
Qt or is a cross-platform application development framework for creating graphical user interfaces as well as cross-platform applications that run on various software and hardware platforms such as Linux, Windows, macOS, Android or embedded systems with little or no change in the underlying codebase while still being a native application with native capabilities and speed.

Maemo is a Linux-based software platform originally developed by Nokia, now developed by the community, for smartphones and Internet tablets. The platform comprises both the Maemo operating system and SDK. Maemo played a key role in Nokia's failed strategy to compete with Apple and Android; the only retail devices that shipped with Maemo were the Nokia Internet tablet line released in 2005 and the Nokia N900 smartphone in 2009.
A desktop environment is a collection of software designed to give functionality and a certain look and feel to an operating system.

Wayland is a communication protocol that specifies the communication between a display server and its clients, as well as a C library implementation of that protocol. A display server using the Wayland protocol is called a Wayland compositor, because it additionally performs the task of a compositing window manager.
oFono is a free software project for mobile telephony (GSM/UMTS) applications. It is built on 3GPP standards and uses a high-level D-Bus API for use by telephony applications. oFono is free software released under the terms of the GNU General Public License v2.

MeeGo is a discontinued Linux distribution hosted by the Linux Foundation, using source code from the operating systems Moblin and Maemo. MeeGo was primarily targeted at mobile devices and information appliances in the consumer electronics market. It was designed to act as an operating system for hardware platforms such as netbooks, entry-level desktops, nettops, tablet computers, mobile computing and communications devices, in-vehicle infotainment devices, SmartTV / ConnectedTV, IPTV-boxes, smart phones, and other embedded systems.
QML is a user interface markup language. It is a declarative language for designing user interface–centric applications. Inline JavaScript code handles imperative aspects. It is associated with Qt Quick, the UI creation kit originally developed by Nokia within the Qt framework. Qt Quick is used for mobile applications where touch input, fluid animations and user experience are crucial. QML is also used with Qt3D to describe a 3D scene and a "frame graph" rendering methodology. A QML document describes a hierarchical object tree. QML modules shipped with Qt include primitive graphical building blocks, modeling components, behavioral components, and more complex controls. These elements can be combined to build components ranging in complexity from simple buttons and sliders, to complete internet-enabled programs.

LightDM is a free and open-source X display manager that aims to be lightweight, fast, extensible and multi-desktop. It can use various front-ends to draw the user interface, also called Greeters. It also supports Wayland.

The Nokia N9 is a flagship smartphone developed by Nokia, running on the Linux-based MeeGo mobile operating system. Announced in June 2011 and released in September, it was the first and only device from Nokia with MeeGo, partly because of the company's partnership with Microsoft announced that year. It was initially released in three colors: black, cyan and magenta, before a white version was announced at Nokia World 2011.

Mer was a free and open-source software distribution, targeted at hardware vendors to serve as a middleware for Linux kernel-based mobile-oriented operating systems. It is a fork of MeeGo.

Falkon is a free and open-source web browser developed by KDE. It is built on the QtWebEngine, which is a wrapper for the Chromium browser core.
Mir is a computer display server and, recently, a Wayland compositor for the Linux operating system that is under development by Canonical Ltd. It was planned to replace the currently used X Window System for Ubuntu; however, the plan changed and Mutter was adopted as part of GNOME Shell.

Trojitá is a free software IMAP and SMTP email client developed using the Qt C++ library. The design goals of the maintainers are to develop a fast e-mail client which respects open standards, is cross-platform and uses the available resources very efficiently.

Accounts & SSO, accounts-sso, or lately gSSO is a single sign-on framework for computers.

Simple Desktop Display Manager (SDDM) is a display manager for the X11 and Wayland windowing systems. SDDM was written from scratch in C++11 and supports theming via QML.
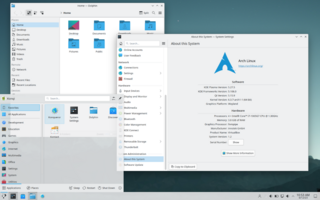
KDE Plasma 5 is the fifth generation of the KDE Plasma graphical workspaces environment, created by KDE primarily for Linux systems. KDE Plasma 5 is the successor of KDE Plasma 4 and was first released on 15 July 2014. It was succeeded by KDE Plasma 6 on 28 February 2024.

postmarketOS is an operating system primarily for smartphones, based on the Alpine Linux distribution.

KaOS is a desktop Linux distribution that features the latest version of the KDE desktop environment, the LibreOffice office suite, and other popular software applications that use the Qt toolkit.

Plasma Mobile is a Plasma variant for smartphones. It is currently available for the Pinephone, and supported devices for postmarketOS such as the OnePlus 6.














