| KWin | |
|---|---|
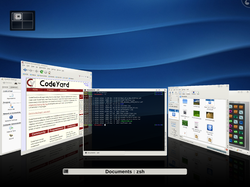
 KWin 5.24 with Cover Switch effect | |
| Developers | KDE (Martin Grässlin, et al.) |
| Stable release | |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C++ (Qt) |
| Operating system | Linux, BSD, other Unix-like |
| Type | |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website | https://invent.kde.org/plasma/kwin |

KWin is a window manager for the X Window System and a Wayland compositor. [2] [3] It is released as a part of KDE Plasma, for which it is the default window manager. KWin can also be used on its own or with other desktop environments.
Contents
KWin can be configured by scripting using QML or QtScript, both of which are based on ECMAScript. [4]