). In today's competitive business environment, effective marketing strategies play a pivotal role in promoting products or services to target audiences. The advent of digital platforms has further intensified competition among businesses, making it imperative for companies to employ innovative and impactful marketing techniques. This essay examines how various types of advertising methods can be utilized effectively to reach out to potential consumers
In marketing, a company’s value proposition is the full mix of benefits or economic value which it promises to deliver to the current and future customers who will buy their products and/or services. It is part of a company's overall marketing strategy which differentiates its brand and fully positions it in the market. A value proposition can apply to an entire organization, parts thereof, customer accounts, or products and services.
Knowledge entrepreneurship involves the exploitation, leveraging, and transformation of knowledge into valuable products, services, or ventures. It emphasizes the application and commercialization of knowledge in order to generate economic and social impact. Knowledge entrepreneurship is different from 'traditional' economic entrepreneurship in the sense that it does not aim to realize monetary profit, but it instead focuses on the opportunities of production (research) and knowledge improvement. It has been argued that knowledge entrepreneurship is a suitable form of entrepreneurship for not-for-profit educators, researchers and educational institutions. While generating economic value is important, knowledge entrepreneurship often aims to address social challenges and contribute to positive societal change.
University spin-offs are companies that transform technological inventions developed from university research that are likely to remain unexploited otherwise. They are a subcategory of research spin-offs. Prominent examples of university spin-offs are Genentech, Crucell, Lycos and Plastic Logic. In most countries, universities can claim the intellectual property (IP) rights on technologies developed in their laboratories. In the United States, the Bayh–Dole Act permits universities to pursue ownership of inventions made by researchers at their institutions using funding from the federal government, where previously federal research funding contracts and grants obligated inventors to assign the resulting IP to the government. This IP typically draws on patents or, in exceptional cases, copyrights. Therefore, the process of establishing the spin-off as a new corporation involves transferring the IP to the new corporation or giving the latter a license on this IP. Most research universities now have Technology Licensing Offices (TLOs) to facilitate and pursue such opportunities.

Marty Neumeier is an American author and speaker who writes about brand, design, innovation, and creativity. He is currently Director of CEO Branding for Liquid Agency, a branding agency in San Jose, California.

Open Data Now is a 2014 book on open data by Joel Gurin.
Category design is a business strategy and discipline that helps companies create, develop, and dominate new categories of products and services.

Hirotaka Takeuchi is a professor of management practice in the Strategy Unit at Harvard Business School. He co-authored The New New Product Development Game which influenced the development of the Scrum framework.
Soren Marcus Kaplan is an author, consultant, and speaker on the subject of innovation and innovation culture in organizations. He is an Affiliate at the Center for Effective Organizations at the University of Southern California's Marshall School of Business, founder of the consulting firm InnovationPoint, co-founder of the software company Praxie.com, and is a columnist for the Innovate column of Inc. Magazine.











