Google Shopping, formerly Google Product Search, Google Products and Froogle, is a Google service created by Craig Nevill-Manning which allows users to search for products on online shopping websites and compare prices between different vendors. Google announced at its Marketing Live event in May 2019 that the new Google Shopping will integrate the existing Google Express marketplace into a revamped shopping experience. In the US, Google Shopping is accessible from the web and mobile apps, available on Android and iOS. Google Shopping is also available in France, accessible from the web only. Like its predecessor, Google Shopping is free and requires a personal Google account in order to purchase from the platform. A colored price tag icon replaces the parachute icon from Google Express.

iWork is an office suite of applications created by Apple for its macOS, iPadOS, and iOS operating systems, and also available cross-platform through the iCloud website.

Google Talk was an instant messaging service that provided both text and voice communication. The instant messaging service was variously referred to colloquially as Gchat, Gtalk, or Gmessage among its users.

The Slingbox was a TV streaming media device made by Sling Media that encoded local video for transmission over the Internet to a remote device. It allowed users to remotely view and control their cable, satellite, or digital video recorder (DVR) system at home from a remote Internet-connected personal computer, smartphone, or tablet as if they were at home.

A tablet computer, commonly shortened to tablet, is a mobile device, typically with a mobile operating system and touchscreen display processing circuitry, and a rechargeable battery in a single, thin and flat package. Tablets, being computers, have similar capabilities, but lack some input/output (I/O) abilities that others have. Modern tablets largely resemble modern smartphones, the only differences being that tablets are relatively larger than smartphones, with screens 7 inches (18 cm) or larger, measured diagonally, and may not support access to a cellular network. Unlike laptops, tablets usually run mobile operating systems, alongside smartphones.
Google Developers is Google's site for software development tools and platforms, application programming interfaces (APIs), and technical resources. The site contains documentation on using Google developer tools and APIs—including discussion groups and blogs for developers using Google's developer products.
Google Workspace is a collection of cloud computing, productivity and collaboration tools, software and products developed and marketed by Google. It consists of Gmail, Contacts, Calendar, Meet and Chat for communication; Currents for employee engagement; Drive for storage; and the Google Docs Editors suite for content creation. An Admin Panel is provided for managing users and services. Depending on edition Google Workspace may also include the digital interactive whiteboard Jamboard and an option to purchase add-ons such as the telephony service Voice. The education edition adds a learning platform Google Classroom and today has the name Workspace for Education.
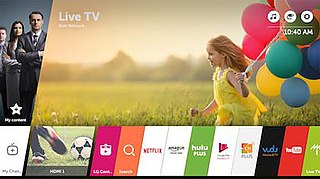
webOS, also known as LG webOS and previously known as Open webOS,HP webOS and Palm webOS, is a Linux kernel-based multitasking operating system for smart devices such as smart TVs that has also been used as a mobile operating system. Initially developed by Palm, Inc., HP made the platform open source, at which point it became Open webOS.

Foursquare City Guide, commonly known as Foursquare, is a local search-and-discovery mobile app developed by Foursquare Labs Inc. The app provides personalized recommendations of places to go near a user's current location based on users' previous browsing history and check-in history.
Jinni was a website-based search engine and recommendation engine for movies, TV shows and short films. The service was powered by the Entertainment Genome, an approach to indexing titles based on attributes like mood, tone, plot, and structure. As of 2015, it was no longer available to the public, but is reportedly available via API and business-to-business licensing, where it reportedly impacts businesses like Comcast's Xfinity product, as well as other businesses using "smart" entertainment search.
Titanium SDK is an open-source framework that allows the creation of native mobile applications on platforms iOS and Android from a single JavaScript codebase. It is presently developed by non-profit software foundation TiDev, Inc.

HipChat was a web service for internal private online chat and instant messaging. As well as one-on-one and group/topic chat, it also featured cloud-based file storage, video calling, searchable message-history and inline-image viewing. The software was available to download onto computers running Windows, Mac or Linux, as well as Android and iOS smartphones and tablets. Since 2014, HipChat used a freemium model, as much of the service was free with some additional features requiring organizations to pay per month. HipChat was launched in 2010 and acquired by Atlassian in 2012. In September 2017, Atlassian replaced the cloud-based HipChat with a new cloud product called Stride, with HipChat continuing on as the client-hosted HipChat Data Center.
Springpad was a free online application and web service that allowed its registered users to save, organize and share collected ideas and information. As users added content to their Springpad accounts, the application automatically identified and categorized it, then generated additional snippets based on the types of objects added—for example, listing price comparisons for products and showtimes for movies.
An app store, also called an app marketplace or app catalog, is a type of digital distribution platform for computer software called applications, often in a mobile context. Apps provide a specific set of functions which, by definition, do not include the running of the computer itself. Complex software designed for use on a personal computer, for example, may have a related app designed for use on a mobile device. Today apps are normally designed to run on a specific operating system—such as the contemporary iOS, macOS, Windows, Linux or Android—but in the past mobile carriers had their own portals for apps and related media content.
A mobile application or app is a computer program or software application designed to run on a mobile device such as a phone, tablet, or watch. Mobile applications often stand in contrast to desktop applications which are designed to run on desktop computers, and web applications which run in mobile web browsers rather than directly on the mobile device.
Polyvore was a community-powered social commerce website headquartered in Mountain View, California. The company's virtual mood board function allowed community members to add products into a shared product index, and use them to create image collages called "Sets". They could browse other users' sets for inspiration, share sets with friends and interact with people through comments and likes. Due to the visual nature of the tool Polyvore was mostly used to build sets in the fields of home decoration, beauty and fashion. Online retailers, too, could upload their product images to Polyvore and link back to their product pages or use Polyvore to encourage users to showcase their products through such activities as board creation competitions.
The Nintendo Network is a defunct online service formerly ran by Nintendo that provided free online functionality for the Nintendo 3DS and Wii U systems and their compatible games. Announced on January 26, 2012, at an investors' conference, it was Nintendo's second online service after Nintendo Wi-Fi Connection. Former president of Nintendo Satoru Iwata said, "Unlike Nintendo Wi-Fi Connection, which has been focused upon specific functionalities and concepts, we are aiming to establish a platform where various services available through the network for our consumers shall be connected via Nintendo Network service so that the company can make comprehensive proposals to consumers."

ChatON was a global mobile communication service provided by Samsung Electronics from September 2011 to March 2015.

Augment is an augmented reality SaaS platform that allows users to visualize their products in 3D in real environment and in real-time through tablets or smartphones. The software can be used for retail, e-commerce, architecture, and other purposes.









